Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Patients with Kidney Disease
Anesthesia for Patients with Kidney Disease
Anesthesia for Patients with Kidney Disease
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common problem, with an incidence
of up to 5% in all hospitalized patients and up to 8% in critically ill
patients. Post-operative AKI may occur in 1% or more of general surgery
patients, and up to 30% of patients un-dergoing cardiothoracic and vascular
procedures. Perioperative AKI greatly increases hospitalization costs,
mortality rate, and perioperative morbid-ity, including fluid and electrolyte
derangements, major cardiovascular events, infection and sepsis, and
gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Preoperative risk factors for perioperative AKI
include preexisting kidney disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, liver
disease, sepsis, trauma, hypovolemia, multiple myeloma, and age greater than 55
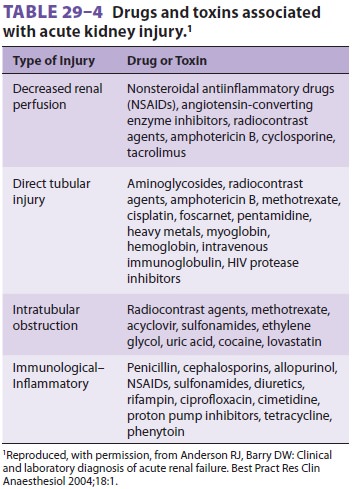
years. The risk of perioperative AKI is also increased by exposure to nephrotoxic
agents such as nonsteroidal antiin-flammatory drugs (NSAIDs), radiocontrast
agents, and antibiotics (see Table 29–4).When addressing abnormalities in renal
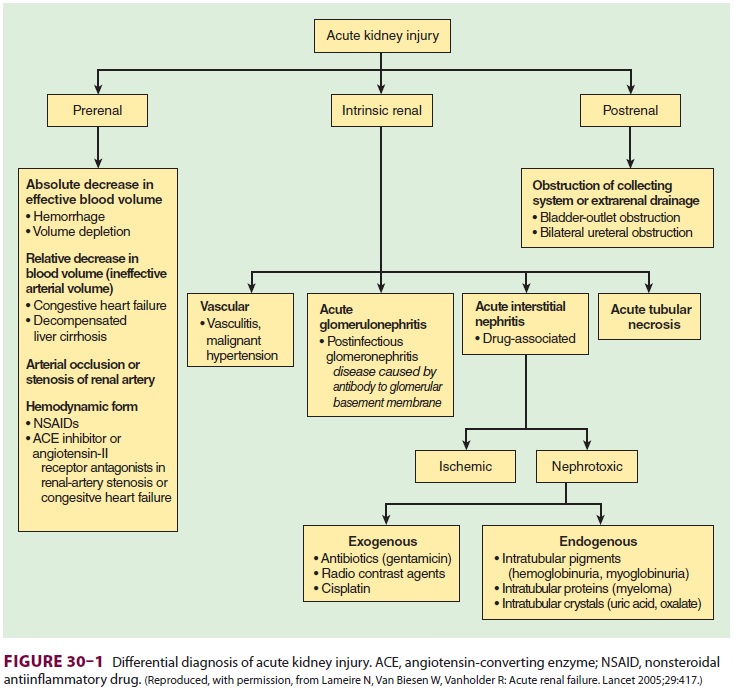
function, the clinician must possess a thorough understanding of the
differential diagnosis of AKI (Figure 30–1).
Related Topics