Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Cardiovascular system
Atrial flutter - Atrial arrhythmias
Atrial flutter
Definition
Atrial flutter is a rapid atrial rate between 280 and 350 bpm, most commonly 300 bpm.
Aetiology
Atrial flutter is almost always a complication of myocardial disease such as ischaemic, hypertensive and rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis and constrictive pericarditis. It may be caused by thyrotoxicosis.
Pathophysiology
Normally once a cardiac cell has been depolarised it is refractory to restimulation for a short period. This prevents waves of cardiac depolarisation flowing in a retrograde direction. If, however, the conduction through the myocardium is slow (usually due to myocardial damage), adjacent cells may have recovered from their refractory period allowing restimulation and hence the formation of a recurrent cycle of depolarisation or circus movement (also termed reentry).
In atrial flutter the circuit is single and has a characteristic location in the right atrium involving an area close to the entrance of the vena cavae. This relatively fixed physical characteristic explains the typical ECG appearance and consistent cycle length between individual patients.
Whilst the atrial rate is between 280 and 350 beats, the normal atrioventricular delay in the AV node limits the ventricular rate. This usually produces a 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1 atrioventricular block.
Clinical features
Atrial flutter presents with palpitations, dizziness, syncope or cardiac failure. It may occur persistently or in episodes (paroxysmal atrial flutter) that last minutes or hours to days. The pulse rate is dependent on the degree to which the AV node blocks the rate but is most commonly around 150 bpm (2:1 block). Massage of the carotid sinus causes a transient increase in block with consequent slowing of the ventricular rate.
Investigations
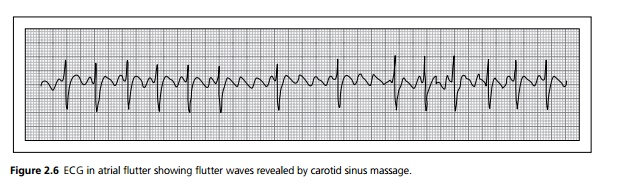
Atrial flutter produces a characteristic regular sawtooth ŌĆśflutterŌĆÖ waves at a rate of 300 bpm seen best in lead V1. If there is 2:1 block, the QRS complexes often obscure the flutter waves, but carotid sinus massage should reveal them (see Fig. 2.6).
Management
DC cardioversion is the best treatment to restore sinus rhythm rapidly. Drug treatment is used to control the ventricular rate, prevent recurrence and may occasionally restore sinus rhythm. Following electrophysiological assessment, recurrence may be prevented by radiofrequency ablation of atrial flutter circuits. Digoxin increases AV block and reduces the ventricular rate, amiodorone may restore sinus rhythm and reduce the frequency of paroxysms.
Related Topics