Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
A Review of anatomy of the female reproductive system:
A Review of anatomy of the female
reproductive system:
The female reproductive system consists of the external and
internal structures.
External genitalia:
The term ' vulva' denotes the external female genital
organs. It consists of the following structures.
Labia majora (greater lips):
Two folds of fat and areolar tissue, covered with skin and
pubic hair on the outer surface.
Labia minora (lesser lips):
Two smaller lips of delicate tissue, which lie within the
labia majora.
The clitoris:
A
small rudimentary organ, which is highly sensitive.
The urethral orifice:
External opening of the female urethra.
The vaginal orifice:
External orifice of the vagina.
Bartholins glands:
Is situated on each side of the vaginal orifice.
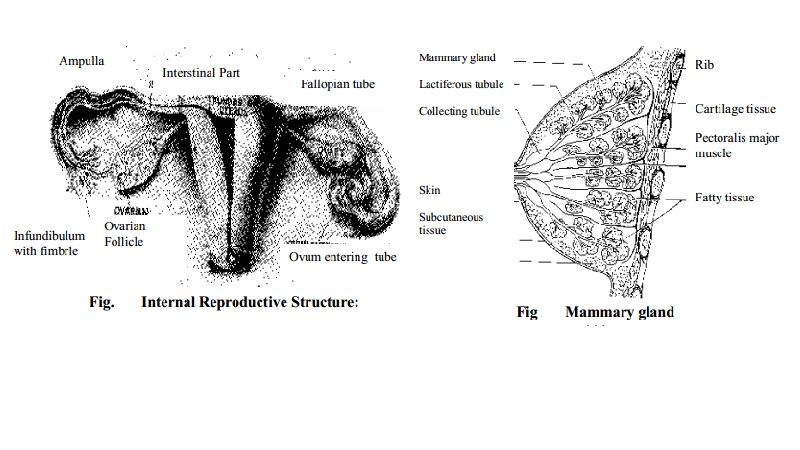
Internal reproductive organs:
The internal structure consists of vagina, uterus, ovaries
and fallopian tubes.
Vagina:
The uterus:
The uterus is a hollow, muscular, pear shaped organ situated
in the true pelvis. It shelters the fetus during pregnancy and it expels the
uterine contents at term.
The uterus consists of the following
parts.
1.
The body or corpus is the upper 2/3rd
of the uterus.
2.
The fundus is the domed upper wall
above the insertion of the fallopian tubes.
3.
The cornua is the place where the
fallopian tubes join the uterus.
4.
The cavity is the triangular shaped
potential space between anterior and posterior wall inside the uterine cavity.
5.
The cervix or neck protrudes into
the vagina, consists of internal OS and external OS.
Layers of the uterus:
The
uterus has three layers:
1.
Endometrium is the inner thin layer.
2.
Myometrium is the middle thick
muscular layer Perimetrium is the outer layer with double serous membrane.
Fallopian tubes or uterine tubes:
The fallopian tubes propel the ovum towards the uterus,
receive the spermatozoa as they travel upwards and provide a site for
fertilization. It supplies nutrition to the fertilised ovum during its journey
towards the uterus.
The uterine tubes extend laterally from the cornua of the
uterus towards the side-walls of the pelvis, arching over the ovaries.
The ovaries:
The ovaries produce ovum and the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone. The cortex
of the ovary is the functioning part
of the ovary. It contains the ovarian follicles in different stages of
development surrounded by stroma.
The breasts:
The
breasts are two hemispherical organs, are also linked with the female
reproductive system. They are secretary glands reaching full development in female
only.
They are composed mainly of glandular tissue arranged in
lobes. Each lobe is divided into lobules called alveoli, which are lined with
secreting cells, which produce milk. The nipple is composed of erectile tissue
covered which epithelium which contains plain muscle fibres which act as
sphincter to control the flow of milk. The loose skin sorrounding the nipple is
called the areola.
Progesterone and oestrogen stimulate the development and
secretary functions of the mammary gland. The hormone prolactin initiates the
production of milk.
Female pelvis:
The female pelvis (gynaecoid pelvis) is well adapted for
childbearing by nature. The gynaecoid pelvis has the characteristics giving
rise to no difficulties in childbirth with a normal size baby.
The size and shape of the female pelvis is the most
important factor during childbearing and childbirth. Fetal head makes certain
movements during its descent through pelvis so that the smallest diameter of
the fetal head is easily brought to the largest diameter of the bony pelvis.
Pelvic bones:
Pelvic
is made up of four bones
1.
Two innominate (nameless) bones or
hipbones.
2.
One sacrum.
3.
One coccyx.
Innominate
bones are made up of three
1.
Ilium-the large flared out part.
2.
Ischium-the thick lower part.
3.
Pubic bone-forms the anterior part.
Sacrum is a wedge shaped bone consists of five fused vertebrae. Coccyx is a vestigial tail consists of
four fused vertebrae forming a small
triangular bone. At the junction of two pubic bones, the symphysis pubis (pubic
joint) is formed.
The
true pelvis is the bony canal through which fetus must pass during birth. It
consists of a brim, cavity and outlet.
Related Topics