Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Nervous system
Brachial plexus injuries - Disorders of Peripheral nerves
Brachial plexus injuries
Definition
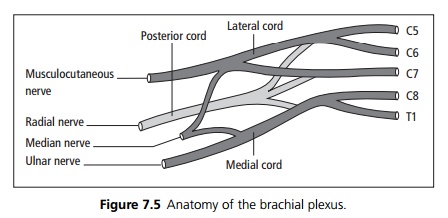
The brachial plexus is formed from the nerve roots of C5–T1, which form into the medial, lateral and posterior cords. These then form the median, ulnar, radial and musculocutaneous nerves supplying the arm (see Fig. 7.5). Lesions of the upper plexus (C5/6) cause Erb’s palsy and lesions of the lower plexus (C8/T1) causes a Klumpke’s palsy.
Aetiology
· Trauma: By severe traction with the arm in abduction (usually after a motorcycle accident), or penetrating trauma. Traction injury during a difficult labour may damage the brachial plexus most commonly causing an Erb’s palsy.
· Cervical rib: A bony or fibrous protrusion from the transverse process of C7 can stretch the lower roots of the brachial plexus.
· Malignant infiltration.
Clinical features
Erb’s palsy (C5/6 lesions) with failure of abduction and external rotation of the arm. The arm is held in adduction and internal rotation (waiter’s tip position).
Klumpke’s palsy (C8/T1 lesions) The intrinsic muscles of the hand are paralysed (ulnar nerve) resulting in wasting of the small muscles, a claw hand (flexor digitorum muscles supplied by the median nerve) and loss of ulnar sensation.
In a total plexus lesion the entire arm is paralysed and numb.
Pain is characteristic of infiltration.
Investigations
Chest X-ray may show an apical lung lesion (Pancoast tumour) or a cervical rib. MRI is the most useful imaging to investigate brachial plexus lesions.
Management
Treatment of the underlying cause. In traumatic injuries open wounds should be explored and clean cut nerves repaired or grafted if possible. Pain relief may be required.
Related Topics