Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Steam Power Plants
Surface Condenser
SURFACE CONDENSER
In surface condensers there is no
direct contact between the steam and cooling water and the condensate can be
re-used in the boiler. In such a condenser even impure water can be used for
cooling purpose whereas the cooling water must be pure in jet condensers. Although
the capital cost and the space needed is more in surface condensers but it is
justified b the saving in running cost and increase in efficiency of plant
achieved by using this condenser. Depending upon the position of condensate
extraction pump, flow of condensate and arrangement of tubes the surface
condensers may be classified as follows:
1. Down flow
condenser
2. Central
flow condenser
3. Evaporative
condenser
1.Down flow condenser
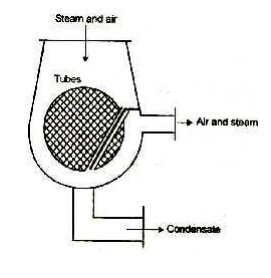
Figure shows a sectional view of
down flow condenser. Steam enters at the top and flows downward. The water
flowing through the tubes in one direction lower half comes out in the opposite
direction in the upper half. In this type of condenser, the cooling water and
exhaust steam do not come in direct contact with each other as in case of jet
condensers.
This is generally used where
large quantities of inferior water are available and better quantity of feed
water to the boiler must be used most economically. The arrangement of the
surface condenser is shown in figure. It consists of cast iron air- tight
cylindrical shell closed at each end as shown in figure. A number of water
tubes are fixed in the tube plates which are located between each cover head
and shell.
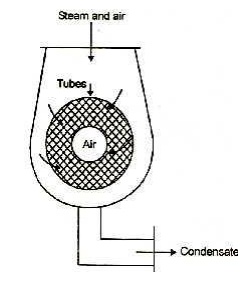
2. Central flow condenser.
Figure shows a central flow
condenser. In this condenser the steam passages are all around the periphery of
the shell. Air is pumped away from the centre of the condenser. The condensate
moves radially towards the centre of the tube next. Some of the exhaust steam
which moving towards the centre meets the under cooled condensate and pre-heats
it thus reducing under cooling.
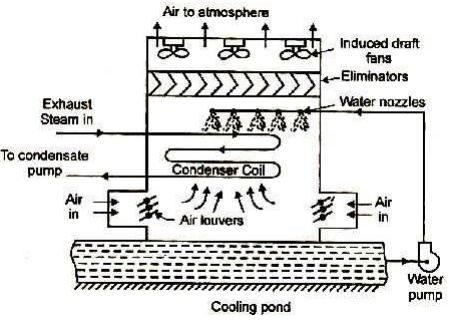
3. Evaporative condenser
In this condenser steam to be
condensed in passed through a series of tubes and the cooling water falls over
these tubes in the form of spray. A steam of air flows over the tubes to
increase evaporation of cooling water which further increases the condensation
of steam.
These condensers are more
preferable where acute shortage of cooling water exists. The arrangement of the
condenser is shown in figure. Water is sprayed through the nozzles over the
pipe carrying exhaust steam and forms a thin film over it. The air is drawn
over the surface of the
Related Topics