Economics - Features, Merits, Demerits of Socialistic Economy (Socialism) | 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
Features, Merits, Demerits of Socialistic Economy (Socialism)
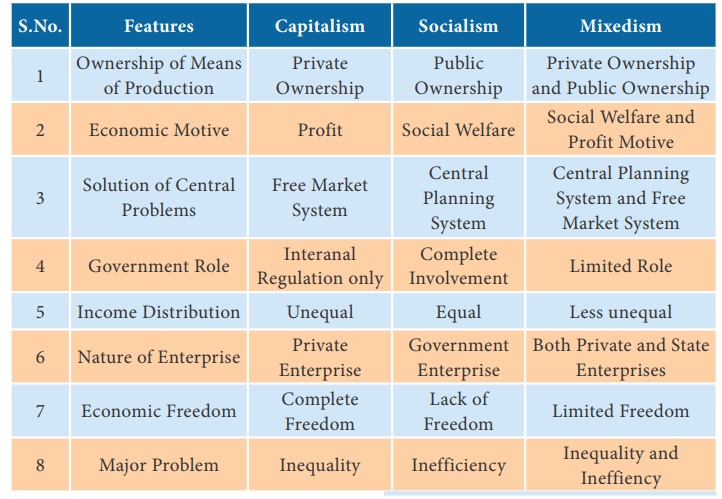
Socialistic Economy (Socialism)
The Father of Socialism is Karl Marx. Socialism refers to a
system of total planning, public ownership and state control on economic
activities. Socialism is defined as a way of organizing a society in which
major industries are owned and controlled by the government, A Socialistic
economy is also known as ‘Planned Economy’ or ‘Command Economy’.

In a socialistic economy, all the resources are owned and operated
by the government. Public welfare is the main motive behind all economic
activities. It aims at equality in the distribution of income and wealth and
equal opportunity for all. Russia, China, Vietnam, Poland and Cuba are the
examples of socialist economies. But, now there are no absolutely socialist
economies.


Features of Socialism:
1. Public Ownership of Means of Production: All resources are owned
by the government. It means that all the factors of production are
nationalized and managed by the public authority.
2. Central Planning: Planning is an integral part of a
socialistic economy. In this system, all decisions are undertaken by the
central planning authority.
3. Maximum Social Benefit: Social welfare is the guiding principle
behind all economic activities. Investments are planned in such a way that the
benefits are distributed to the society at large.
4. Non-existence of Competition: Under the socialist
economic system there is absence of competition in the market. The state has
full control over production and distribution of goods and services. The
consumers will have a limited choice.
5. Absence of Price Mechanism: The pricing system works under the
control and regulation of the central planning authority.
6. Equality of Income: Another essential feature of socialism is
the removal and reduction of economic inequalities. Under socialism private
property and the law of inheritance do not exist.
7. Equality of Opportunity: Socialism provides equal opportunity for
all through free health, education and professional training.
8. Classless Society: Under socialism, there is a classless
society and so no class conflicts. In a true socialist society, everyone is
equal as far as economic status is concerned.![]()
![]()
Merits of Socialism
1. Reduction in Inequalities: No one is allowed to own and use private
property to exploit others.
2. Rational Allocation of Resources: The central planning
authority allocates the resources in a planned manner. Wastages are minimised
and investments are made in a pre planned manner.
3. Absence of Class Conflicts: As inequalities are minimum, there is no
conflict between rich and poor class. Society functions in a harmonious manner.
4. End of Trade Cycles: Planning authority takes control over
production and distribution of goods and services. Therefore, economic
fluctuations can be avoided.
5. Promotes Social Welfare: Absence of exploitation, reduction in
economic inequalities, avoidance of trade cycles and increase in productive
efficiency help to promote social welfare.
Demerits of Socialism
1. Red Tapism and Bureaucracy: As decision are taken by government agencies,
approval of many officials and movement of files from one table to other takes
time and leads to red tapism.
2. Absence of Incentive: The major limitation of socialism is that this
system does not provide any incentive for efficiency. Therefore, productivity
also suffers.
3. Limited Freedom of Choice: Consumers do not enjoy freedom of choice over
the consumption of goods and services.
4. Concentration of Power: The State takes all major decisions. The private
takes no initiative in making economic decisions. Hence, the State is more
powerful and misuse of power can also take place.
Related Topics