Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Cardiomyopathy Managed With A Left Ventricular Assist Device
What is a cardiomyopathy?
What is
a cardiomyopathy?
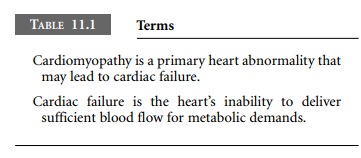
Cardiac failure is the heart’s inability to
deliver sufficient blood flow for metabolic demands. Cardiomyopathy is a myocardial
abnormality that may lead to cardiac failure (Table 11.1). Cardiomyopathy may
result from a primary abnormality of the myocardium, or may be secondary to
valvular, hypertensive, ischemic, infiltrative, structural, or pericardial
disease processes. Regardless of the underlying etiology, compensatory changes
(e.g., dilation and/or hypertrophy of the heart chambers) represent a final
common outcome of adverse myocardial remodeling. A thorough evaluation of the
patient presenting with typi-cal signs and symptoms of heart failure (e.g.,
fatigue, short-ness of breath, impaired exercise tolerance, peripheral edema,
pulmonary rales, and renal insufficiency) is often required to establish the
true underlying etiology. In addi-tion to history, physical examination and
focused labora-tory testing, evaluation often requires both noninvasive and
invasive modalities, including echocardiography, car-diac catheterization, and
endomyocardial biopsies.
Related Topics