Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
Chemical Description of Follicle Stimulating Hormone
CHEMICAL DESCRIPTION
FSH belongs to a family of structurally related glyco-proteins which
includes LH, chorionic gonadotropin and thyroid-stimulating hormone. Each
hormone is a dimeric protein consisting of two non-covalently associated
glycoprotein subunits, denoted a and b. The α-subunit is identical for all these gonadotropins, and it is the
β-subunit that provides each hormone with its specific biological function.
The glycoprotein subunits of FSH consist of two polypeptide backbones
with carbohydrate side chains attached to the two asparagine (Asn) amino acid
residues on each subunit. The oligosaccharides are attached to Asn-52 and
Asn-78 on the α-subunit (92 amino acids), and to Asn-7 and Asn-24 on the β-subunit
(111 amino acids). The glycoprotein FSH has a molecular mass of
approximately 35 kDa. For the FSH preparation to be biologically active,
the two subunits must be correctly assembled into their three-dimensional
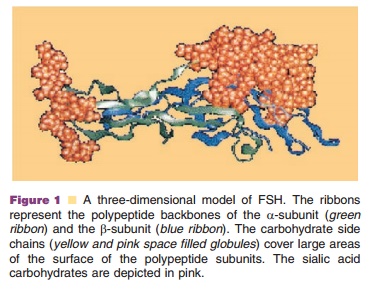
dimeric protein structure and post-translationally modified (Fig. 1).
Assembly and glycosylation are intracellular processes that take place
in the endoplasmatic reticulum and in the Golgi apparatus. This glycosylation
process leads to the formation of a population of hormone isoforms differing in
their carbohydrate side-chain composition. The carbohydrate side-chains of FSH
are essential for its biological activity since they (i) influence FSH receptor binding, (ii) play an
important role in the signal transduction into the FSH target cell, and (iii) affect the plasma residence time of the hormone.
Recombinant FSH contains approximately 36% carbohydrate on a mass per
mass basis. The carbohy-drate side chains are composed of mannose, fucose,
N-acetyl-glucosamine, galactose, and sialic acid. Structure analysis by 1H-NMR-spectroscopy on
oligosaccharides enzymatically cleaved from follitropin b, reveals minor differences with natural FSH. For instance, the
bisecting GlcNAc residues are lacking in the recombinant molecule, simply
because the FSH-producing CHO1 cells do not possess the enzymes to incorporate
these residues. Furthermore, the carbohydrate side-chains of recombinant FSH
exclusively contain a 2-3 linked sialic acid, whereas
in the natural hormone a 1-6 linked sialic acid occurs,
as well. All carbohydrate side-chains identified in recombinant FSH are,
however, moieties normally found in other natural human glycoproteins.
Related Topics