Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Geographic Information System
Geographic Information System: Map Projections
GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEM
MAP PROJECTIONS
A
projection is a method by which the curved surface of the earth is represented
on a flat surface and it involved the use of mathematical transformations
between the location of places on the earth and their projected locations on
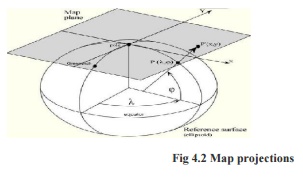
the plane. A map projection is any transformation between the curved reference surface of
the earth and the flat plane of the map.
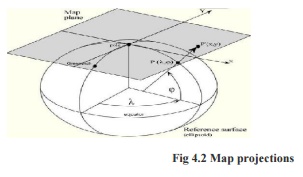
For each map projection the following equations are available:
X,Y = f ( j, l ) Forward equation
j, l = f ( X,Y ) Inverse equation
The forward equations are used to transform geographic
coordinates - latitude (j) and longitude (l) - into Cartesian coordinates
(X,Y), while the inverse equations of a map projection are used to
transform Cartesian coordinates into geographic coordinates
Properties of Map Projections
The following properties would be present on a
map projection without any scale distortions: Areas are everywhere correctly
represented
All distances are correctly represented.
All directions on the map are the same as on
Earth All angles are correctly represented.
The shape of any area is correctly represented General
projections Classified as folloes:
EQUAL AREA PROJECTIONS: An equivalent map projection,
also known as an equal-area map projection, correctly represents areas
sizes of the sphere on the map. Conformal projections:
A conformal map projection represents angles and shapes
correctly at infinitely small locations.
EQUIDISTANT PROJECTIONS:They represent the distances to places from one or two points. Types of projection Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM), Transverse Mercator (also known as Gauss-Kruger),
Polyconic
POLYCONIC PROJECTION
It is
used to project for preparing world map.
In this projection all parallels are projected without any
distortion, which means scale is exact along all parallels. Scale is exact
along the central meridian also.
1. The
projection is called polyconic as many cones are involved to make all parallels
exact.
Transverse
Mercator Project it is used to project near the pole regions.
This widely used conformal projection was invented by
mathematician and cartographer Johnn Heinrich Lambert in 1772. Carl F. Gauss
analysed the projection in 1882 and L. Kruger completed the development of the
projection by developing the formulae further in order to be suitable for
numerical calculations in 1912. This is a beautiful example or creating for
malising - implementing, all three processes taking
over a century time.
1. A policy decision for a gradual switch over. Both, transverse mercator and conformal conic projection with two standard parallels, are suitable and do not have the drawbacks mentioned in respect of polyconic projection. Suitable zones of 60x60 or 80x80 or statewise can be designed. All maps from village to subdivision to taluka to district to state on various scales can be on the same projection within a particular zone.
Universal Transverse Mercator Projection UTM) It
is used to project near the equator regions.
The Universal Transverse Mercator Projection is a particular
case of transverse mercator projection. This is a world wide plane coordinate
system brought up by the military during World War II. This was adopted by the
U.S. Army in 1947 for designating rectangular coordinates on large scale
military maps of the entire world.
Related Topics