Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Therapy of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Drug Therapy of HIV Infection: Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Nonnucleoside Reverse
Transcriptase Inhibitors
The NNRTIs inhibit viral reverse transcriptase by bind-ing adjacent
to its active site and inducing a conforma-tional change that causes the
enzyme’s inactivation. When combined with NRTIs or protease inhibitors, NNRTIs produce
additive and possibly synergistic ef-fects against HIV. The pharmacokinetic
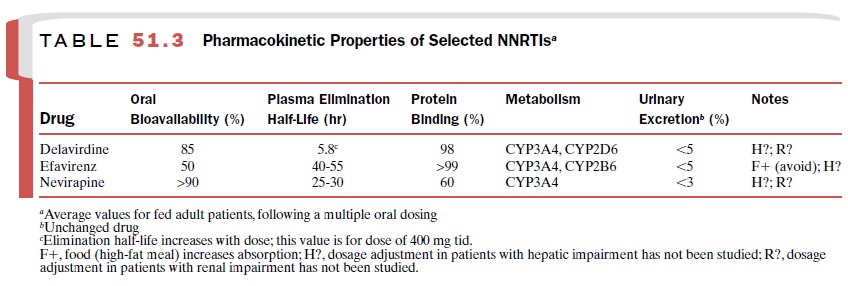
parameters of these agents are listed in Table 51.3.
All NNRTIs are active against
HIV-1 reverse tran-scriptase only and do not require phosphorylation for
activation. These agents share certain adverse effects (e.g., rash) and are
subject to numerous drug interac-tions due to their metabolism by and induction
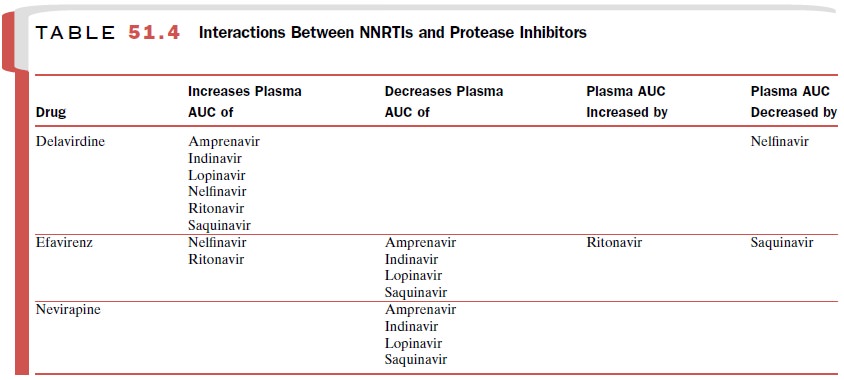
of he-patic cytochrome P450 enzymes. NNRTIs may modify plasma levels of
protease inhibitors, which are also me-tabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes (Table
51.4). The list of drug interactions
provided in this text is not all-inclusive; it is necessary to check for all
drug interac-tions when prescribing NNRTIs. These agents should be used with caution in patients with
hepatic disease.
When NNRTIs are used alone,
resistance develops rapidly as a result of the development of mutations in
reverse transcriptase; therefore, monotherapy with these agents is not
recommended. Cross-resistance be-
tween NNRTIs occurs
frequently but is not seen be-tween NNRTIs and NRTIs or the protease
inhibitors.
Efavirenz
Efavirenz (Sustiva) is approved for the therapy of
HIV infection of adults and children and is also used for pos-texposure
prophylaxis. It is the only NNRTI approved for once-daily dosing. Rash,
although rarely severe, is a common adverse effect of efavirenz. Elevated liver
en-zymes and serum cholesterol also may occur. Central nervous system (CNS)
effects in approximately half of patients may include dizziness, headache,
insomnia, drowsiness, euphoria, agitation, impaired cognition, nightmares,
vivid dreams, and hallucinations. These ef-fects often subside after several
weeks to months of therapy.
Efavirenz should be avoided during pregnancy be-cause primate studies have shown it to be teratogenic at doses near therapeutic levels. Women of childbearing potential should use two methods of birth control to avoid becoming pregnant when taking this drug.
Efavirenz interacts with many
drugs via the cy-tochrome P450 pathways. It induces and is metabolized by
CYP3A4 and inhibits CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. It should not be given with cisapride,
ergot alkaloids, mi-dazolam, or triazolam because of the potential for
life-threatening reactions. Efavirenz has the potential to decrease blood
levels of methadone, rifabutin, keto-conazole, and itraconazole. It may inhibit
the metabo-lism of drugs such as alosetron, diazepam, ethinyl es-tradiol,
imipramine, losartan, omeprazole, warfarin, tolbutamide, and topiramate.
Efavirenz interacts with cytochrome P450 inducers and substrates (e.g.,
phenyt-oin, phenobarbital) in a complex manner; blood levels and side effects
should be closely monitored. Patients taking efavirenz should avoid herbal
preparations con-taining St. John’s wort because the herb induces CYP3A4 and
may cause drug failure or viral resistance. Saquinavir should not be used as
the sole protease in-hibitor in a regimen containing efavirenz.
Nevirapine
Nevirapine (Viramune) is approved for the treatment
of HIV infection in adults and children as part of a combi-nation therapy. During the first 12 weeks of treatment, patients must be closely monitored for the
development of potentially fatal hepatic toxicity (i.e., hepatitis, hepatic
necrosis, and hepatic failure) and skin reactions (i.e., Stevens-Johnson
syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions). Although
these toxici-ties are rare, common side effects include mild to mod-erate rash,
fever, nausea, fatigue, headache, and ele-vated liver enzymes.
Nevirapine induces and is
metabolized by CYP3A4; therefore, coadministration of drugs that induce or are
metabolized by this isoenzyme may result in interac-tions. Nevirapine may
decrease the effectiveness of ethinyl estradiol–based contraceptives and can
lower plasma concentrations of methadone. Nevirapine should not be administered
with ketoconazole, rifampin, or ri-fabutin.
Delavirdine
Delavirdine (Rescriptor) is approved for the
treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents over age 16 as part of a
combination therapy. Rash accompanied by pruritus is the most frequent adverse
effect of this agent; however, it usually resolves within several weeks of
treatment. Severe skin reactions are rare. Headache, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea, fatigue, and elevated hepatic enzymes also may be associated with
delavirdine ad-ministration.
Drugs that decrease stomach
acidity (e.g., antacids, H2 receptor blockers, and proton pump
inhibitors) de- crease the absorption of delavirdine. In vivo and in vitro
studies have shown that delavirdine is metabolized by and inhibits CYP3A4. In
vitro studies have shown that it also is metabolized by CYP2D6 and inhibits
CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP2C19. Delavirdine should not be used in combination with
alprazolam, cisapride, ergot al-kaloids, midazolam, or triazolam because of the
poten-tial for serious adverse reactions. Delavirdine increases serum
concentrations of certain protease inhibitors and may reverse the resistance of
zidovudine-resistant HIV.
Related Topics