Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Nutrition, Metabolism, and body Temperature Regulation
Protein Metabolism
Protein Metabolism
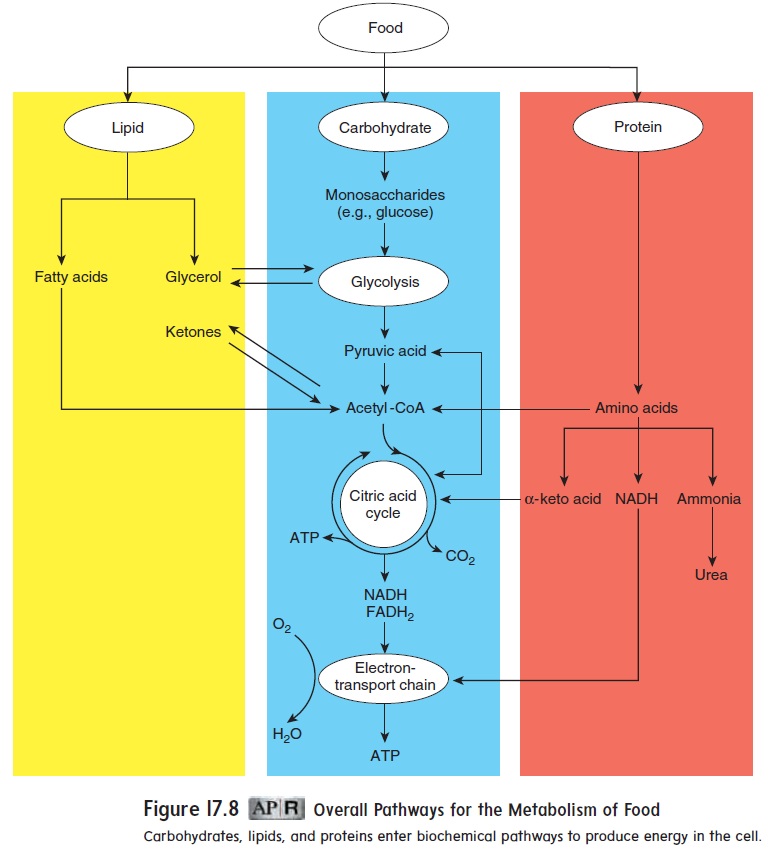
Amino acids are the products of protein digestion. Once amino acids are absorbed into the body, they are quickly taken up by cells, especially in the liver. Amino acids are used primarily to synthesize needed proteins and only secondarily as a source of energy. If serving as a source of energy, amino acids can be used in two ways (figure 17.8): (1) The amino acids can be converted into the molecules of carbohydrate metabolism, such as pyruvic acid and acetyl-CoA. These molecules can be metabolized to yield ATP. (2) The amine group (−NH2) can be removed from the amino acid, leaving ammonia and an α-keto acid. This process produces NADH, which can enter the electron-transport chain to produce ATP. Ammonia is toxic to cells, so the liver converts it to urea, which the blood carries to the kidneys, where it is elimi-nated. The α-keto acid can enter the citric acid cycle or can be converted into pyruvic acid, acetyl-CoA, or glucose. Although proteins can serve as an energy source, they are not considered major storage molecules.
Related Topics