Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Musculo-Skeletal
Arthritis Overview
Arthritis Overview
Exam
·
Screening exam (OHCS, p 666):
o Observe from behind: muscle bulk (shoulders, buttocks), straight spine,
swellings, deformities
o Observe from the side: cervical and lumbar lordosis, thoracic kyphosis
o Touch your toes: spine and hip flexion
o Observe from in front
o Ear to shoulder: lateral cervical flexion, flexion, extension and
rotation
o Open and close the mouth: TMJ, orofacial pain
o Hands behind head: shoulder and sternoclavicular movement, then straight
above
o Arms straight: elbow extension
o Examine hands: nails, pray sign, press dorsum of both hands together
o Observe legs: bulk, swelling, deformity
o Knee effusion
o Observe feet
o Observe walking
Differentials for Arthritis
Causes of Monoarthritis
·
Acute Monoarthritis:
o Septic arthritis: either haematogenous (staph or gonococcal) or
following penetrating injury
o Traumatic
o Gout, pseudogout
o Haemarthrosis (eg haemophilia)
o Sometimes seronegative spondyloarthritis
·
Chronic monoarthritis:
o Chronic infection (eg Tb)
o Osteoarthritis
o Seronegative spondyloarthritis
o Metastasis
Causes of Polyarthritis
·
Acute polyarthritis
o Infection: viral (mumps, rubella, EBV, etc), bacterial
o Rheumatic fever
o Onset of chronic polyarthritis
o Drug allergies
·
Chronic polyarthritis:
o Rheumatoid arthritis
o Seronegative spondyloarthritis
o Primary osteoarthritis
o Gout, pseudogout or hydroxyapatite arthropathy
o Connective tissue disease (eg SLE)
o Infection (eg Tb)
Differential by Distribution
·
Inflammatory:
o Peripheral, symmetrical, small joint polyarthritis:
§ RA
§ Lupus and Connective Tissue Diseases (non-deforming and non-nodular)
o Asymmetrical, large joint, oligoarthritis, possibly with spinal disease:
Sero-negative spondyloarthropathies:
§ Ankylosing Spondylitis
§ Reactive Arthritis and Reiter‟s Disease
§ Psoriatic Arthritis
§ Arthritis of IBD
o Acute inflammatory mono or oligo arthritis: septic arthritis or gout
·
Non-inflammatory:
o Osteoarthritis: weight bearing joints or hands
o Soft tissue or locomotor pain syndromes
·
Sacro-ilitis: occurs in
Ankylosing Spondylitis, Reiter‟s Syndrome, Crohn‟s Disease, Chronic
·
Polyarthritis
Causes of Arthritis and Nodules
·
Rheumatoid arthritis
·
SLE (rare)
·
Rheumatic fever (very rare)
·
Granulomas, eg sarcoid (very
rare)
Raynaud’s Syndrome
·
Episodic digital ischaemia,
precipitated by cold or emotion
·
Fingers ache and go pale ® blue ®
red/purple (pain most severe in this stage, during reperfusion)
·
May be:
o Idiopathic: Raynaud‟s disease
o Associated with underlying cause (Raynaud‟s phenomenon): Scleroderma,
SLE, RA, arteriosclerosis, leukaemia, drugs, etc. Not polyarteritis nordosa
·
Keep warm, stop smoking, try Ca
channel blockers (eg diltiazem)
Radiology
·
Principles: Looking for:
o Morphologic change in an individual joint
o The skeletal distribution
·
Features:
o Joint space narrowing, either localised or uniform
o Erosions (if at the margin then periarticular erosions)
o Osteophytes: bony lip at edge of joint
o Subchondral cysts: formed by synovium getting through fissures in the cartilage
o Subchondral Sclerosis: micro-fractures in the subchondral bone ® attempted repair ® dense white band
o Periarticular osteopenia: cytokine mediated thinning of the surrounding
bone (check other joints)
o Periarticular soft tissue swelling:
§ Fusiform: in inflammatory
§ Asymmetric: in gout
·
Features of different
arthropathies:
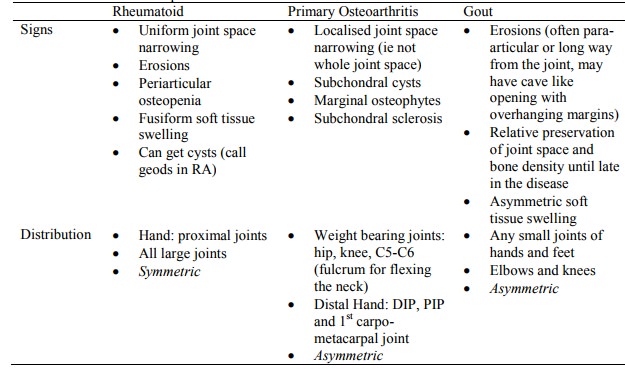
o Other arthropathies are variations on this:
§ Secondary osteoarthritis (eg due to previous trauma or infection). Looks like OA but not standard (eg uniform joint space)
§ If inflammatory but wrong distribution ®
?sero-negative
·
Idiot‟s rule of thumb for hand
arthritis:
o Rheumatoid: MCP and MTP joints
o Psoriasis: PIP joints
o Osteoarthritis: DIP
Related Topics