Chapter: 9th Science : Fluids
Archimedes' Principle
Archimedes'
Principle
Archimedes principle is
the consequence of Pascal’s law. According to legend, Archimedes devised the
principle of the “hydrostatic balance” after he noticed his own apparent loss
in weight while sitting in his bath. The story goes that he was so enthused
with his discovery that he jumped out of his bath and ran through the town,
shouting "eureka". Archimedes principle states that ‘a body immersed
in a fluid experiences a vertical upward buoyant force equal to the weight of
the fluid it displaces’.
When a body is partially
or completely immersed in a fluid at rest, it experiences an upthrust which is
equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. Due to the upthrust acting on
the body, it apparently loses a part of its weight and the apparent loss of
weight is equal to the upthrust.
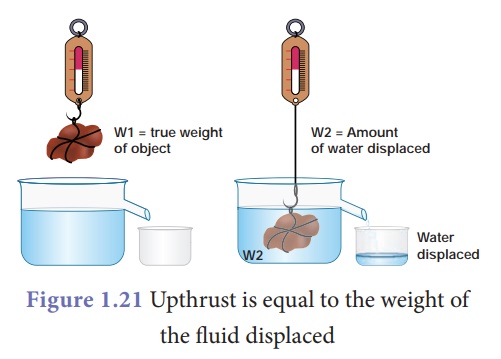
Thus, for a body either
partially or completely immersed in a fluid,
Upthrust = Weight of the
fluid displaced = Apparent loss of weight of the body.
Apparent weight of an
object = True weight of an object in air – Upthrust (weight of water displaced)

Example 1.11
What is the mass of
the object floating in the given diagram?
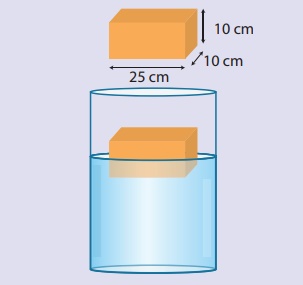
Solution:
Weight of the object =
Buoyant force
ρ = 1000 kg m-3
V = (25x10x10) cm3
= 2500 x 10-6 m3
m = ρV = 1000 x 2500 x
10-6 = 2.5 kg
Related Topics