Chapter: Biotechnology: Microbial Cell Culture and its Applications
Isolation of microbial products
Isolation of microbial products
Once the fermentation is complete, it is necessary to recover the desired metabolite. Minimally, this will involve separation of the cells from the fermentation broth. But it may also include, purification of the metabolite with or without cell disruption; cell disruption will be necessary if the metabolite is intracellular. Such operations are referred to as downstream processing. The steps involved in isolation of the desired microbial product are: (1) separation of cells from the fermented broth, (2) cell disruption if the product is intracellular or concentration of the broth if the product is extracellular (3) initial purification of the metabolite, (4) metabolite-specific purification in which the metabolite of interest is purified to a high degree, and (5) polishing of the metabolite (bringing it to 98 -100% purity) where it is further concentrated and formulated for use.
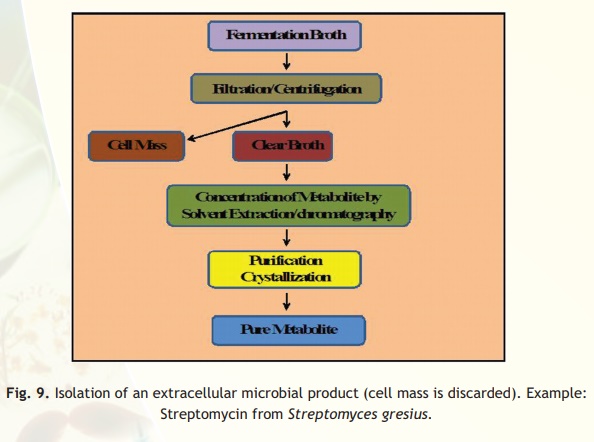
Fig. 9 and 10 depict the steps involved in isolation of microbial products or metabolites ofextracellular and intracellular origin respectively. The important steps are: separation of microbial cells (biomass / pellet) from the fermentation broth, concentration, metabolite-specific purification and final purification. Isolation of cells from the fermented broth is, in general, carried out by either centrifugation or ultra filtration. Some cells rapidly settle out of suspension once aeration and agitation of the fermented broth ceases. The settling of cells may also be assisted by the addition of certain flocculating agents. Where cell settling does not occur, cell removal can be effected by centrifugation. An alternative to centrifugation is ultra filtration. The term ultra filtration describes processes in which particles significantly greater in size than the solvent are retained when the solution is forced through a membrane of very fine pore size, usually less than 0.5 mm. Microbial cells can be concentrated using ultra filtration so that the fermented broth is separated from cells.
The clarified fermentation liquor will contain microbial metabolites and extra cellular enzymes. Several methods are available for recovery of metabolites such as precipitation, solvent extraction and ion exchange chromatography.
Different downstream operations are available for concentration as well as purification of the metabolite. But it is always advisable to use lesser number of steps to achieve desired purity of the metabolite or product. This is because, more the number of steps involved, more will be the cost of the production and lower would be the yield.
Most of the antibiotics are secreted into the medium, so their isolation mainly involves steps
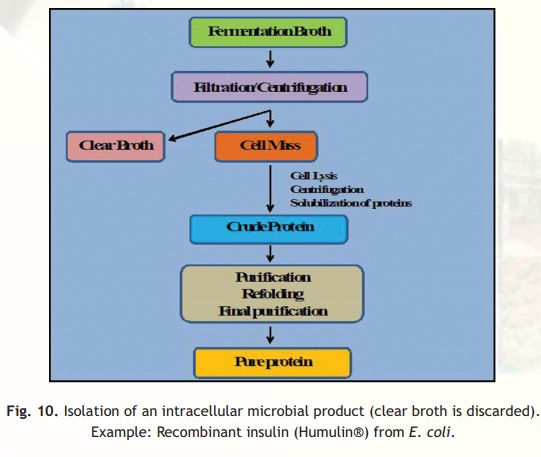
Most of the recombinant proteins expressed in E. coli accumulate intracellularly as protein aggregates. So their isolation and purification involve steps as described in Fig. 10. Once the pure metabolite is obtained, a stabilized formulation is made using several ingredients known as excipients.
Related Topics