Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Asthma
Briefly describe the pharmacology of medications available to treat asthma.
Briefly describe the pharmacology of
medications available to treat asthma. Which medications are used for long-term
control, and which ones for acute attacks? Outline a treatment plan based on
the degree of severity.
The medications used to treat asthma are
detailed in Table 80.3.
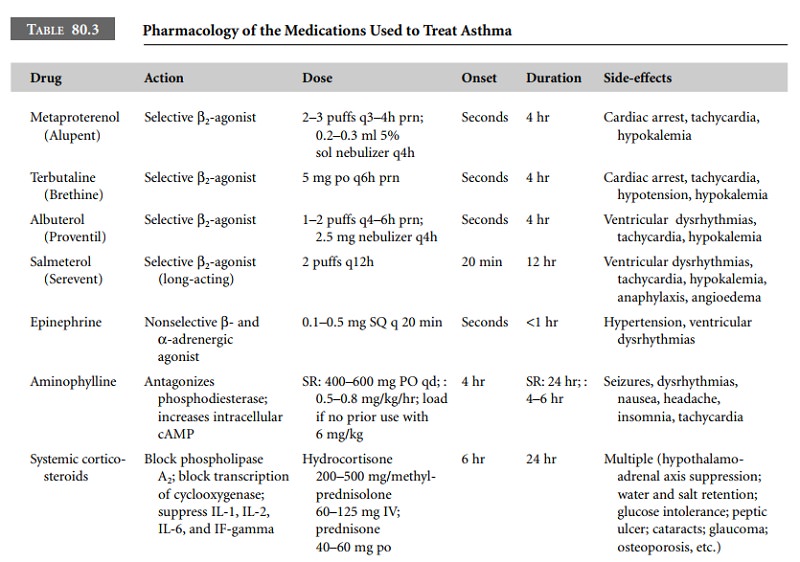
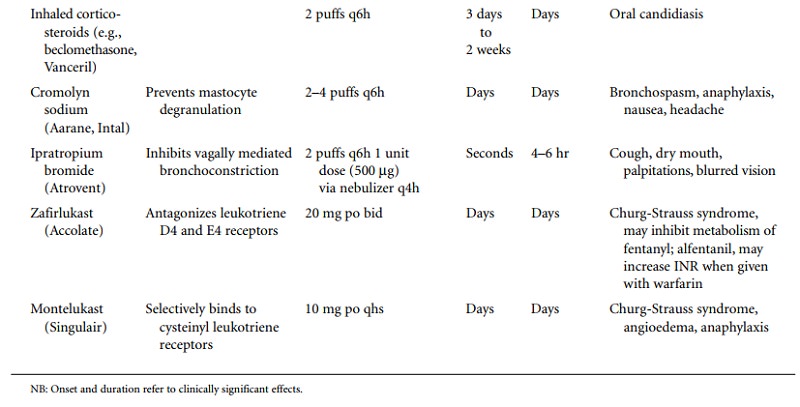
Short-acting β2-agonists and systemic steroids are used for the treatment of acute
attacks. All other medications are used for the long-term control of asthma.
Patients with severe disease occasionally need to be given oral steroids for
long periods of time.
A detailed discussion of the long-term
treatment of asthma is beyond the scope of this chapter, and recom-mendations
vary among authors. Suggested regimens are as follows:
·
Mild intermittent asthma: short-acting β2 agonist used on an
as-needed basis.
·
Mild persistent asthma: low dose of inhaled steroid or a leukotriene antagonist as a long-term
treatment, in addition to a short-acting β2-agonist inhaler.
·
Moderate persistent asthma: medium dose of inhaled steroid with or without a long-acting β2-agonist.
·
Severe persistent asthma: high dose of inhaled steroid and a long-acting bronchodilator. In
addition, long-term oral steroids are often required. An extended-release
theo-phylline can be used to decrease the frequency of attacks and nocturnal
symptoms.
Acute attacks not responding to
self-administered metered-dose inhaler (MDI) β2-agonist are usually treated with β2-agonist nebulizers and systemic steroids (e.g., methylprednisolone
125 mg IV) that will then be tapered over a few days. In case of failure after
escalating doses of a β2-agonist (15 mg of albuterol nebulized over 1 hour), sub-cutaneous
epinephrine (0.3 mg q 20 min) can be used with electrocardiogram (ECG)
monitoring. Magnesium has been used as a last-resort bronchodilator for
refractory bronchospasm.
Related Topics