Chapter: 12th Geography : Chapter 7 : Sustainable Development
Watershed management and its importance
Watershed management and
its importance
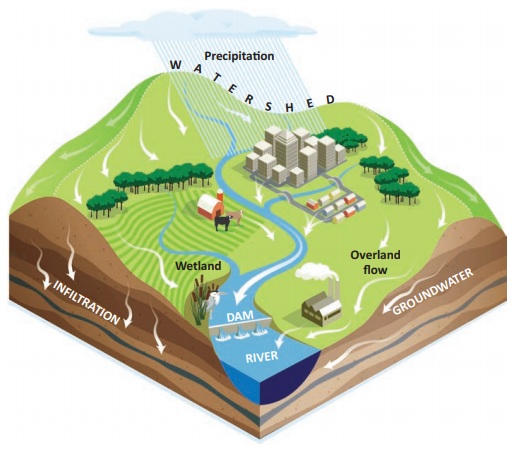
Watershed is a geographical area drained
by a stream or a system connecting stream in which water from all over an area flow
under gravity to a common drainage channel. A watershed system delivers water through
rills, gullies and streams to a larger body of water.
Watershed
management is proper utilization of land and water resource for optimum production
with minimum hazards to natural resources. It relates to soil and water conservation
proper land uses, promote afforestation and sustainable farming practices, conserve
farmland and pastureland, maintaining soil fertility, proper management of local
water for farming, drainage, construct small dams for flood protection, improving
individuals standard of living and thereby promote ecological balance.
Key steps in watershed management
Watershed plans should first identify
the characteristics of the watershed and inventory the watershed’s natural resources.
The first steps in watershed management planning are to:
i. Delineate and map the watershed’s
boundaries and the smaller drainage basins within the watershed.
ii. Map and
prepare an Inventory of resources in the watershed. Prepare an Inventory and map
the natural and manmade drainage systems in the watershed.
iii.
Prepare an Inventory and map land use and land cover.
iv. Prepare
a soil map of the watershed
v. Identify
areas of erosion, including stream banks and construction sites.
vi)
Identify the quality of water resources in the watershed as a baseline; and
Watershed Management in India:
Watershed
development project in the country has been sponsored and implemented by Government
of India from early 1970s onwards. Various watershed development programs like Drought
Prone Area Program (DPAP), Desert Development Program (DDP), River Valley Project
(RVP), National Watershed Development Project for Rain-fed Areas (NWDPRA) and Integrated
Wasteland Development Program (IWDP) were launched subsequently in various hydro-ecological
regions. Entire watershed development programs primarily focused on soil conservation
and rainwater harvesting during 1980s and before.
Rain Water Harvesting (RWH)
Millions
of people throughout the world do not have access to clean water for domestic purposes.
In many parts of the world conventional piped water is either absent, unreliable
or too expensive. One of the biggest challenges of the 21st century is to overcome
the growing water shortage. Rain Water Harvesting (RWH) has thus regained its importance
as a valuable alternative or supplementary water resource, along with more conventional
water supply technologies. Water shortages can be relieved if rain water harvesting
is practiced more widely.
Need for Rain Water Harvesting
i. To overcome
the situation of inadequacy of water supply.
ii. The most
economical way to increase the ground water table.
iii. To replenish
the sub soil of the urban area covered with pavements.
iv. To recharge
the underground water table at places where the availability of rain water is higher
or to overcome the situation of water logging.
v. Rain water
harvesting also improves the quality of underground water through a process called
dilution.
vi.
To get water for irrigation of greenbelts, farms, gardens, etc.
Rain Water Harvesting Techniques
There are two main techniques of rain
water harvestings:
1.
Storage of rain water on surface for future use.
2.
Recharge to ground water.
The storage of rain water on surface
is a traditional technique and structures used were underground tanks, ponds, check
dams, weirs, etc. Recharge of ground water is a new concept of rain water harvesting
and the structures generally used are: Recharge pits filled with boulders, gravels,
and coarse-sand, Wells, Trenches etc.
Related Topics