Classification, Properties and Uses of Acids, Aquaregia - What are Acids? | 9th Science : Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter: 9th Science : Acids, Bases and Salts
What are Acids?
What are Acids?
Look at the pictures of
some of the materials used in our daily life given below:

All these edible items
taste similar i.e. sour. What cause them to taste sour? A certain type of
chemical compounds present in them gives sour taste. These are called acids.
The word ‘acid’ is derived from the Latin name “acidus” which means sour taste.
Substances with sour taste are called acids.
In 1884, a Swedish
chemist Svante Arrhenius proposed a theory on acids and bases. According to
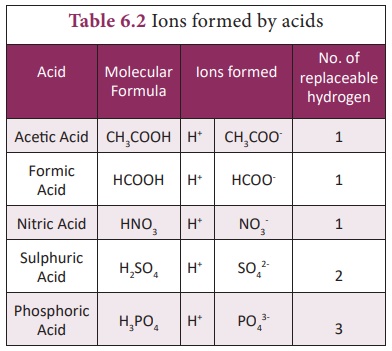
Arrhenius theory, an acid is a substance which furnishes H+ ions or
H3O+ ions in aqueous solution. They contain one or more
replaceable hydrogen atoms. For example, when hydrogen chloride is dissolved in
water, it gives H+ and Cl- ions in water.
HCl(aq) → H+(aq)
+ Cl-(aq)
What happens to an acid
or a base in water? Do acids produce ions only in aqueous solution?
Hydrogen ions in HCl are
produced in the presence of water. The separation of H+ ion from HCl molecules
cannot occur in the absence of water.
HCl + H2O → H3O+
+ Cl-
Hydrogen ions cannot
exist alone, but they exist in combined state with water molecules.
Thus, hydrogen ions must
always be H+ (or)
Hydronium (H3O+)
H+ + H2O
→ H3O+
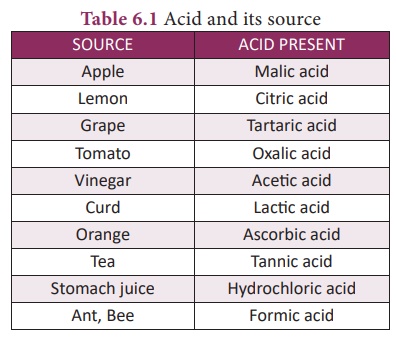
The following table
enlists various acids and the ions formed by them in water.
1. Classification of Acids
Acids are classified in
different ways as follows:
Based on their sources:
(i) Organic acids
(ii) Inorganic acids
Organic Acids:
Acids present in plants
and animals (living things) are organic acids.
Example: HCOOH, CH3COOH
Inorganic Acids:
Acids prepared from
rocks and minerals are inorganic acids or mineral acids.
Example: HCl, HNO3,
H2SO4
Based on their Basicity
Monobasic Acid:
Acid that contain only
one replaceable hydrogen atom per molecule is called monobasic acid. It gives
one hydrogen ion per molecule of the acid in solution.
Example: HCl, HNO3
Dibasic Acid:
An acid which gives two
hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution.
Example: H2SO4,
H2CO3
Tribasic Acid:
An acid which gives
three hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution.
Example: H3PO4
Based on Ionisation
Acids get ionised in
water (produce H+ ions) completely or partially. Based on the extent
of ionisation acids are classified as follows:
Strong Acids:
These are acids that
ionise completely in water. Example: HCl
Weak Acids:
These are acids that
ionise partially in water. Example: CH3COOH.
Based on Concentration
Concentrated Acid:
It has relatively large
amount of acid dissolved in a solvent.
Dilute Acid:
It has relatively
smaller amount of acid dissolved in solvent.
2. Properties of Acids
a) They have sour taste
b) Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity since they contain
ions
c) Acids turns blue litmus red
d) Acids react with
active metals to give hydrogen gas.
Mg + H2SO4
→ MgSO4 + H2 ↑
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2
+ H2 ↑
e. Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate
to give carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3
+ 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
NaHCO3 + HCl →
NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
f) Acids react with metallic oxides to give salt and water.
CaO + H2SO4
→ CaSO4 + H2O
g) Acids react with bases to give salt and water.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
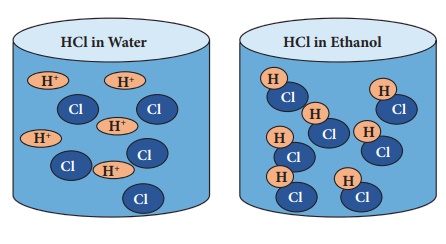
Role of water in acid solution
Acids show their properties only when dissolved in water. In water, they ionise to form H+ ions which determine the properties of acids. They do not ionise in organic solvents.
For example, when HCl is dissolved in water it produces H+ ions and Cl- ions whereas in organic solvent like ethanol they do not ionise and remain as molecule.
3. Uses of Acids
·
Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals because it is used in
the preparation of many other compounds. It is used in car batteries also.
·
Hydrochloric acid is used as a cleansing agent in toilets.
·
Citric acid is used in the preparation of effervescent salts
and as a food preservative.
·
Nitric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes,
paints and drugs.
·
Oxalic acid is used to clean iron and manganese deposits from
quartz crystals. It is also used as bleach for wood and removing black stains.
·
Carbonic acid is used in aerated drinks.
·
Tartaric acid is a constituent of baking powder.
4. Aquaregia
We know that metals like
gold and silver are not reactive with either HCl or HNO3. But the mixture of
these two acids can dissolve gold. This mixture is called Aquaregia. It is a
mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid prepared optimally in a molar
ratio of 3:1. It is a yellow-orange fuming liquid. It is a highly corrosive
liquid, able to attack gold and other resistant substances.
Chemical formula : 3 HCl
+ HNO3
Solubility in Water : Miscible
in water
Melting point : - 42˚ C
(- 44˚ F, 231K)
Boiling point : 108 ˚ C
(226 ˚ F , 381K)
The term aquaregia is a
Latin phrase meaning “King’s Water”. The name reflects the ability of aquaregia
to dissolve the noble metals such as gold, platinum and palladium.
Uses of Aquaregia:
1. It is used chiefly to
dissolve metals such as gold and platinum.
2. It is used for
cleaning and refining gold.
Related Topics