Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Permanganate, Dichromate and Ceric Sulphate Titration Methods
Ceric Sulphate Titration Methods
CERIC SULPHATE TITRATION METHODS
Ammonium ceric sulphate serves as a powerful oxidizing
agent in an acidic medium. The salt has a bright yellow colour and so its
solution. On reduction, the resulting cerous salt obtained is colourless in
appearance and, therefore, strong solutions may be considered as
self-indicating. In general practice, 0.05 N solutions are employed invariably
for estimations. As this concentration is very dilute for observation of the
respective end-point, hence the inclusion of an appropriate indicator becomes
necessary. The oxidation reac-tion involved may be expressed as follows :
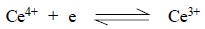
It is interesting to observe that the solutions of
ammoniurn ceric sulphate possess a number of advantages over permanganate and
dichromate methods discussed earlier, viz.,
(i) solutions
remain fairly stable even when boiled,
(ii) solutions
quantitatively react with either arsenite (AsO33–) or
oxalate [(COO)2]2– ion, and there-fore, either arsenic
trioxide or sodium oxalate may be employed as a primary standard,
(iii) cerous
ion Ce3+ is colourless and hence offers no interference with the
indicator end-point,
(i)
Ce3+ always solely results on reduction of Ce4+,
whereas permanganate (MaO4– ) can be reduced to any of
several oxidation states,
(ii)
ammonium ceric sulphate unlike potassium permanganate,
may be conveniently employed as an oxidizing agent in the presence of high
concentrations of HCl, thereby facilitating determinations of Fe2+
in the presence of Cl–, and
(iii)
ferrous phenanthrolone ion (ferroin) has proved to be a
very successful indicator in titrations with ceric salts. Thus, we have :
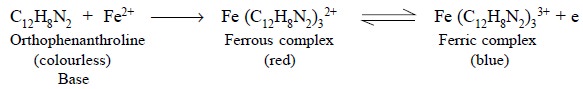
Orthophenanthroline (base) dissolves rapidly in aqueous
solutions of ferrous salts, thereby three moles combine with one Fe2+
ion to give a complex termed as ‘ferroin’
having an, intense red colour. Now, any strong oxidizing agent converts the
ferrous to a corresponding ferric complex having a slight blue colour.
1. Preparation of 0.1 N Ammonium Ceric Sulphate Solution
Materials Required : Ceric ammonium sulphate : 66 g
; sulphuric acid (conc.) : 30 ml.
Procedure : Dissolve 66 g of ceric
ammonium sulphate, with the help of gentle heat, in a mixture of ml of
sulphuric acid and 500 ml DW. Cool, filter the solution through a fine-porosity
sintered-glass crucible, dilute to 1 litre mark in a volumetric flask and mix
thoroughly.
Since the oxidation reaction is given by :

2. Stadardization of 0.1 N Ammonium Ceric Sulphate Solution
Materials Required : Arsenic trioxide : 0.2 g ;
sodium hydroxide solution (8.0% w/v) : 25 ml ; diluted sulphuric acid (10% w/v) : 30 ml ; osmic acid solution
(1.0% w/v in water) : 0.15 ml ; ferroin sulphate solution (dissolve 0.7 g of
ferrous sulphate in 70 ml of DW and add 1.5 g of 1, 10-phenanthroline and
sufficient water to produce 100 ml) : 0.1 ml.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.2 g
of arsenic trioxide previously dried at 105°C for 1 hour and transfer to a 500 ml conical flask.
Wash down the inner walls of the flask with 25 ml of sodium hydroxide solution,
swirl to dissolve, add 100 ml of water and mix. Add 30 ml of diluted sulphuric
acid, 0.15 ml of osmic acid solution, 0.1 ml of ferroin sulphate solution and
slowly titrate with ceric ammonium sulphate solution until the pink colour is
changed to a very pale blue. Each 4.946 mg of arsenic trioxide is equivalent to
1 ml of 0.1 N ammonium ceric sulphate or 0.06326 g of Ce(SO4)2.
2(NH4)2SO4 . 2H2O.
Equations :
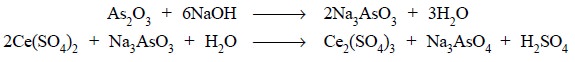
It is evident from the above equations that 4 equivalents
of ceric sulphate is required to oxidise 1 mole of arsenic trioxide, hence, 1
equivalent weight of arsenic trioxide is 1/4 mole or 197.84/4 or 49.46 g and 1
milliequivalent shall contain 49.46 mg or 0.04946 g.
Calculations : Therefore, the normality of
ammonium ceric sulphate solution may be expressed as follows :

2.1. Ferrous Fumarate
Materials Required : Ferrous fumarate : 0.3 g ;
diluted H2SO4 (10%
w/v) : 15 ml ; ferroin sulphate solution
; 0.1 N ammonium ceric sulphate solution.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.3 g
of ferrous fumarate and dissolve in 15 ml of dilute sulphu-ric acid by the help
of gentle heating. Cool, add 50 ml of water and titrate immediately with 0.1 N
ammonium ceric sulphate, employing ferroin sulphate solution as indicator. Each
ml of 0.1 N ammonium ceric sulphate is equivalent to 0.01699 g of C4H2FeO4.
Equations and Calculations :
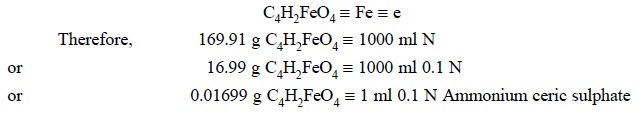
2.2. Acetomenaphthone
Materials Required : Acetomenaphthone : 0.2 g ;
glacial acetic acid : 15 ml ; dilute hydrochloric acid (10% w/v) : 15 ml ;
ammonium ceric sulphate 0.05 N ; ferroin sulphate solution.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.2 g
of acetomenaphthone and boil it with 15 ml of glacial acetic acid and 15 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid under a reflux
condenser for 15 minutes. Cool the contents carefully and taking adequate
precautions to avoid any atmospheric oxidation. Add 0.1 ml of ferroin sulphate
solution as indicator and titrate with 0.05 N ammonium ceric sulphate. Repeat
the assay without the substance being examined (blank determination) and incorporate
the correction, if any. Each ml of 0.05 N ammonium ceric sulphate is equivalent
to 0.006457 g of C15H14O4.
Equations :
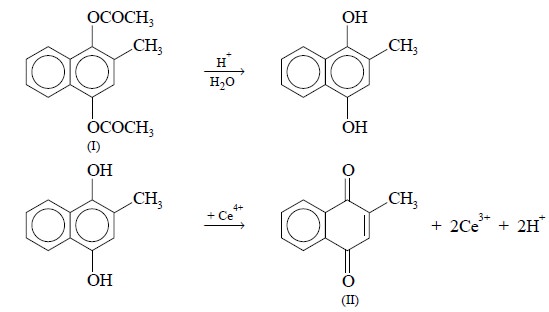
First, acetamenaphthone (I) undergoes hydrolysis in
acidic medium to yield the corresponding phenol and secondly, this phenol is
oxidised quantitatively with ammonium ceric sulphate to give the resulting 1,
4-dione derivative (II).
Calculations :
Thus, we have :
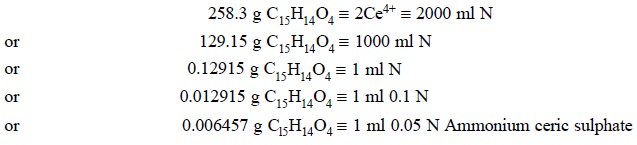
2.3. Cognate Assays
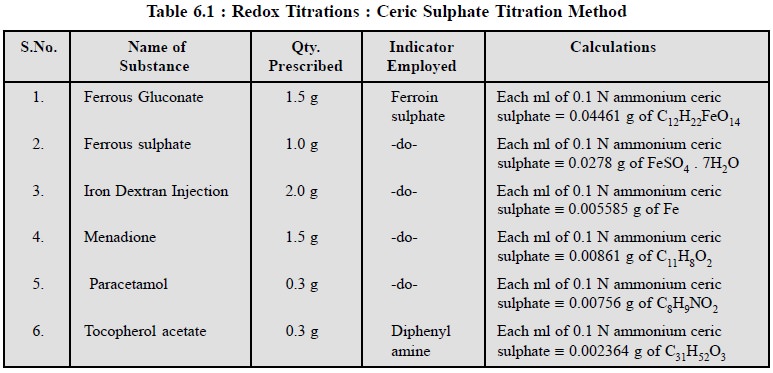
A number of pharmaceutical substances and dosage forms
may be determined by the help of ceric sulphate titration methods as given in
Table 6.1.
Related Topics