Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Urinary System
Kidneys
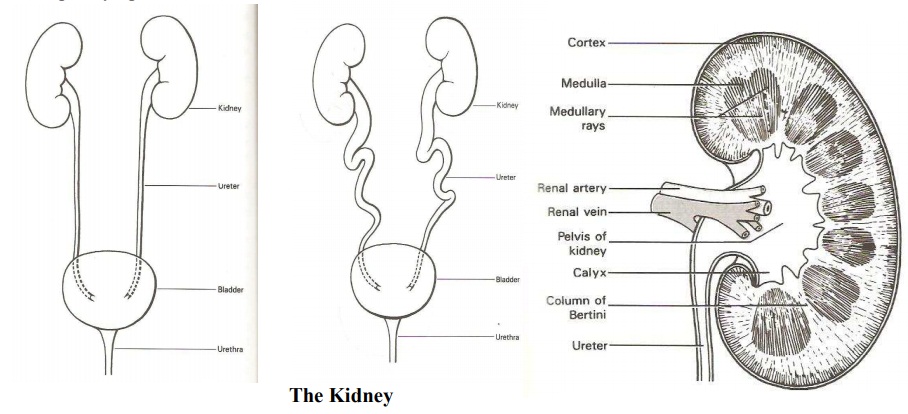
The urinary system
The
Unitary system consists of two kidneys, a single bladder, two ureters, which
carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder and a single urethra, which
carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The kidneys
The
kidneys are two bean- shaped glands about the size of a tightly clenched first.
They lie behind the peritoneum on the posterior aspect of the abdominal wall on
either side of the vertebral column. The kidneys extend from the level of the
last thoracic (T12) to the third lumber (L3) vertebrae and the rib cage (diaphragm)
partially protects them. The liver lies superiorly over the right kidney,
causing it to be slightly lower than the left one.
Size
Each
kidney is about 10cm long, 6.5cm wide and 3cm thick. It weighs about 120g.
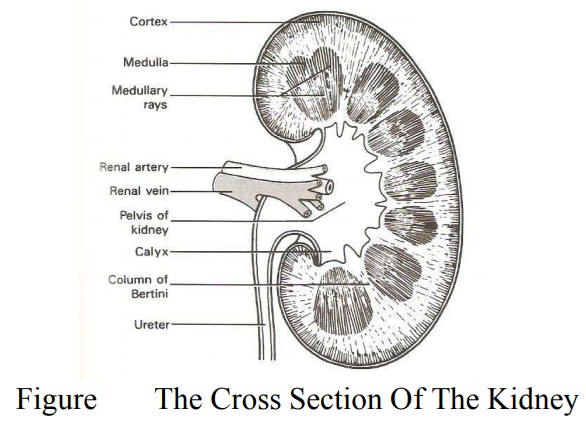
The
kidney is dark red in color and covered by tough fibrous capsule. Microscopic Structure
The
kidney is composed of two zones, the outer portion of cortex and the inner part
medulla. The cortex is dark red in color with rich blood supply while the
medulla is paler in color. The collecting area for urine which merges with the
upper pelvis is divided into major branches or calyces which later subdivided
into smaller calyces; they are referred to as minor calyces. Each calyx cups
over projections from the medulla known as pyramid.
The Nephrons
The
Nephrons are the functioning units of the kidneys. There are about 1 million
nephrons in each kidney and about 50-55mm in length. Each nephron starts at a
knot of capillaries called glomerulus. It is fed by a branch of the renal
artery, the afferent arterioles takes blood to it and efferent arterioles
collect the blood back.
Blood Supply: Renal entries early branches of
thedescending abdominal aorta
Venous
Return: Corresponding vein, lymphatic drainage: Aortic lymph glands, nerve
supply: sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
Functions of the kidney
1.
Manufacture Urine:
2.
Elimination of wastes from the body e.g. breakdown
production of protein-urea, urates uric Acid, creatinine, ammonia and sulphate.
3.
Elimination of toxins.
4.
Secretion of useful substances to the body. Rennin
and erythropoietin.
5.
Regulation of the concentration of solute in the
blood, regulate concentration of major ions in the body such as sodium No,
chlorine CL potassium K+ and calcium C2+.
6.
Regulation of pH of the extracellular fluid; the
kidneys secrete variable amount of H+ to help regulate the extra cellular fluid
pH.
7.
Regulation of RBC synthesis. The erythro
erythropoietin secreted by the kidneys regulates the synthesis of RBC in the
bone marrow.
8.
Vitamin D synthesis: it plays important role in
controlling C2+ level in blood by regulating the synthesis of
vitamin D.
9.
Regulation of blood volume: by producing either a
large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine.
Related Topics