Chapter: Medical Physiology: Sports Physiology
Muscle Metabolic Systems in Exercise
Muscle Metabolic Systems in Exercise
The same basic metabolic systems are present in muscle as in other parts of the body;. However, special quantitative measures of the activities of three meta-bolic systems are exceedingly important in understand-ing the limits of physical activity. These systems are (1) the phosphocreatine-creatine system, (2) the glycogen-lactic acid system, and (3) the aerobic system.
Adenosine Triphosphate. The source of energy actuallyused to cause muscle contraction is adenosine triphos-phate (ATP), which has the following basic formula:
Adenosine-PO3 ~ PO3 ~ PO3-
The bonds attaching the last two phosphate radicals to the molecule, designated by the symbol ~, are high-energy phosphate bonds.Each of these bonds stores7300 calories of energy per mole of ATP under standard conditions (and even slightly more than this under the physical conditions in the body). Therefore, when one phosphate radical is removed, more than 7300 calories of energy are released to energize the muscle contractile process. Then, when the second phosphate radical is removed, still another 7300 calories become available. Removal of the first phosphate converts the ATP into adenosinediphosphate (ADP), and removal of the second convertsthis ADP into adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
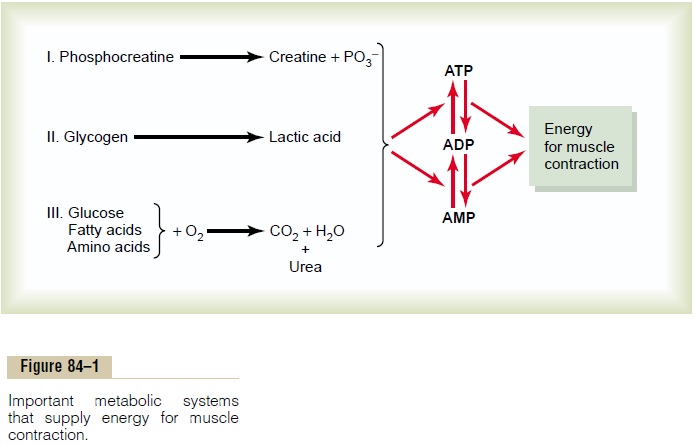
The amount of ATP present in the muscles, even in a well-trained athlete, is sufficient to sustain maximal muscle power for only about 3 seconds, maybe enough for one half of a 50-meter dash. Therefore, except for a few seconds at a time, it is essential that new ATP be formed continuously, even during the performance of short athletic events. Figure 84–1 shows the overall metabolic system, demonstrating the breakdown of ATP first to ADP and then to AMP, with the release of energy to the muscles for contraction.The left-hand side of the figure shows the three metabolic systems that provide a continuous supply of ATP in the muscle fibers.
Related Topics