Flow of Control | C++ - C++ Switch statement | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 10 : Flow of Control
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 10 : Flow of Control
C++ Switch statement
Switch statement
The switch statement is a multi-way branch statement. It provides an easy way to dispatch execution to different parts of code based on the value of the expression. The switch statement replaces multiple if-else sequence.
The syntax of the switch statement is;
switch(expression)
{
case constant 1:
statement(s);
break;
case constant 2:
statement(s);
break;
.
.
.
.
default:
statement(s);
}
In the above syntax, the expression is evaluated and if its value matches against the constant value specified in one of the case statements, that respective set of statementsare executed. Otherwise, the statements under the default option are executed. The workflow of switch statement and flow chart are shown below.
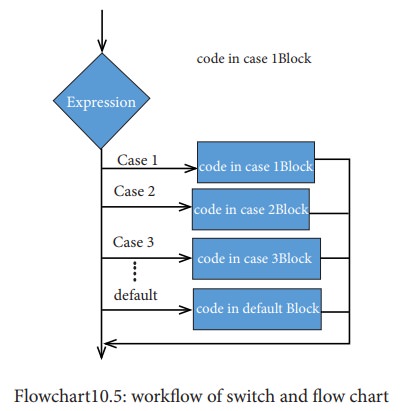
Rules:
1. The expression provided in the switch should result in a constant value otherwise it would not be valid.
2. Duplicate case values are not allowed.
3. The default statement is optional.
4. The break statement is used inside the switch to terminate a statement sequence. When a break statement is reached, the switch terminates, and the flow of control jumps to the next line following the switch statement.
5. The break statement is optional. If omitted, execution will continue on into the next case. The flow of control will fall through to subsequent cases until a break is reached.
6. Nesting of switch statements is also allowed.
Illustration 10.8 – C++ program to demonstrate switch statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num;
cout << "\n Enter week day number: ";
cin >> num;
switch (num)
{
case 1 : cout << "\n Sunday"; break;
case 2 : cout << "\n Monday"; break;
case 3 : cout << "\n Tuesday"; break;
case 4 : cout << "\n Wednessday"; break;
case 5 : cout << "\n Thursday"; break;
case 6 : cout << "\n Friday"; break;
case 7 : cout << "\n Saturday"; break;
default: cout << "\n Wrong input....";
}
}
Output:
Enter week day number: 6
Friday
Illustration 10.9 – C++ program to demonstrate switch statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char grade;
cout << "\n Enter Grade: ";
cin >> grade;
switch(grade)
{
case 'A' : cout << "\n Excellent...";
break;
case 'B' :
case 'C' : cout << "\n Welldone ...";
break;
case 'D' : cout << "\n You passed ...";
break;
case 'E' : cout << "\n Better try again ...";
break;
default : cout << "\n Invalid Grade ...";
}
cout << "\n Your grade is " << grade;
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter Grade: C
Welldone ...
Your grade is C
Related Topics