India | Economics - Industrial Sector Reforms | 11th Economics : Chapter 9 : Development Experiences in India
Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 9 : Development Experiences in India
Industrial Sector Reforms
Industrial
Sector Reforms
The Prime
Minister of India announced the new industrial policy on July 24, 1991. The new
policy radically liberalized the industrial policy itself and de-regulated the
industrial sector substantially. The primary objectives of the industrial
policy were to promote major industries from the clutches of bureaucrats, to
abolish restrictions on foreign direct investment, to liberate the indigenous
enterprise from the restrictions of MRTP Act, to maintain a sustained growth in
productivity and employment and also to achieve international competitiveness.
Important Initiatives by the Government towards Industrial Policy
The
policy has brought changes in the following aspects of industrial regulation:
1.
Industrial delicensing
2.
Dereservation of the industrial sector
3.
Public sector policy (dereservation and reform of
PSEs)
4.
Abolition of MRTP Act
5.
Foreign investment policy and foreign technology
policy.
Industrial delicensing policy: the most
important objective of the new industrial
policy of 1991 was the end of the industrial licensing or the license raj
or red tapism. Under the industrial licensing policies, private sector firms
had to secure licenses to start an industry.
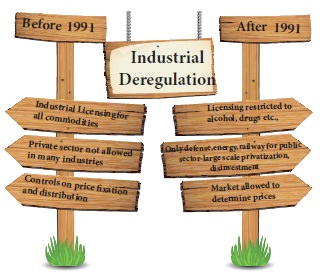
Dereservation of the industrial sector Previously,
the public sector was given reservation
especially in the capital goods and key industries. Under industrial
deregulation, most of the industrial sectors were opened to the private sector
as well. Under the new industrial policy, only three sectors viz., atomic
energy, mining and railways will continue as reserved for public sector. All
other sectors have been opened for private sector participation.
Reforms related to the Public sector enterprises: Reforms
in the public sector were aimed at
enhancing efficiency and competitiveness of the sector. The government
identified strategic and priority areas for the public sector to concentrate.
Loss making PSUs were sold to the private sector.
Abolition of MRTP Act: The New
Industrial Policy of 1991 has abolished the
Monopoly and Restrictive Trade Practices Act 1969. In 2010, the Competition
Commission has emerged as the watchdog in monitoring competitive practices in
the economy.
The policy
caused big changes including emergence of a strong and competitive private
sector and a sizable number of foreign companies in India.
Foreign investment policy: Another
major feature of the economic reform was red carpet welcome to foreign investment and foreign technology. This
measure has enhanced the industrial competition and improved business
environment in the country. Foreign investment including FDI and FPI were
allowed. In 1991, the government announced a specified list of high-technology
and high-investment priority industries wherein automatic permission was
granted for foreign direct investment (FDI) upto 51 percent foreign equity. The
limit was raised to 74 percent and subsequently to 100 percent for many of
these industries. Moreover, many new industries have been added to the list
over the years.
Foreign
Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) has been set up to negotiate with
international firms and approve foreign direct investment in select areas.
Related Topics