Classification, Properties and Uses of Bases | alkalis - What are Bases? | 9th Science : Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter: 9th Science : Acids, Bases and Salts
What are Bases?
What are Bases?
According to Arrhenius
theory, bases are substances that ionise in water to form hydroxyl ions (OH–).
There are some metal oxides which give salt and water on reaction with
acids.These are also called bases. Bases that are soluble in water are called
alkalis. A base reacts with an acid to give salt and water only.
Base + Acid → Salt +
Water
For example, zinc oxide
(ZnO) reacts with HCl to give the salt zinc chloride and water
ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq)
→ ZnCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
Similarly,sodium hydroxide
ionises in water to give hydroxyl ions and thus get dissolved in water. So it
is an alkali.
NaOH(aq) → Na+(aq)
+ OH-(aq)
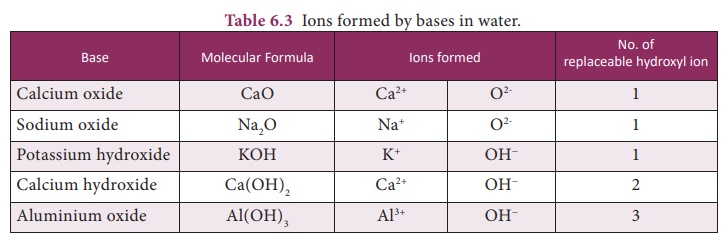
Bases contain one or
more replaceable oxide or hydroxyl ions in solution. Table 6.3 enlists various
bases and ions formed by them in water.
1. Classification of Bases
Based on their Acidity
a) Monoacidic Base:
It is a base that
ionises in water to give one hydroxide ion per molecule.
Example: NaOH, KOH
b) Diacidic Base:
It is a base that
ionises in water to give two hydroxide ions per molecule.
Example: Ca(OH)2.
Mg(OH)2
c) Triacidic Base:
It is a base that
ionises in water to give three hydroxide ions per molecule.
Example: Al(OH)3,
Fe(OH)3
Based on concentration
a) Concentrated Alkali
It is an alkali having a
relatively high percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution.
b) Dilute Alkali
It is an alkali having a
relatively low percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution.
Based on Ionisation
a) Strong Bases:
These are bases which
ionise completely in aqueous solution.
Example: NaOH, KOH
b) Weak Bases
These are bases that
ionise partially in aqueous solution.
Example: NH4OH, Ca(OH)2
2. Properties of Bases:
a) They have bitter taste.
b) Their aqueous solutions have soapy touch.
c) They turn red litmus blue
d) Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity
e) Bases react with metals to form salt with the liberation of
hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2 NaOH → Na2ZnO2
+ H2 ↑
f) Bases react with
non-metallic oxides to produce salt and water. Since this is similar to the
reaction between a base and an acid, we can conclude that non-metallic oxides
are acidic in nature.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2
→ CaCO3+ H2O
g) Bases react with acids to form salt and water.
KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
The above reaction
between a base and an acid is known as Neutralisation reaction.
h) On heating with
ammonium salts, bases give ammonia gas.
NaOH + NH4Cl
→ NaCl + H2O + NH3 ↑
In the above activity
you can observe that the bulb will start glowing only in the case of acids. But
you will observe that glucose and alcohol solution do not conduct electricity.
Glowing of the bulb indicates that there is a flow of electric current through
the solution. The electric current is carried through the solution by ions.
Repeat the same activity
using alkalis such as sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide.
3. Uses of Bases
·
Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of soap.
·
Calcium hydroxide is used in white washing of building.
·
Magnesium hydroxide is used as a medicine for stomach disorder.
·
Ammonium hydroxide is used to remove grease stains from cloths.
Related Topics