Classification, Composition and nutritive value, Selection - Fish | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 4 : Flesh Foods, Milk and Milk Products
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 4 : Flesh Foods, Milk and Milk Products
Fish
Fish
India has a coast line
of 5,100 km. Over 200 edible fish varieties are known to be commercially important.
Marine types of fish are sardines, mackerel, tuna, catfish, brown duck, ribbon
fish, prawns and cuttle. Fresh
water fish are carps,
catla, rohu, murrels and hilsa. Fish contains complete proteins and can be an
alternative for meat in the diet, but unfortunately fish consumption per capita
is far lower than that of meat.
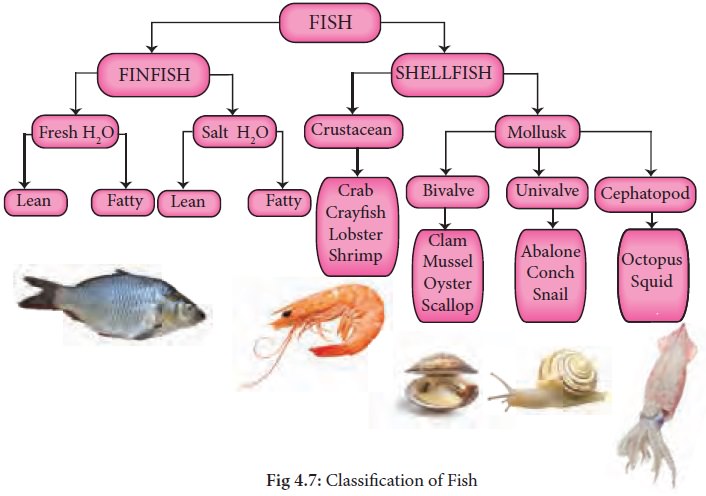
Classification of Fish
Edible fish are
categorized as either fin fish of shell fish. The term fin fish refers to the
fishes that have bony skeleton. Shell fish is used to designate both mollusks
and crustaceans. Shellfish are highly perishable.
Crustacea have legs
with partly joined outer shells. They include crabs, lobsters, prawns and
shrimps. Molluscs have harder outer shells and no legs. They have hinged shells
like oysters, scallops and mussels.
Composition and nutritive value
Commonly consumed fish
are carp, rohu, sardine, mackerel pomfrets, seer fish,
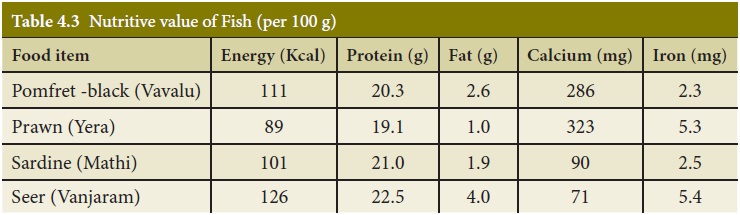
The composition of
fish varies. Fish are not good source of energy because they are not good
sources of carbohydrate and fat.
Carbohydrate: The shell fish has
less fat and more carbohydrate than fin fish. Like meat, fish contain some
glycogen in muscle tissues. In the live fish, glycogen is the source of stored
energy. Oysters are notable for their high content of glycogen.
Protein : Fish is an excellent
source of protein due to its quality and quantity. They contain around
20percent protein. The biological value of fish protein is 80. Fish is rich in
lysine and methionine hence it has supplementary value with cereals and pulses.
Fat : Fish contains less
amount of fat compared to meat and poultry. Fresh
Minerals: Fish is rich in calcium particularly small fish when eaten with bones. Marine fish are good sources of iodine, selenium and fluoride. Selenium is a powerful antioxidant. Oysters are good source of copper and iron. Sodium content of freshwater fish is slightly less than meat. Shell fish such as oysters are nature’s richest source of zinc. The bioavailability of iron and zinc is higher in fish than plant foods.
Vitamins: Sea foods contain
significant amounts of vitamin B12
especially shell fishes. Fish liver oils are excellent source of fat-soluble vitamins. Shark liver oil contains
10,000-24,000 IU of vitamin A per gram of oil. Rohu contains vitamin C. Fish
are good source of niacin and vitamin D. Sea foods contain significant amounts of vitamin B12
especially shell fishes.
Fish and health
Eskimos living in
Greenland and the fishing community in Japan, enjoy complete freedom from
cardiovascular diseases. Their
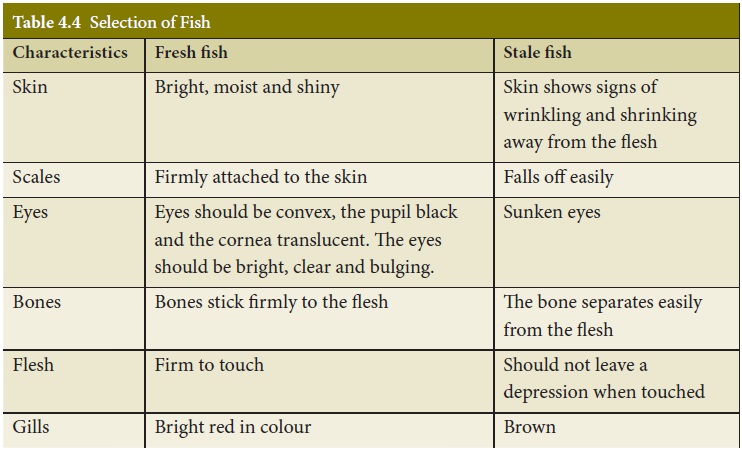
Selection of Fish
Fish thatare
freshcanbeeasilyidentified by the following qualities:
Prawns : Fresh and firm, strong
colour, no unpleasant smell.
Scallops : Pinkish white or pale
yellow, feel firm, give-off clear liquid.
Clams, oysters and
mussels : Tightly
closed and heavy for their size, shells should not be cracked.
Related Topics