Structure, composition, properties of eggs, Use, value of eggs in the diet - Egg - Nutrition and Dietetics | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 4 : Flesh Foods, Milk and Milk Products
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 4 : Flesh Foods, Milk and Milk Products
Egg - Nutrition and Dietetics
EGG
Structure and composition of eggs
An egg is designed to
give protection and food for a developing chick. It is therefore a very
nutritious food. There are three main parts: the shell, the white and the yolk.
The shell consists of
two parts
·
An outer shell composed mainly of calcium carbonate
·
Two thin inner
membranes composed
mainly of phosphates
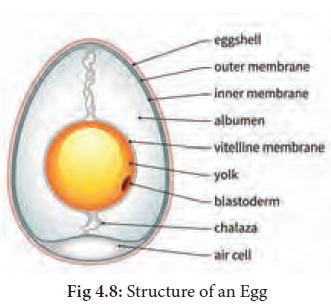
The outer shell
protects the egg, or the developing chick in a fertilized egg. The shell is
porous and contains numerous tiny holes, which enable a chick to breathe. The
colour of the shell varies from white to deep brown depending on the breed of
the hen
The two inner
membranes lining the shell act as chemical filters to obstruct bacteria which
may enter through the porous shell. The two membranes separate to form a small
air pocket between them at the rounded end.
The egg white has two
distinctly visible layers. The egg white immediately surrounding the yolk is
thick and viscous. This is surrounded by a thinner more transparent white.
The egg yolk is
anchored to the membranes inside the egg shell by two rope- like structures
known as the chalazae. These hold the yolk centrally in position. The yolk is
separated from the white by a membrane known as the vitelline membrane.
The white of the egg
(albumin) consists of largely water with no fat or carbohydrate but contains
8-12 percent protein. Different types of proteins are present in egg white
like ovalbumin,
conalbumin, ovamucoid, ovomucin and avidin. The protein ovomucin is responsible
for the jelly-like character of egg white and thickness of the albumin. Avidin
binds with biotin and makes the vitamin unavailable. But avidin is denatured by
heat and thus cooked egg does not affect the availability of biotin.
Egg yolk comprises
mostly 25-33 percent of fat and 15-17 percent protein and the remaining water.
The major proteins in egg yolk are lipoproteins which include lipovitellins and
lipovitellinin. These lipoproteins are responsible for the excellent
emulsifying properties of egg yolk, when it is used in products such as
mayonnaise.
The value of eggs in the diet
Eggs are an excellent and
relatively cheap source of high biological value protein. Egg proteins have an
excellent supplementary value to all other plant protein foods. Hence a
combination of eggs with any of the cereal
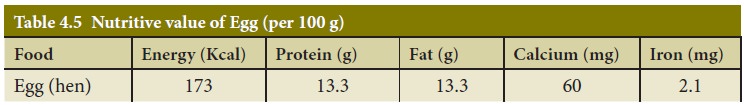
They also provide vitamins A,
D, E and riboflavin. Egg yolk is a good source of carotene and iron. Egg is one
of the richest sources of lecithin- a phospholipid which forms a part of the
structure of every cell wall in the body. Egg also provides essential fatty
acids like linoleic acid and arachidonic acid.
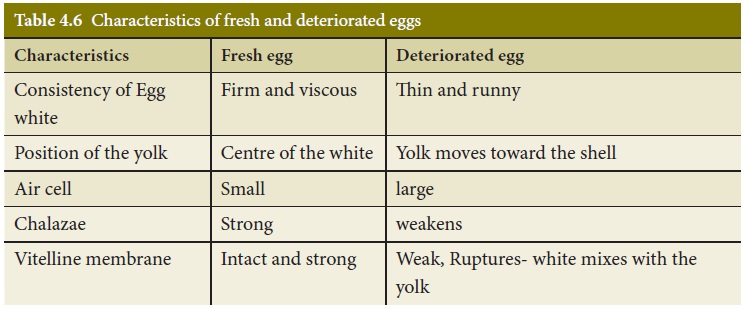
Evaluation of egg quality
Egg is an excellent
food and hence its quality is of very great importance. Fresh eggs have the
best quality. Quality of eggs can be determined by candling where the egg is
held against a source of strong light.
Candling will reveal
a. a crack in the shell.
b. the size of the air
cell.
c. the firmness of the
white.
d. the position of the
yolk.
e. the presence of foreign substances .
The properties of eggs
There are three main
properties of the proteins in eggs which enable them to be used in so many
different ways in cookery.
a. Egg proteins coagulate
on heating.
b. Egg proteins stretch
when beaten and hold air in the structure.
c. Egg
yolk
proteins
are
good emulsifying
agents.
Use of egg in cookery
Eggs can be used in many ways in cookery. Eggs when used alone or in combination with other foods they become the major protein source of a meal. Eggs can be used as boiled, scrambled, fried (omelettes) or poached for table use. Eggs are used as :
Thickening Agent: Egg proteins coagulate
on heating. Therefore, eggs can be used as thickening agents for making stirred
and baked custards, soups and puddings.
Binding Agent: Egg proteins coagulate
between 65 and 70°C and help to hold shape of the products in which it is used. They can
be used for making cutlets, French toast or Bombay toast and banana fritters .
Leavening Agent: Eggs when beaten, form
elastic films which can trap air. This air expands during baking and gives a
fluffy spongy product. Thus they can be used in cakes, foamy omelette, souffiés
and meringue.
An Emulsifying Agent: Besides protein, egg
contains phospholids such as lecithin which are known for their emulsifying quality. Hence egg can be
used an excellent emulsifying agent in products such as mayonnaise as it is
able to stabilise the oil in water dispersion .
As a Flavouring and
Colouring Agent: Egg is used in food mixtures to contribute flavour and colour to
products such as cakes and puddings.
As a Clarifying Agent: Egg helps in the preparation of clear soups. When a small amount of egg white is added to the liquid soup and heated, the egg albumin coagulates and carries along with it suspended particles. On allowing it to settle, a clear soup is obtained.
As a Garnishing Agent:
Hard boiled eggs are
diced and are used to garnish dishes like biryani.
As an Enriching Agent:
Eggs are used to
enhance the nutritive value of various preparations.
Related Topics