Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Drugs Used in Dermatological Disorders
Drugs For Cutaneous Fungal Infections
DRUGS FOR
CUTANEOUS FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Like bacterial infections of
skin, cutaneous fungal in-fections are treated with either topical or systemic
agents.
Systemic Agents
Griseofulvin
Griseofulvin (Fulvicin, Grifulvin V) has been used
safely and effectively for decades for dermatophyte in-fections of scalp and
nails and for more widespread skin eruptions. However, infections in certain
sites (e.g.. toe-nails) respond poorly. The drug is generally well toler-ated,
even in the long-term courses necessary for nail disease.
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole (Nizoral) is approved for treating der-matophyte infections unresponsive to griseofulvin and for patients unable to tolerate that drug. A single oral dose is also effective for the treatment of pityriasis ver-sicolor. Other effective drugs that are less hepatotoxic may be preferred, however.
Fluconazole
Fluconazole (Diflucan) may be better absorbed and is
possibly less hepatotoxic than ketoconazole, but it is considerably more
expensive, an important considera-tion given the required length of therapy for
most cuta-neous fungal diseases.
Itraconazole
Itraconazole (Sporanox), a triazole, is highly
lipophilic and concentrates in skin. It is approved for both cuta-neous deep
fungal infections and dermatophyte nail dis-ease, for which shorter courses of
therapy are probably effective. Pulse therapy, whereby the drug is
adminis-tered for 1 week and then the patient is off treatment for 3 weeks
between pulses, may reduce toxicity without compromising antifungal efficacy.
Terbinafine
Terbinafine (Lamisil), an antifungal drug, is highly
lipophilic and concentrates in stratum corneum and nail plate. It is very
effective for many dermatophyte infec-tions, especially those of the nails,
with which it may permit shorter courses of therapy than other drugs.
Meta-analysis suggests that long-term efficacy of terbinafine is superior to
that of the other antifungal drugs used in treating onychomycosis.
Potassium Iodide
Potassium iodide is used to
treat the cutaneous lym-phatic form of sporotrichosis, although newer agents
are also effective in this disorder and may be better to erated. The drug is
also used for erythema nodosum and nodular vasculitis.
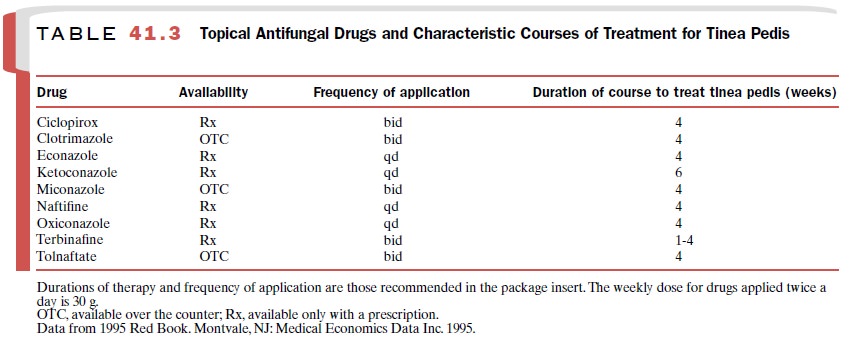
Topical Agents
Many effective topical agents
are available both with and without a prescription for treating cutaneous
der-matophyte infections and seborrheic dermatitis (Table 41.3); the azole
drugs are also active against superficial candidal infections.
Related Topics