Term 3 Unit 1 | Geography | 6th Social Science - Asia | 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 1 : Asia and Europe
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 1 : Asia and Europe
Asia
PART
A.
ASIA
Asia is the largest and the most populous
continent in the world. It covers about 30 percent of the world’s land area and
about 60 percent of the world’s population. Most of the land of Asia lies in
the northern hemisphere. It has different types of physical and cultural
features. Lofty mountains, plateaus, plains, islands and peninsulas are the
major physiographic features of Asia. Many perennial rivers flow through
different parts of Asia. These river valleys are the cradles of ancient
civilizations (Indus valley, Mesopotamian and Chinese civilizations). Let us
know more about our home continent.
Location and
Area
Asia extends from 10˚11' South to 81˚12' North
latitudes and from 26˚2' East to 169˚40' West, longitudes. It spreads for an
area of 44 million km2.
Boundaries
Asia is surrounded by the Arctic Ocean in the
north, Pacific Ocean in the east, Indian Ocean in the south and the Ural
Mountains, Caucasus Mountains, Red Sea, Mediterranean Sea, Caspian Sea and
Black Sea in the west.
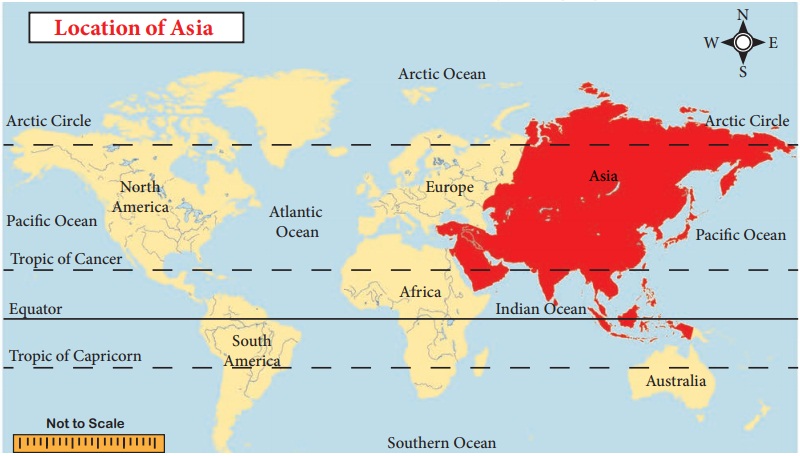
The Suez Canal separates Asia from Africa. The
narrow Bering Strait separates Asia from North America.
Political
Divisions
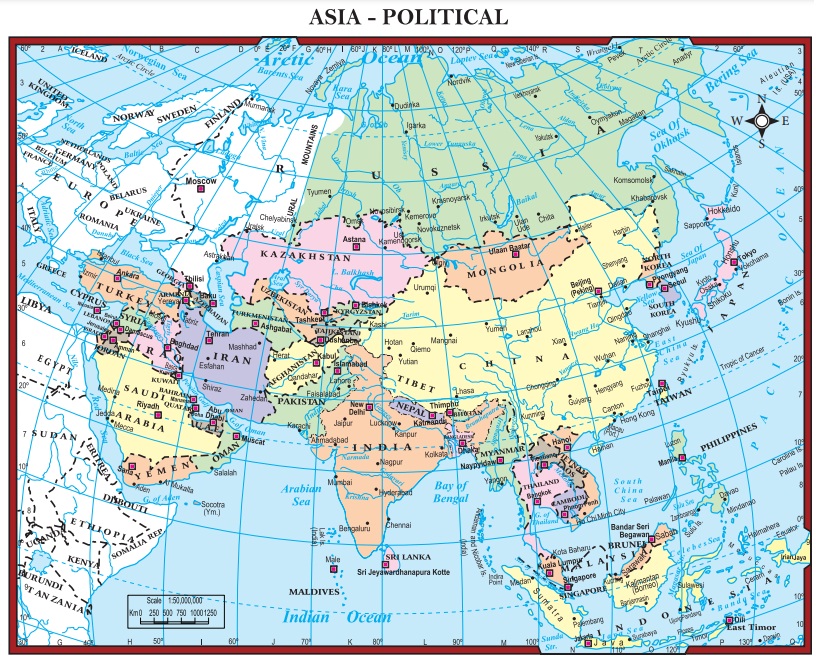
There are forty eight countries in Asia. The
countries are grouped into several realms based on landscape and political
status such as
1. East Asia
2. Southeast Asia
3. South
Asia
4. Southwest and
5. Central Asia
Physiographic
Divisions
Asia is the land of long mountain ranges, snow capped high mountains, vast plateaus, extensive plains, river valleys and sea coasts. These diverse physical features encourage the people of this continent to involve in diverse economic activities.
Fact :
There are 12 landlocked countries in Asia. Among these, only one is doubly landlocked which means it is surrounded
entirely by other landlocked countries. Find out the doubly landlocked country.
The physiography of Asia can be divided into five
major groups. They are;
1. The Northern lowlands
2. The Central High Mountains
3. The Southern Plateaus
4. The Great Plains and
5. The Island Groups
1. The Northern Lowlands
The most extensive
lowland in Asia is the Siberian plain. It extends from the Ural
Mountains in the west to the Verkhoyansk Range in the east.
2. The Central Highlands
The central
highlands stretches from Turkey to the Bering Strait. There are two knots found
in Asia. They are 1. The Pamir Knot 2.The Armenian Knot.
'Knot' refers to the on vergence of
mountain ranges
The Hindukush
range, the Sulaiman range, the Himalayan range and the Tian Shan range radiate from the
Pamir Knot.
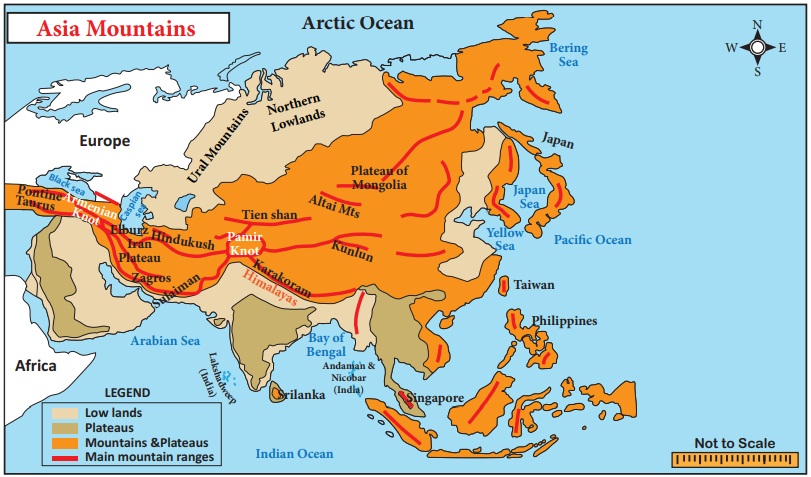
Mountain Ranges radiate
from the Pamir and the Armenian Knot
The Hindukush range
continues westward as the Elburz, whereas the Sulaiman range
continues south west as the Zagros range. The Elburz and the Zagros
converge at the Armenian knot. The Taurus and the Pontine
ranges radiate from the Armenian knot. The other important mountain ranges are
the great Khingan, the Altai, the Verkoyansk and the Arakan
yoma. The Himalayan mountain range is the highest mountain range in the
world Mt. Everest (8848 m) is the highest peak in Asia, as well as the world.
The lowest point in
the world is located in Dead Sea in Asia. Intermontane plateaus are
found in these mountain ranges. The important plateaus are
1. The plateau of Anatolia (Pontine
to Taurus)
2. The plateau
of Iran (Elburz to Zagros mt)
3. The plateau
of Tibet (Kunlun
to Himalayas )
Tibet
is called the ‘Roof of the world’ and it is also known as the third
pole because of its cold weather, largest reserve of freshwater
and inhospitable environment.
HOTS :
The Khyber Pass is located in the
Sulaiman range, the Bolan Pass is located in Toba Kakar range. What is the
importance of these two passes?
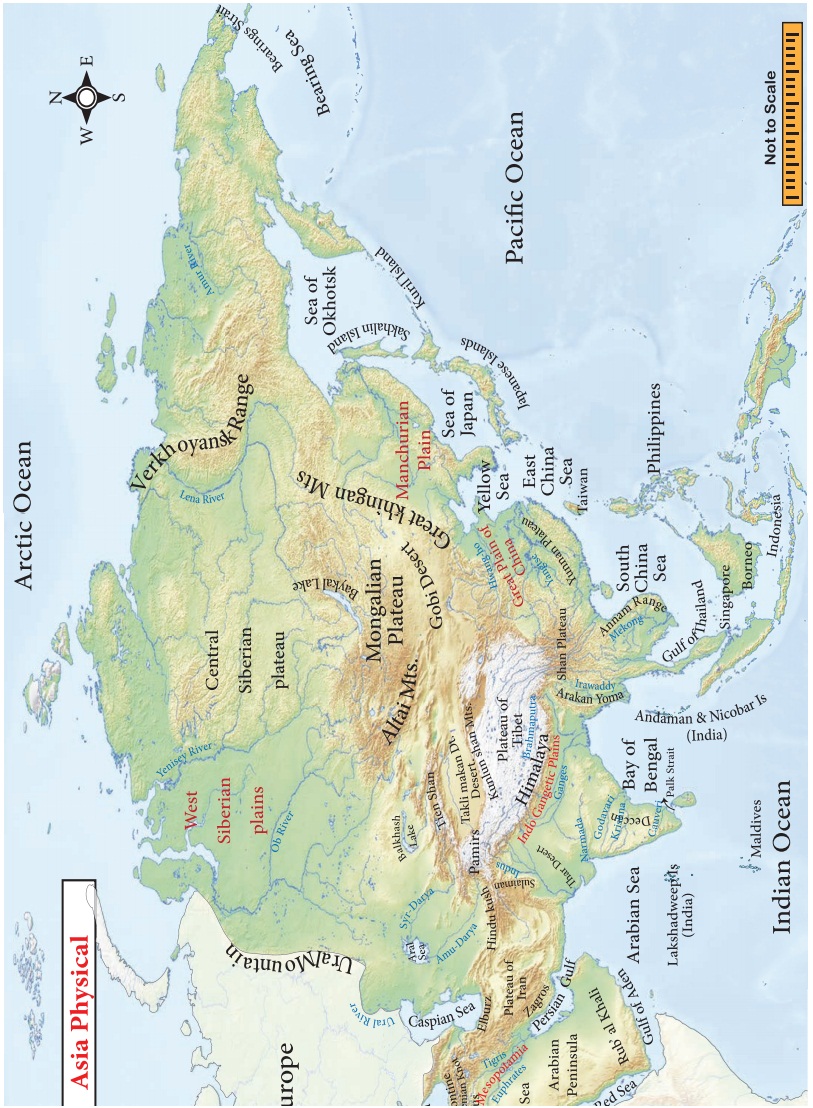
3. The Southern Plateaus
The southern
plateaus are relatively lower than the northern plateaus. The four important
southern plateaus are the Arabian Plateau (Saudi Arabia), Deccan
Plateau (India), Shan Plateau (Myanmar) and the Yunnan
Plateau (China). Among these plateaus, the Arabian Plateau is the largest
Plateau.
4. The Great Plains
The great plains
are formed by the major rivers of Asia. They are the West Siberian plain
(Ob and Yenisey), Manchurian Plain (Amur), Great Plain of China (Yangtze
and Sikiang), Indo- Gangetic Plain (Indus and Ganga),
Mesopotamian plain (Tigris and Euphrates) and the Irrawaddy plain (Irrawaddy).
5. The Island Groups
Numerous islands
are found in the Pacific coast of Southeast Asia. Kuril, Taiwan,
Singapore and Borneo are the important island groups.
The Philippines,
Japan islands and Indonesia are the major archipelagos in Asia.
Smaller archipelagos are also located in the Indian Ocean such as the islands of
Maldives and Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea. Bahrain is in
the Persian Gulf. Sri Lanka is an island, which is located in the Bay of
Bengal.
A group of islands is called an
archipelago. The largest archipelago
is Indonesia.
Drainage
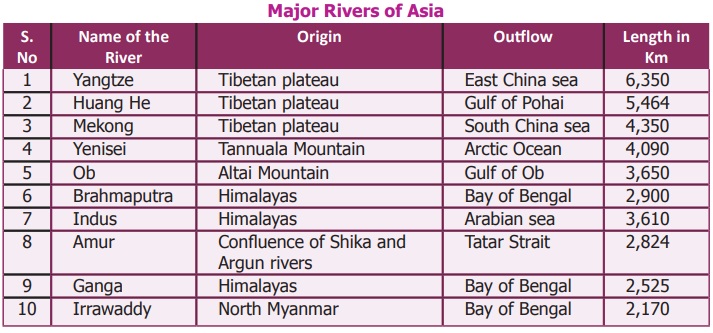
The rivers of Asia
originate mostly from the central highlands. The Ob, Yenise and Lena are
the major rivers that flow towards the north and drain into the Arctic
Ocean. These rivers remain frozen during winter. On the other hand, South Asia
has many perennial rivers (e.g.) Brahmaputra, Indus, Ganga and
Irrawaddy which originate from the snow covered high mountains that
do not freeze during winter. The Euphrates and Tigris flow in
West Asia. The Amur, Huang He, Yangtze and Mekong rivers flow in
the south and south eastern parts of Asia. Yangtze is the longest river
in Asia.
The Three Gorges dam has been
constructed across the river Yangtze. It is the largest power station dam in
the world. It fulfills ten percent of power needs of China.


Climate
Asia exhibits a
variety of climate. The northern part of Asia experiences severe long winter
and cool summer. (Winter -37°C and Summer 10°C). Precipitation
is in the form of snow (250 mm to 300 mm).The north eastern
part of Asia experiences cold winter and warm summer and a moderate
rainfall of 50 mm to 250 mm.
The south, south
east and eastern parts of Asia are strongly influenced by monsoon winds. Summer
is hot and humid while winter is cool and dry. The summer monsoon winds bring
heavy rainfall to India, Bangladesh, Indo-China, Philippines and Southern China
(1500 mm to 2500 mm). In India, Mawsynram (11871 receives
the highest rainfall. So, this place is called the wettest place in the world.
The areas found in
and around the equator have uniform climate throughout the year. There is no
winter. The average temperature is 27°C and the mean rainfall is 1270
mm.
HOTS :
There is no winter in the equatorial
region. Why?
The west and
central parts of Asia have hot, dry climate. The temperature is very high
during the day and very low during the night. Rainfall varies from 25 mm to
200 mm. The West coastal fringe of Asia (along the Mediterranean
Sea) receives rainfall in winter and is warm in summer.
Deserts are found
along the western part of Asia. The major hot deserts are the Arabian (Saudi
Arabia) and Thar (India and Pakistan) deserts. The cold
deserts of Asia are Gobi and Taklamakan. The largest desert in
Asia is the Arabian Desert.
Natural
Vegetation
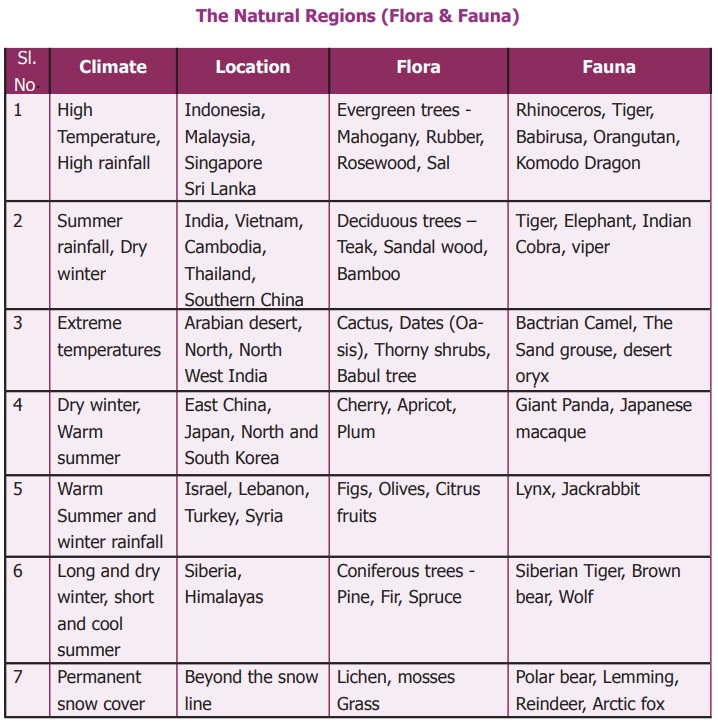
Natural vegetation
depends upon rainfall, temperature and soil. As Asia stretches
from the equator to poles, all types of vegetation are found here. Some rare
species are found in Asia. (Orang-Utan, Komodo Dragon, Giant panda ).The
Asian flora and fauna are listed below:

Fact :
A Desert is a large area that gets
very low rainfall and very few plants and animals. There are two types of
deserts found in Asia, Hot and cold deserts. Rub’al Khali desert is thelargest, continuous sandy desert in
the world.It is found in the southeastern part of Saudi Arabia.
Resource
Base and Economic Activities of Asia
Mineral Resources
Asia has a variety
of mineral deposits. It holds an important place in the production of Iron,
Coal, Manganese, Bauxite, Zinc, Tungsten, Petroleum, Tin etc. Oil
and Natural Gas found in the west Asian countries. One third
of the world’s oil is produced in Asia. Among the west Asian countries, Iran
has a considerable wealth of mineral resources. The important minerals found in
Asia are:
Iron Ore: Asia has the largest deposits of iron
ore in the world. China and India are the important iron ore
deposit countries of Asia. Turkey, Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand,
Myanmar etc., are a few other countries that have iron ore deposits.
Coal: Coal is a fossil fuel. Asia has the largest
deposits of coal in the world. China and India are the largest
producers of coal in Asia.
Petroleum: Petroleum is a mineral
oil. The largest petroleum reserves are found in South West Asia. The important
petroleum producing countries are Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iran, Bahrain, Qatar
and UAE. South China, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, India, Russia are the
other important petroleum producing countries in Asia.

Bauxite is found in India and Indonesia.
India is the largest producer of Mica in the world. Tin
is found in Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia.
Agriculture
Only about 18
percent of the total area is cultivable in Asia. Agriculture is the chief
occupation of the people here. The river valleys in the South, South East and
East Asia have rich alluvial soil. Agriculture is intensively practised in the
riverine plains of Asia. However, some areas are not suitable for agricultural
practices. India has the largest area of arable lands in Asia.
Most of the west Asian countries cultivate their crops where the ground water
level is nearer to the surface. Iraq practices agricultural activities based on
the availability of rainfall and supply of water from Euphrates and Tigris
rivers.
Rice and Wheat are the staple food crops
in Asia. China and India are the leading producers of rice in the world. Other
important rice producing countries are Myanmar, Japan, Bangladesh and Thailand.
Monsoon Asia is suitable for rice cultivation because of the abundant
rainfall, fertile plains and availability of labour. Thailand is called
the Rice bowl of South East
Asia.
Banaue rice terrace: The Banaue rice
terraces were built 2000 year ago by the Ifugaos people in the Philippines. It
is located approximately about 1524 m above sea level.

Wheat is grown in the temperate regions of
Asia. Russia, India, China and Pakistan are the leading producers of wheat in Asia. Millets
like Bajra, Jower, Ragi and Sorgham are grown in the drier
parts of Asia. These are widely cultivated in India, Pakistan and a few gulf
countries. Apart from these, pulses, spices and oil seeds are
also cultivated in various parts of Asia.
Jute and
cotton are the important natural
fibres cultivated in Asia. One third of the world’s cotton is produced by Asia.
The major cotton
producing countries are India, China, Russia and Kazakhstan.
India, Pakistan, China and Bangladesh are the leading producers of jute.
The tropical wet
and dry climate is suitable for sugarcane cultivaiton in Asia. India,
Indonesia and Philippines are the major producers of sugarcane. Coffee,
Tea, Rubber, Palm trees and Cocoa are the important plantation
crops.
India, Sri
Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia and
Indonesia are importantan producers of plantation crops. Malaysia
and Thailand are the leading producers of natural rubber.
Dates are produced in west Asia, among the
countries Iran is the largest producer of dates in the world.

Fishing
Fishing is an
important economic activity in Asia. It is prevalent in open seas as well as
inland water bodies. China and Japan are the leading fishing
nations. In Cambodia, Tonle Sap lake is one of the world’s
richest sources of fresh water fishing. Bay of Bengal is the major
fishing ground for India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Bangladesh. Fishing is the
mainstay of the national economy in Maldives. Pearl fishing
(Bahrein) is popular in the eastern coast of Arabia.
Industrial
Regions
In China,
Manchurian, Shanghai-Wuhan, Peking—Shenyang, Guangdone-Hongkong regions are the
major industrial regions. In Japan, the major regions are Tokyo,
Yokohama and Osaka-Kyoto regions. In India, Mumbai, Ahmedabad,
Coimbatore, Bengaluru and Chottanagpur are the important industrial regions.
Trasport
Transport is the backbone of the economic
development of a region. Many Asian countries are developing their transport
network for their economic progress. Roadway is the most common mode of
transport in Asia.
Roadways
The Asian Highway connects Tokyo in the east to
Turkey in the west, Russia in the north to Indonesia in the south and the total
length of road is 1,41,000 km. It passes through 32 countries. The Asian
Highway 1(AH 1) is the longest highway among the Asian Highway Network (20557
km). It connects Tokyo to Turkey. The Asian Highway 43 (AH 43) runs from Agra
in India to Matara in Sri Lanka (3024 km).
Railways
The Trans -
Siberian Railways (9258 km) is the longest rail route in the world.
It is a transcontinental railway line which connects Leningrad
and Vladivostok. The Trans Asian Railway links Singapore and
Istanbul in Turkey. The Shinkansen, bullet train is the world
famous super express train that runs between Osaka and Tokyo in Japan at
a speed of 352 km/h. The Indian railway network is the second largest railway
network in Asia.
Waterways
The Cape of Good
Hope route connects Europe to South Asia. The Trans
Pacific route connects the ports of eastern Asia to the ports of
western American countries. The Suez Canal route passes through
the heart of the world trade route and connects Europe with South and
Southeast Asia. Tokyo, Shanghai,
Singapore, Hong Kong, Chennai, Mumbai, Karachi and Dubai are the important seaports in
Asia.

CULTURAL
MOSAIC OF ASIA
Population
Asia is the most populated continent in the world.
Approximately six-tenth of the world’s population lives in Asia. The population
is unevenly distributed because of various physical features. China and
India alone covers three fifth of Asia’s population. Apart from these two countries, Bangladesh, Indonesia,
Japan, Pakistan and Philippines have more than 100 million populations.
The population density in Asia is 143 persons per Km2. India, Japan,
Bangladesh and Singapore have high population density. River plains and
industrial regions have high density of population, whereas low density is
found in the interior parts of Asia.
HOTS :
Few countries in Asia have high
population. Give reasons
ANKORWAT: It is a world heritage site. It was built by king Suriya Varma
II in 1100 AD (CE) at Cambodia. 'Ankorwat' means 'the city of temples' in Khmer
language. It is the largest Hindu Temple in the world.

Religion
& Language:
Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism Christianity and
Sikhism are the major creeds in Asia. The minor creeds Zoroastrianism,
Jainism, Shintoism, Confucianism and Taoism are also practised in Asia.
Mandarin, English Indonesian, Japanese, Arabic, Korea, Vietnamese
and Hindi are the most widely spoken languages in Asia.
Art and
Architecture:
Asia is the home
land of three civilizations.(Mesopotamian, Indus valley and Chinese
civilizations).These three contributed to the architectural works at an early
stage.
Among the seven
wonders of the world, two are located in Asia (The Tajmahal in India,
The Great wall of China).The people of Yemen built a mud
skyscraper thousands of years ago. Ankorwat in Cambodia, Buddhist
Temple in East and Southeast Asia, Mosques in west Asia and the temples and
forts in India are fine examples of Asian architecture.
Food:
Rice, Wheat,
Maize and Barley are the
staple food in Asia. Dairy products, fruits and nuts are also consumed. In East
Asia, bread and noodles are the staple food where rice is not available. Tea,
Coffee and green tea are the chief beverages. In West Asia, meat,
herbs and olive oil are the prime ingredients in their food.
Dance and
Music:

In Asia, Yangee,
Dragon Dance, Kabaki are popular in East Asia Ram Thai in
Thailand, Bhangra, Kathak and Bharathanatyam in India are also
important dances in Asia. Sufi music and Arabic classical music are
common in west Asia. Tinikling is the national dance of
Philippines.
Festivals:

The mid autumn
festival / moon festival in China, Taiwan and Vietnam. Holi and
Mahara Sankaranthi / Pongal in major parts of India and Sukkoth in
Israel are the important harvest festivals of Asia. The snow
sculpture festival, Chinese New Year, Thaipusam, Diwali, Taiwan Lantern festival, Songkran, winter light
festival are also some of the famous
festivals in Asia.
Land of
contrasts
Asia is the biggest continent. It has different types of land features such as mountain, plateau, plain, valley, bay, island etc. It also has different climatic conditions from the equator to polar region. Apart from this, many races, languages, religions and cultures are followed by people who live in Asia. So, Asia is called 'the land of contrasts'.
Related Topics