Chapter: Civil Engineering : Building Components and Structures
Bridges
BRIDGES
INTRODUCTION
A bridge is a structure providing
passage over an obstacle without closing the way beneath.
The required passage may be for a
road, a railway pedestrian or a canal of a pipeline. The obstacle to be crossed
may be river, a road, a railway or a valley.
CLASSIFICATION OF BRIDGES
Bridges can be classified into various types depending upon
the following factors:
Materials used for construction : Under
this category bridges may be classified as:
a) Timber bridges b) Masonry bridges
c) Steel bridges d)
Reinforced cement concrete bridges
e) Pre-stressed concrete bridges f) Composite bridges
Alignment : Under this category, the
bridge can be classified as
a)
Straight or square bridges and b) Skew
bridges
Straight
or square are the bridges which are at right angles to the axis of the river.
Skew
bridges are not at right angles to the axis of the river.
The Relative position of bridge floor: Under
this category, the bridge and classified as
a)
Deck bridge b) Semi
through bridge and c) Through bridge
Deck bridges are the bridges whose floorings are supported at the top of the super
structure. Through bridges are the bridges whose floorings are supported at the
bottom of the super structure. Semi-through bridges are the bridges
whose floorings are supported at some intermediate level of the super
structure.
Function of Purpose : Under
this, the bridge can be classified as
a) Highway bridge b) Railway bridge c)
Foot bridge
d) Viaduct and e)
Aqueduct etc.
Position of High floor level : Under
this, the bridges may be classified as
a)
Submersible bridge and b)
Non-submersible bridge
Submersible Bridges are the
bridges whose floor levels are below the high flood level. During flood
seasons, it allows the water to pass over the bridge submerging the
communication route. In economic point of view, these bridges are constructed.
Non-submergible bridges are the
bridges whose floor levels are above the high flood level.
Life : Under this, the bridges may be
classified as
a)
Permanent bridges b) Temporary bridges
Type of Superstructure : Under
this, the bridges may be classified as
a)
Arch bridges b) Truss
bridges
c)
Portal frame bridges d)
Balanced cantilever bridges
e)
Suspension bridges etc.,
Span length : Under this category,
the bridges can be classified as
a) Culverts
(span less than 6m)
b) Minor
bridges (span between 6 to 30m)
c) Major
bridges (span above 30m
d) Long span
bridges (span above 120m)
Loading : Road bridges and culverts have
been classified by Indian raod congress into
a)
Class AA bridges b) Class
A bridges
c) Class B
bridges according to the loadings they are designed to carry.
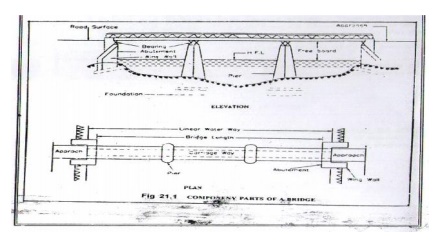
COMPONENT PARTS OF A
BRIDGE
Broadly, a Bridge can be divided into two major parts.
1. Sub structure 2. Super structure
1. SUB STRUCTURE
The function of the sub structure
is similar to that of foundations, columns and walls of a buildings, becaus e
it supports the super structure of the bridges and transmits the load safely to
the ground.
The substructure consists of the following:
a. Abutments b. Piers
c. Wi ng walls d. Approaches
e. Foundations for the piers and abutments
a. Abutments: The end of su perstructure
of a bridge is called abutments.
Its main functions are
1. To
laterally support t he earth work of the embankment of the approac hes.
2. To
transmit the load f rom the bridge superstructure.
3. To give
final formati on level to the bridge.
Bridge abutments can be made of
brick masonry, stone masonry, plain concrete or reinforced concrete
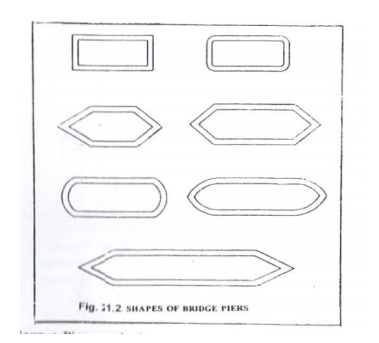
b. Piers : Piers are
the intermediate supports for the superstructure. Piers transmit the loads
from the superstructur e of the bridge to the foundations. A pier essent ially
consists of a column or shat and a fo undation. They may have different
configurati ons as shown in figure. These piers may be constructed with stone
masonry or concrete.
c. Wing walls : These
are th e walls provided at both ends of the abutments to retain the earth
filling of the approach road. They are constructed of the same materi al as
those of the main abutment.
d. Approaches: The
portio n of the road constructed to reach the bridg e from their general
route or height is known as approach of the bridge. The alignment and the level
of the approaches mainly dep end on the design and layout of the bridge.
e. Foundations for the Piers and
Abutments : The foundation of a bridge structure distributes
the load from the piers and abutments over the larger area of sub soil. It
prevents the tilting and ov er-turning of the piers and abutments and also
unequal settlement of the sub soil.
The different types of funct ions adopted for
bridges are:
i. Spread foundation
ii. Raft foundation iii. Pile
foundation
iv. Caisson foundation v. Well foundation
2. Super structure : The
super structure is that part of the bridge over which the traffic moves
with safely.
It consists of:
a. Decking b. Parapet or hand rails, guard
stones etc. c.
Bearing
a. Decking :
It
is provided to allow the road surface to be built in over it. It may consist
of a slab, trusses, arches etc.
b. Parapet
or Hand rails, guard stones: These are the protective works
provided on both sides of the deck along the roadway in order to safe
guard the moving vehicles and the passengers on a bridge. Foot paths are also
provided for pedestrians to walk along the bridge. In order to prevent a
vehicle from striking the parapet wall of the hand rails, guard stones painted
white are provided at the ends of the road surfaces.
c. Bearing: It is
part of the bearing structure provided to distribute the load coming from the
superstructure and also to allow for longitudinal and angular movements.
Related Topics