Chapter: Graphics and Multimedia : Multimedia Systems Design
Multimedia Data Interface Standards
MULTIMEDIA DATA INTERFACE STANDARDS
File Formats for Multimedia Systems:
(i)
Device-independent Bitrnap
(DIB): This file format contains bit map, color, and color paJlette information.
(ii)
RIFF device Independent
Bitrnap (RDIB): Resource Interchange File Frmat
(RIFF) is the standard file
format defined for Microsoft Windows and OS/2. It allows a more complex set of
bit maps than can be handled by DIB.
(iii)
Musical Instrument Digital
interface (MIDI): This is the interface standard for file transfer between a computer and a musical
instrument such as a digital piano. It is also, used for full-motion video and
voice-mail messaging systems. It has the advantage of ready availability of
MIDI device controller boards for personal computers.
RIFF Musical Instrument Digital Interface
A MIDI format within a RIFF
envelope provides a more complex interface.
Palette File Format (PAL)An interface that allows defining a palette of
1 to 256 colours in a representation
as RGB values.
Rich Text Format (RTF) This file format allows embedding graphics and
other file formats within a document. This format is used by products such as
Lotus Notus. This format is also the basis for the use of OLE.
Waveform Audio File Format (WAVE) A digital file representation
of digital audio.
Windows Metafile Format (WMF) This is a vector graphic format used by
Microsoft Windows as an interchange
format.
Multimedia Movie Format (MMM) This is a format used for digital video animation.
Apple's Movie Format This format was defined as the standard for
file exchange by Quick Time enabled
systems.
Digital Video Command Set (DVCS) This is the set of digital video commands
simulating VCR controls.
Digital Video Media Control Interface Microsoft's high level
control interface for VCR controls, including
play, rewind, record and so on.
Vendor - Independent Messaging (VIM) Developed by a consortium of
Vendors providing a standardized
format for cross-product messages.
Apple's Audio Interchange File Format Apple's standard file format
for compressed audio and voice data.
SDTS GIS Standard The Spatial Data Transfer Standard (SDTS) is
designed to provide a common storage
format for geographic and cartographic data.
VIDEO PROCESSING STANDARDS
INTELS
DVI
DVI is an achronym of Digital
Video Interface.
DVI standard is to provide a
processor independent specification for a video interface. That video interface
should accomodate most compression algorithms for fast multimedia displays. An
example of custom-designed chip which supports DVI is Intel's i750 B. This chip
is designed for enhancing low-end, software based PC video.
Advantages of the DVI Chip
(i) It can operate software
video processing real time. (ii) It can share the processing with the host CPU.
(iii) It can handle additional vector-quantization-type algorithms in
conjunction with host processing. DVI silicon chip relies on a programmable
video processor. It gives potential to DVI chips to run a range of compression
algorithms.
APPLE QUICK TIME
Quick Time standard is
developed by Apple Computer. It is designed to Support multimedia applications.
It is integrated with the operating system. Quick time refers to both the
extensions to the Mac Operating system and to the compression/decompression
functionality Of the environment. Quick Time is designed to be the graphics
standard for timebased graphic data types.
Quick Time's definition has
been extended to include (i) System Software, (ii) File Formats, (Hi)
Compression! decompression algorithms, (iv) Human Interface Standards.
Figure Shows the components
in the Quick Time Architecture.
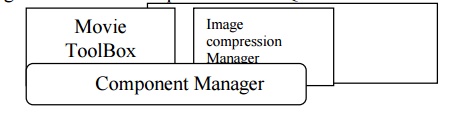
Quick Time adjust
automatically to the hardware being used by the user. MPEG is another competing
standard which is comparitively higher-end, hardware-assisted standard. It can
produce better resolutions at faster rates.
MICROSOFT AVI
A VI is an achronym for Audio
Video Interleave Standard. It is similar to Apple's Quick Time. It offers
low-cost, low-resolution video processing for the average desktop user. It is a
layered product. A VI is scalable. It allows users to set parameter such as
window size, frame rate, quality and compression algorithm through a number of
dialog boxes. AVI-compatible hardware allows enhancing performance through
hardware-accelerated compression algorithms such as DVI and MPEG. A VI supports
several compression algorithms
Related Topics