Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: General Organization and Functions of the Nervous System
Autonomic Neurotransmitters
AUTONOMIC
NEUROTRANSMITTERS
Two PNS neurotransmitters,
acetylcholine and norepi-nephrine, have particular clinical importance. Both
are synthesized and stored primarily in the nerve terminals until released by a
nerve impulse. It should be noted, to avoid confusion, that in the United
States the transmit-ter in the sympathetic nervous system is referred to as norepinephrine and the major adrenal
medullary hor-mone is referred to as epinephrine.
In Europe and most of the world these two substances are called noradrena-line and adrenaline, respectively.
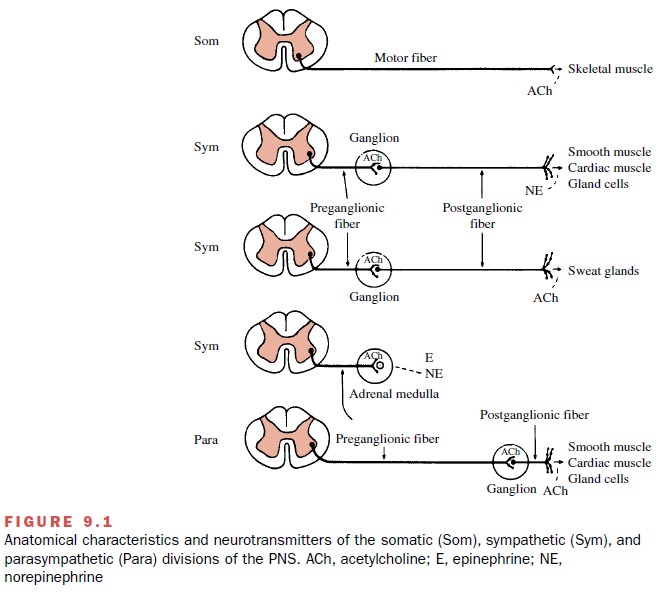
Neurotransmission in the PNS
occurs at three major sites: (1) preganglionic synapses in both
parasympa-thetic and sympathetic ganglia, (2) parasympathetic and sympathetic
postganglionic neuroeffector junctions, and all somatic motor end plates on
skeletal muscle. Acetylcholine is the transmitter released at all of these
sites except for the majority of sympathetic neuroeffec-tor junctions. Neurons
that release acetylcholine are called cholinergic
neurons.
Norepinephrine is the
transmitter released at most sympathetic postganglionic neuroeffector
junctions. Neurons that release this substance are called adrener-gic or noradrenergic neurons.
Not all sympathetic post-ganglionic neurons are noradrenergic. The sympathetic
postganglionic neurons that innervate the sweat glands and some of the blood
vessels in skeletal muscle are cholinergic; that is, they release acetylcholine
rather than norepinephrine, even though anatomically they are sympathetic
neurons (Fig. 9.1).
Drugs that mimic the actions
of acetylcholine are termed cholinomimetic,
and those that mimic epineph-rine and/or norepinephrine are adrenomimetic. The cholinomimetic drugs
are also called parasympatho-mimetic drugs. The adrenomimetic drugs are often
called sympathomimetic.
The receptors with which
acetylcholine and other cholinomimetic drugs interact are called cholinorecep-tors, while the receptors
with which norepinephrine, epinephrine,
or other adrenomimetic drugs combine are called adrenoceptors. It is common both in textbooks and the scientific
literature to see these receptors re-ferred to as cholinergic or adrenergic
receptors. This is improper usage of the terms cholinergic and adrenergic,
since these terms should be applied only to nerves.
Drugs that antagonize the
actions of acetylcholine are known as cholinoreceptor
antagonists; those that an-tagonize norepinephrine are known as adrenoceptor an-tagonists.
A number of other substances
are released by sym-pathetic and parasympathetic neurons, often the same
neurons that release norepinephrine or acetylcholine. These substances include
adenosine triphosphate (ATP), neuropeptide Y, and substance P.
Related Topics