Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 15 : E-Commerce
Classification of E- Commerce Business models
Classification
of E- Commerce Business models
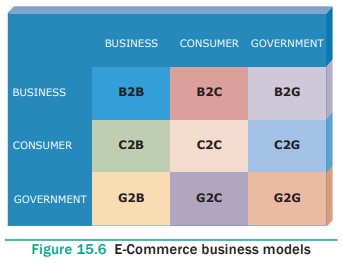
Business organizations, Consumers and Government (also
called as Administrations) are the major parties in the E-Commerce. Sometimes
Employees (Informal workers) also indulge in this system. Based upon the
entities involved in transaction, E-Commerce is classified into the following
categories. The model in which the government plays as an entity is termed as
e- Governance. See Figure 15.6
1. Business to Business (B2B)
2. Business to Consumer (B2C)
3. Business to Government (B2G)
4. Consumer to Business (C2B)
5. Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
6. Consumer to Government (C2G)
7. Government to Business (G2B)
8. Government to Consumer (G2C)
9. Government to Government (G2G)
Business to Business (B2B)
In B2B E-Commerce, commercial transactions take
place between different business organizations, through the Internet. For
example, a cycle company may buy tyres from another company for their cycles.
When compared to other models, the value per transaction in B2B transaction is
high, because of bulk purchase. The company also might get the advantage of
discounts on bulk purchases. See Figure 15.7
Out-sourcing and Off-shoring are generally
associated with B2B E-Commerce.
● If a company’s work is hired to another company,
it would be termed as out-sourcing.
● If the work is outsourced to a company, which is
outside its own country, it is called as off-shoring.
Business to Consumer (B2C)
In B2C E-Commerce, commercial transactions take
place between business firms and their consumers. It is the direct trade between
companies and end-consumers via the Internet. B2C companies sell goods,
information or services to customers through online in a more personalized
dynamic environment and is considered as real competitor for a traditional
storekeeper. An example of B2C transaction is a book company selling books to
customers. This mode is intended to benefit the consumer and can say B2C
E-Commerce works as ’retail store’ over Internet. See Figure 15.8

Business to Government (B2G)
B2G is a business model that refers to business
organizations sells products, services or information to Governments or to its
administrations. In other words, when a company get paid for its goods,
services by the Government through Internet it is called as B2G model. e.g. The
Government or its administration buys laptops for students. See Figure 15.9

Consumer to Business (C2B)
C2B can be described as a form of E-Commerce where,
the transaction is originated by the consumers. The consumers will fix a
requirement or specific price for a service or a commodity. C2B model, is also
called as reverse auction model. Here, customer bid his price for a service or
a product. Then E-Commerce business entity will match the requirement of the
consumer to the best possible extent.
For instance, in a travel website (eg.yatra.com) a
consumer may specify his dates of travel, his source and destination, number of
tickets required and range of hotel etc. The website then finds out the various
options for him which best meets his requirements. These websites generate
revenue through affiliate links, sponsored advertisement or even a small
commission in every booking. e.g. Name-your-price websites. See Figure 15.10

Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
C2C in E-Commerce provides opportunity for trading
of products or services among consumers who are connected through the Internet.
In brief when something is bought and sold between two consumers using Internet
it is called C2C E-Commerce. Here the websites act as a platform to facilitate
the transaction. The electronic tools and Internet infrastructure are employed
to support transactions between individuals. Typically, this type of E-
Commerce works as Consumer to Business to Consumer (C2B2C). It means that a
consumer would contact a business in search of a suitable customer. Most of the
auction websites and matrimonial websites are working on this methodology.
For example, a consumer who wants to sell his
property can post an advertisement on the website (eg:timesclassifieds.com).
Another person who is interested in buying a property can browse the property,
advertisement posted on this site. Thus, the two consumers can get in touch
with each other for sale/purchase of property through another business’
website. See Figure 15.11
Consumer to Government (C2G)
Citizens as Consumers and Government engage in C2G
E -Commerce. Here an individual consumer interacts with the Government. C2G
models usually include income tax or house tax payments, fees for issue of
certificates or other documents. People paying for renewal of license online
may also fall under this category. See Figure 15.12

Government to Business (G2B)
G2B is closely related to B2G. G2B in E-Commerce
refers to a business model where Government providing services or information
to business organization. It may be a formal offer such as a takeover bid for a
road project. See Figure 15.13

G2B is a part of e- governance. The Government
provides information about business rules, requirement and permission needed
for starting a new business, and other specifications in its portal. The
objective of G2B is to reduce burdens on business, provide one-stop access to
information thereby boost the economy. e.g. ebiz.gov.in See Figure 15.14
Government to Consumer (G2C)
G2C in E-Commerce is very similar to C2G. Here the
Government provides platform for its citizens to avail its services and
information through the Internet. The services may be issue of certificates
through online.e.g. https://csc.gov.in/governmenttocitizen. See Figure 15.15

Government to Government (G2G)
G2G is the online (usually non-commercial)
interaction between Government organizations or departments. G2G’s principle
objective is to implement e-governance rather than commerce. G2G model in
e-governance involves distributing data or information between its
agencies/departments. G2G systems can be classified into two types
● Internal facing or local level - joining up a
single Government’s bureaucracy. e.g. https://www.nic.in/
● External facing or international level - joining
up multiple Governments’ bureaucracy.
See Figure 15.16

Related Topics