Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Intraoperative Coagulopathies
Which blood products are used to treat intraoperative coagulopathies?
Which
blood products are used to treat intraoperative coagulopathies?
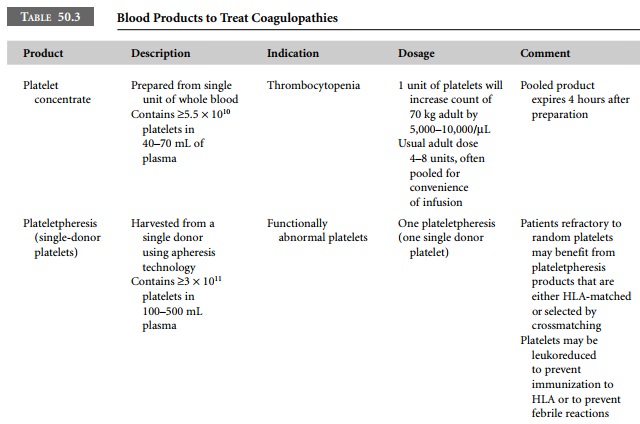
Traditional blood components used to treat
coagu-lopathies are presented in Table 50.3 and derivatives are presented in
Table 50.4.
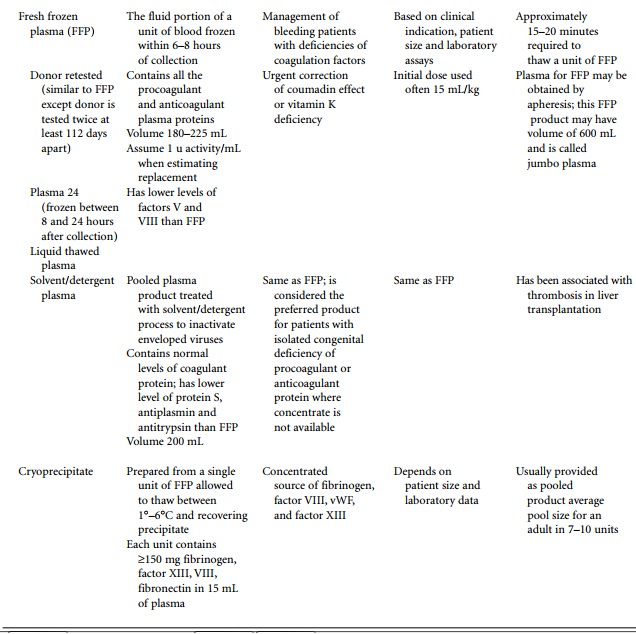
Solvent/detergent-treated plasma (SD-plasma)
and donor retested plasma are the only additions to the list of components.
Both products were developed to identify safer types of plasma for use in
clinical conditions that require multiple and long-term exposure to plasma
(i.e., therapeutic plasma exchange, replacement of congenital factor
deficiencies where concentrates are unavailable). SD-plasma is a pooled plasma
product containing plasma from many donors. The plasma is pooled by ABO type
and treated with a solvent/detergent process that inactivates enveloped
viruses. There is virtually no risk of trans-mission of HIV or hepatitis B and
C. However, because this is a pooled product, the risk of transmission of
par-vovirus B19 and other non-enveloped viruses is increased. SD-plasma is just
as efficacious as FFP in most clinical situations. However, unexpected
thrombosis reported in several cases of liver transplantation resulted in a
warning from the US Food and Drugs Administration about the use of SD-plasma in
liver transplantation. SD-plasma has lower levels of protein S and anti-plasmin
than FFP.
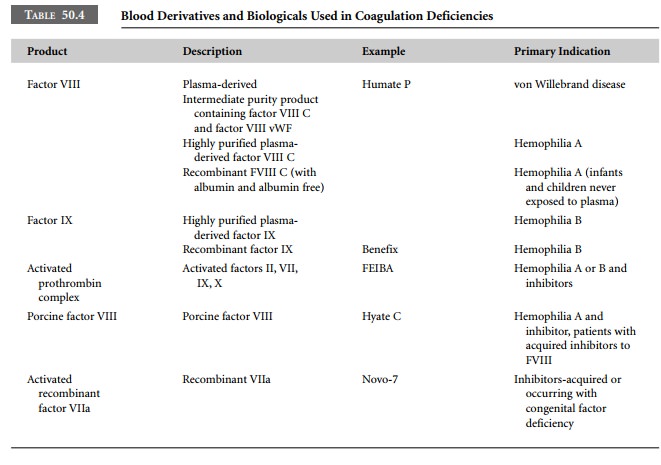
Two recombinant coagulation products, recombinant
factor VIIa (Novo-7) and recombinant activated protein C, are relatively new.
Although recombinant factor VIIa (rFVIIa) was developed for use in patients
with hemo-philia, it has been used in other clinical situations where thrombin
production is impaired. A hemostatic effect of rFVIIa has been reported in
thrombocytopathies such as Glanzman thrombasthenia and Bernard-Soulier syndrome
and in severe thrombocytopenia. The product has also been used when profuse
bleeding has occurred in trauma and extensive surgery. These case reports
suggest the need for controlled clinical trials.
Recombinant activated protein C was licensed
for use in severe sepsis, and many patients at risk of bleeding were excluded
from the initial trials. Because it is an extremely expensive product,
off-label use will undoubtedly be limited. However, studies from Japan have
demonstrated the product to be useful in managing placental abruption.
Post-market-ing studies may identify other clinical indications.
Related Topics