Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Intraoperative Coagulopathies
What should be included in the preoperative evaluation?
What should be included in the preoperative evaluation?
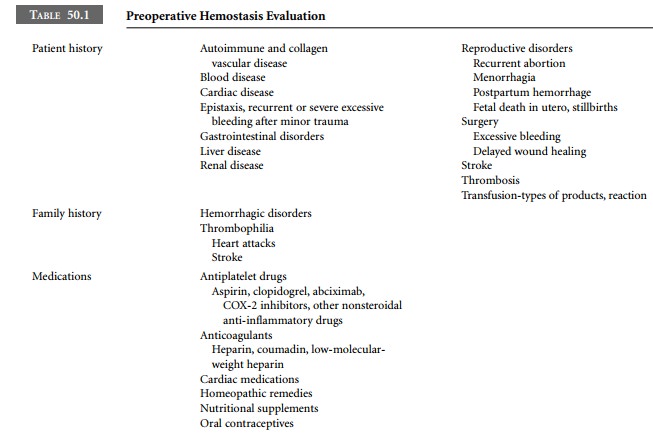
The goal of the preoperative evaluation is to
identify pre-existing conditions that could cause excessive bleeding or
thrombosis in the perioperative period. Table 50.1 lists items that should be
included. The complete medical history (personal and family), list of recent
medications, physical examination results, and preoperative laboratory studies
should be reviewed on every patient. In obtaining a med-ical history one must
specifically inquire about over-the-counter medications, vitamins, other
nutritional supplements, and homeopathic or natural remedies. Many patients do
not consider these to be medications and forget to mention them. However, many
of these natural reme-dies such as ginkgo biloba, garlic, ginseng, feverfew,
and vitamin E inhibit platelet function and may cause bleeding if not
discontinued prior to surgery.

The physical examination and blood chemistry
profiles may identify other medical problems that could lead to surgical
bleeding. Examination of the skin and mucous membranes may provide evidence of
a hemorrhagic predisposition (vascular purpura, hereditary hemorrhagic
telangiectasia), or collagen vascular disease. Splenomegaly, if present, may be
associated with hereditary spherocytosis, myeloproliferative disorders,
lymphoma, chronic leukemias, or liver disease with portal hypertension. Renal
or liver abnormalities identified in the chemistry profile may sug-gest a need
for specialized coagulation tests.
In the absence of a personal or family history
of a bleed-ing disorder, coagulation tests are usually confined to a complete
blood count, PT, and aPTT. Any abnormalities identified in the screening tests
must be investigated and evaluated in terms of the operative procedure that is
planned. Preoperative correction is advisable. If that is not possible, plans
for intraoperative treatment and management must be developed. If there is a
personal history of excessive bleeding, additional studies may be indicated
even if screening tests are normal. The most common inherited abnormality of
Approximately 1:1,000
individuals have clinically significant disease. In the most common form of the
disease, the aPTT may be normal and assays for factor VIIIc, von Willebrand
antigen, and ristocetin cofactor activity may be necessary to establish the
diagnosis.
Medications known to inhibit platelet function
should be discontinued in time to insure normal platelet function at the time
of surgery. Patients should be advised about over-the-counter medications to
avoid in the period immediately before surgery. If patients are on coumadin,
vitamin K should be administered. If anticoagulation must continue until
sur-gery, coumadin reversal and substitution of low-molecular-weight heparin,
or regular heparin, may be advisable.
Finally, consultation with a hematologist to
plan the management of patients with significant alterations in hemostasis or a
predisposition to thrombosis is advisable.
Related Topics