Flow of Control | C++ - C++ if-else statement | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 10 : Flow of Control
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 10 : Flow of Control
C++ if-else statement
if-else statement
In the previous examples of if, you have seen so for allow you to execute a set of statement is a condition evaluates to true. What if there is another course of action to be followed if the condition evaluates to false. There is another form of if that allows for this kind of either or condition by providing an else clause. The syntax of the if-else statement is given below:
if ( expression)
{
True-block;
}
else
{
False-block;
}
Statement-x
In if-else statement, first the expression or condition is evaluated either true of false. If the result is true, then the statements inside true-block is executed and false-block is skipped. If the result is false, then the statement inside the false-block is executed i.e., the true-block is skipped.
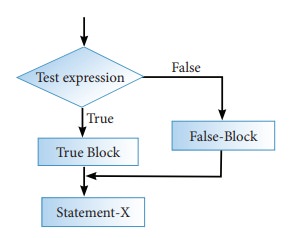
Illustration 10.4 C++ program to find whether the given number is even number or odd number using if-else statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num, rem;
cout<< "\n Enter a number: ";
cin>>num;
rem = num % 2;
if (rem==0)
cout<< "\n The given number" <<num<< " is Even";
else
cout<< "\n The given number "<<num<< " is Odd";
return 0;
}
Output
Enter number: 10
The given number 10 is Even
In the above program, the remainder of the given number is stored in rem. If the value of rem is zero, the given number is inferred as an even number otherwise, it is inferred as on odd number.
Related Topics