Production, Steps, Applications - Biogas Production | 11th Microbiology : Chapter 9 : Environmental Microbiology
Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 9 : Environmental Microbiology
Biogas Production
Biogas Production
Worldwide energy consumption and demand are growing up since
past 50 years. With the growth of population, demand for energy is also
increasing leading to an uneven supply and distribution of resources.
Therefore, the requirement of sustainable and eco friendly energy in India to
satisfy the energy demand is inevitable. Along with the source of sustainable
green energy, biogas production is an alternative way to produce clean energy
through solid waste management.
Biogas is a type of renewable energy that can be produced from
decomposition of animal and plant waste. It is composed of 50– 75% methane,
25–50% carbon dioxide, 0–10% nitrogen, 0–3% hydrogen sulphide, 0–1% hydrogen
and traces of other gases. The term “anaerobic” suggests that the process
occurs in the absence of free oxygen and produces CH4 through
decomposition of waste in nature and reduces environmental pollution.
Biogas generating technology is a favorable dual purpose
technology at present since used as fuel and fertiliser.
Leftover foods fruit & vegetable wastes and cow dung can be subjected to anaerobic digestion for energy production in a variety of ways.
Production of Biogas
Biogas production is carried out in an airtight cylindrical tank
called biogas digester Cow dung is mixed with equal volume of water and made
into slurry and fed through the inlet of the biogas unit. The digestion
proceeds at 37°C with sufficent amount of nitrogen and phosphorus. The
production of biogas sets around 40-50 days, under anaerobic conditions.
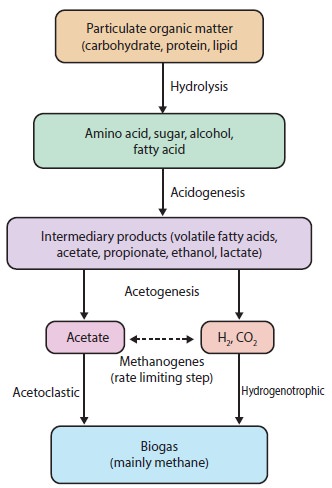
Production of biogas accomplished in 3 stages namely Hydrolysis, Acetogenesis
and Methanogenesis
Steps
Hydrolytic fermentative stage
In this step, several microbes secrete different enzymes, which
cleave the complex macromolecules into simpler forms. Organisms that are active
in a biogas process during the hydrolysis of polysaccharides include various
bacterial groups such as Bacillus, Clostridium, Cellulomonas.
Acetogenic stage
Through various fermentation reactions, the products from
hydrolysis are converted mainly into various organic acids (acetic acid,
propionic acid, butyric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid), alcohols, ammonia
(from amino acids), carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Facultative anaerobes and
hydrogen producing bacteria Example: Acetovibrio
cellulosolvens, Bacteroid cellulosolvens are involved.
Methanogenic stage
In this step, obligate anaerobic methane producing bacteria produce Methane gas as the major end product
along with Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen and traces of other gases. Methanogenesis
has six major pathways, each converting a different substrate into Methane gas.
The six major substrates used are Carbon dioxide, Formic acid, Acetic acid,
Methanol, Methylamine, and Dimethyl sulphate. The methanogenic bacteria include
Methanococcus voltae and Methanobacterium formicum (Figure 9.14
a, b).
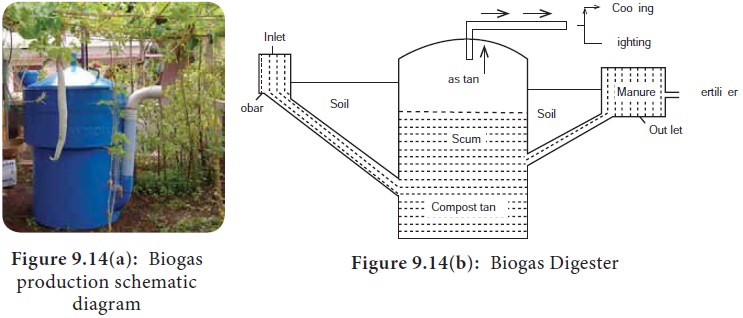
Small scale biogas unit
The biogas production is carried out in an air tight cylindrical tank called biogas digester (Figure9.15).
Applications
· Biogas used as fuel
·
Used to generate electricity
·
Biogas is used to run any type of heat engine in order to generate
electrical and mechanical power.
·
Producing high quality fertilizer.
·
Reducing water and air pollution.

Related Topics