Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Nervous system
Carpal tunnel syndrome - Disorders of Peripheral nerves
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Definition
Syndrome of compression of the median nerve as it passes under the flexor retinaculum.
Age
Usually 40–50 years.
Sex
F > M (8:1)
Aetiology
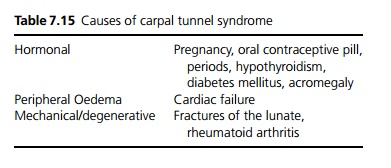
Often idiopathic (for other causes see Table 7.15).
Pathophysiology
The carpal tunnel is a tight space through which all the tendons to the hand and the median nerve pass. Any cause of swelling is therefore likely to cause compression of the medial nerve. The condition is commonly bilateral.
Clinical features
Tingling and numbness in the thumb, index finger and middle finger. Characteristically the pain wakes the patient at night and the patient shakes the wrist or hangs it over the side of the bed to relieve symptoms (unlike in cervical spondylosis). Symptoms are also induced by repetitive actions, or when the wrists are held flexed for some time, for example whilst knitting or reading a news-paper, and this latter can be used as a test (Phalen’s test), with the wrist hyperflexed for 1–2 minutes. Alternatively, tapping on the carpal tunnel (Tinel’s sign) may reproduce the symptoms although both tests are unreliable. Usually the dominant hand is affected first, but the condition is normally bilateral.
Clumsiness and weakness may occur in late cases, when there is often wasting of the thenar eminence and decreased palmar sensation.
Investigations
Median nerve conduction studies show impaired conduction at the wrist.
Management
Splinting the wrist in extension, particularly at night is useful prior to surgery, during pregnancy, or in those who wish to avoid surgery. Diuretics may help. Corticosteroid injection provides temporary relief. Definitive treatment is by surgical division of the flexor retinaculum, usually under local or regional anaesthetic. Treatment of underlying cause may relieve symptoms.
Related Topics