Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Application of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
APPLICATION OF ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY IN PHARMA-CEUTICAL ANALYSIS
The elements present in a host of pharmaceutical
substances are determined quantitatively by atomic absorption spectroscopy, for
example : Pd in carbenicillin sodium ; Cu, Pb and Zn in activated charcoal ; Fe
in ascorbic acid ; Ag in cisplatin ; Ph and Zn in copper sulphate ; Zn in glucogen
; Zn in insulin ; Pb in oxprenolol hydrochloride ; Ni in prazosin hydrochloride
; Zn in sodium sulphite heptahydrate, and Cd and Pb in zinc oxide.
1. ASSAY OF TOTAL ZINC IN INSULIN ZINC SUSPENSION
Theory :
Insulin zinc suspension is
nothing but a neutral suspension of insulin in the form of water insoluble complex with ZnCl2.
Determination of both total zinc and zinc in solution is performed on a sample
of the supernatant liquid obtained by centrifuging the suspension. The
percentage of total zinc and of zinc in solution varies according to the
strength of the preparation viz., 40,
80 or 100 units ml–1.
Materials Required :
Stock
solution of Zn (5000 mcg ml–1) : Dissolve Zn metal
(Anala-R-Grade) 2.5 g in 5 M HCl (20 ml) and dilute to 500 ml with DW ; HCl
(0.1 M) : 10 ml ;
Procedure :
To the 2 ml of well-shaken
suspension add HCl (0.1 M ; 1 ml) and dilute with water to 200 ml. Spray the solution by adopting the standard procedure and
read off the concentration of zinc from a calibration curve prepared with
solution containing 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 mcg ml–1 of Zn.
2. ASSAY OF PALLADIUM IN CARBENICILLIN SODIUM
Materials Required :
Carbenicillin sodium : 1.0 g ;
sulphuric acid (36 N or 18 M) : 2.0 ml ;
mixture of nitric acid (70% w/v) and hydrochloric acid (35% w/w or 11.5 M)
[3 : 4] : 5.0 ml ; hydrochloric acid (11.5 M) : 3.0 ml ; palladiun solution
(standard) [Dissolve 1.670 g of Palladium (II) chloride in 200 ml of a 50% v/v
solution of hydrochloric acid (11.5 M) with the aid of heat, cool and add
sufficient water to produce 1 litre] : This standard palladium solution
contains 1 mg of Pd in 1 ml ;
Procedure* :
Moisten 1 g of carbenicillin
sodium in a silica crucible with 2 ml of sulphuric acid. Heat, gently at first, then more strongly until all carbon is removed
and a white ash is obtained. Allow to cool and add 5 ml of a mixture of nitric
acid and hydrochloric acid and evaporate to dryness on a water-bath. Add 3 ml
of hydrochloric acid, warm to dissolve and add sufficient water to produce 25
ml.
Place in each of three similar graduated flasks equal
volumes of the solution of the substance pre-pared as above. Add to all but one
of these flasks a measured quantity of the specified standard solution of
palladium to produce a series of solutions containing increases amounts of Pd.
Dilute the contents of each flask to the required volume with DW.
After calibrating the instrument as stated above,
introduce each solution into the generator 3 times and record the steady
reading at 248 nm. If the generator is a flame, wash the apparatus thoroughly
with DW after each introduction ; if a furnace is used, fire it after each
introduction. Plot the mean of the readings against concentration on a graph
the axes of which intersect at zero added Pd and zero reading. Extrapolate the
straight line joining the points until it meets the extrapolated concentration
axis. The distance between this point and the intersection of the axes
represents the concentration of Pd present in the prepared solution of
carbenicillin sodium.
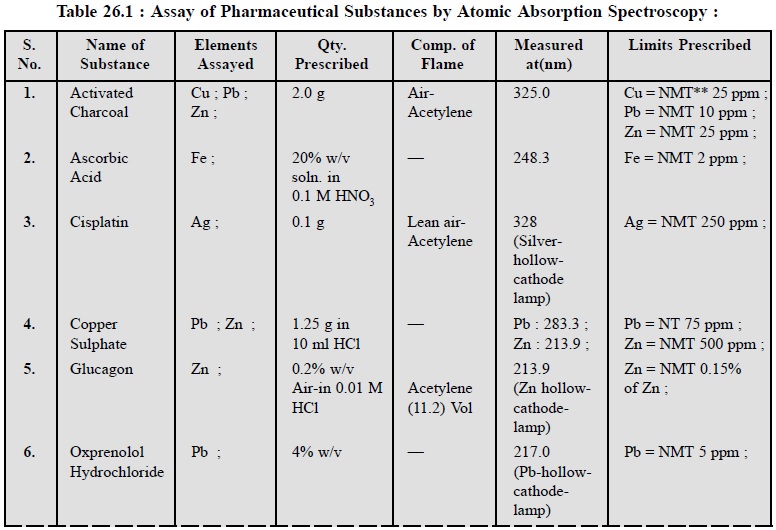
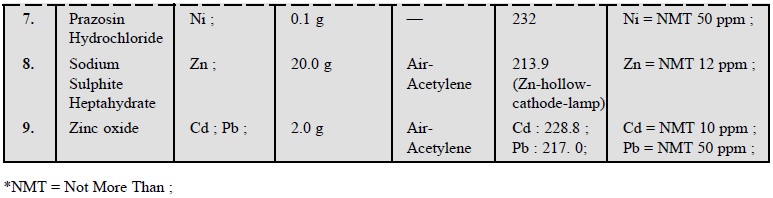
3. COGNATE ASSAYS
A number of pharmaceutical substances official in BP
(1993) can be assayed by adopting the above procedures of AAS as detailed in
the following Table 26.1.
Related Topics