Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
What are the treatment options for HOCM?
What are the treatment options for HOCM?
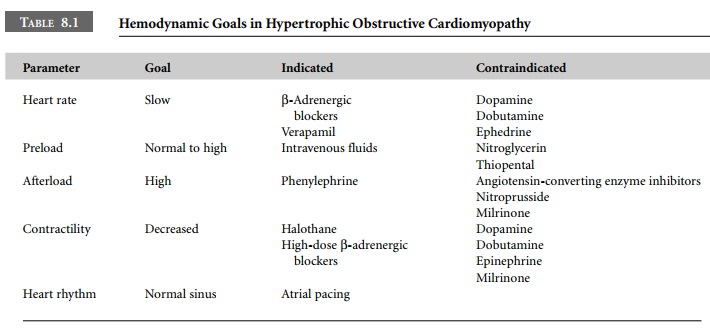
Medical therapy of HOCM is based on β-blockers (Table 8.1). Their beneficial effects are likely due to a
depression of systolic function and an improvement in diastolic filling and
relaxation. However, it is still not clear whether life expectancy is prolonged
by this treatment. Amiodarone is a commonly used agent for the control of
supraventricular and ventricular dysrhythmias.
Nonmedical treatment options are surgical
myotomy/ myomectomy, percutaneous transluminal septal myo-cardial ablation,
alcohol septal ablation, mitral valve replacement/valvuloplasty, or a
combination of the former. The potential complications of surgical correction
of the LVOT obstruction include complete heart block and late formation of a
ventricular septal defect due to septal infarction.
Controlled studies did not confirm earlier
reports that atrioventricular sequential (DDD) pacing is beneficial for
patients with HOCM. Dual-chamber pacing can currently be recommended only in
selected patients. The reported annual mortality rate is 1–3%, mostly due to
ventricular dysrhythmias, sudden death, progressive heart failure, and atrial
fibrillation with embolic stroke. There is accumulat-ing evidence that
implantable automated defibrillator devices are highly effective in terminating
malignant ventricular dysrhythmias in HOCM patients and, thus, decreasing the
incidence of sudden death.
Related Topics