Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Ophthalmic Surgery
Anesthesia for Systemic Effects of Ophthalmic Drugs
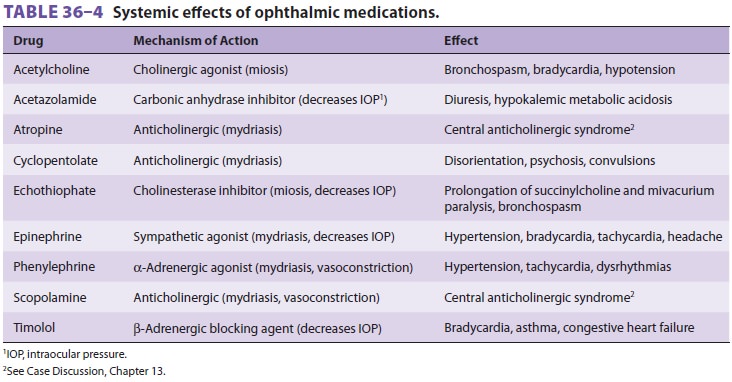
SYSTEMIC EFFECTSOF OPHTHALMIC DRUGS
Topically applied eye drops are systemically
absorbed by vessels in the conjunctival sac and the nasolacri-mal duct mucosa
(see Case Discussion). One drop (typically, approximately 1/20 mL) of 10%
phenylephrine contains approximately 5 mg of drug. Compare this dose with the
intravenous dose of phenylephrine (0.05–0.1 mg) used to treat an adultpatient with acute hypotension. Medications
applied topically to mucosa are absorbed systemically
at a rate intermediate between absorption following intravenous and
subcutaneous injection (the toxic subcutaneous dose of phenylephrine is 10 mg).
Children and the elderly are at particular risk of the toxic effects of
topically applied medica-tions and should receive at most a 2.5% phenyleph-rine
solution (Table 36–4). Coincidentally, these
patients are most apt to require eye surgery.Echothiophate
is an irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor used in the treatment of glaucoma.
Topical application leads to systemic
absorption and a reduction in plasma cholinesterase activity.Because
succinylcholine is metabolized by this enzyme, echothiophate will prolong its
dura-tion of action. Paralysis usually does not exceed 20–30 min, however, and
postoperative apnea is
unlikely. The inhibition of cholinesterase
activity lasts for 3–7 weeks after discontinuation of echo-thiophate drops.
Muscarinic side effects of echothio-phate, such as bradycardia during
induction, can be prevented with intravenous anticholinergic drugs (eg,
atropine, glycopyrrolate).
Epinephrine eye drops can cause hypertension, tachycardia, and
ventricular dysrhythmias; the dys-rhythmogenic effects are potentiated by
halothane. Direct instillation of epinephrine into the anterior chamber of the
eye has not been associated with car-diovascular toxicity.
Timolol, a nonselective β-adrenergic antagonist, reduces intraocular
pressure by decreasing produc-tion of aqueous humor. Topically-applied timolol
eye drops, commonly used to treat glaucoma, will often result in reduced heart
rate. In rare cases, it has been associated with atropine-resistant
bradycardia, hypo-tension, and bronchospasm during general anesthesia.
Related Topics