Auditing - Verification and Valuation of Fixed Assets | 12th Auditing : Chapter 4 : Verification and Valuation of Fixed Assets
Chapter: 12th Auditing : Chapter 4 : Verification and Valuation of Fixed Assets
Verification and Valuation of Fixed Assets
Verification and Valuation of Fixed Assets
Fixed
assets of are a permanent nature with which the business is carried on and
which are held for earning income and not for re-sale in the ordinary course of
the business. It is a long-term tangible property that a firm owns and uses in
its operations to generate income. Fixed assets are not converted into cash or
consumed within a year. They are also called as Capital Assets. Example: land
and buildings, plant and machinery, furniture etc. These assets are to be
valued at cost price less total depreciation in their value by constant use.
Additions by way of purchase and deletions by way of sales should be taken into
account.The mode of valuation of different types of assets differs depending
upon the nature of the business and the purpose for which the assets are held.
Verification of Fixed Assets can be explained as follows:
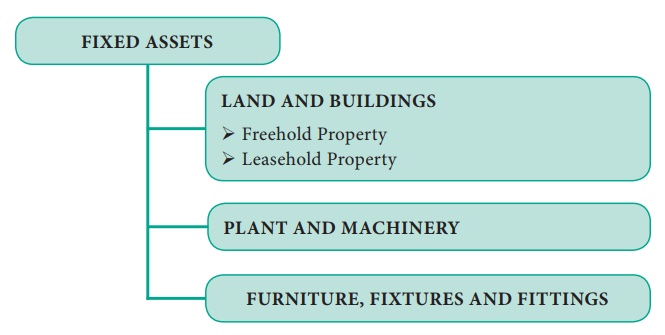
1. Land and Buildings

Land
means a long -term asset that refers to the cost of real property exclusive of
the cost of any constructed assets on the property. The value of land has an
appreciated value and is not subject to depreciation. A building is a
noncurrent or long-term asset which shows the cost of a building (excluding the
cost of the land) . Buildings will be depreciated over their useful life of the
asset.
·
Classified
into two types
Land and
Buildings can further be classified as –
A Freehold
property.
B Leasehold
property
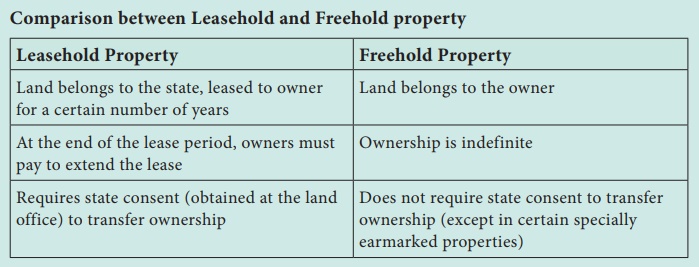
(A) Freehold Property
A
property which is free from hold (Possession/Rights) is called as freehold
property. This means that the property is free from the hold of anybody besides
the owner who enjoys complete ownership.
Auditor’s Duty
1. Where
Freehold property has been purchased, the auditor should examine the title
deeds e.g., purchase deed, certificate of registration, the broker’s note and
auctioneer’s account etc., to verify the correct position.
2. When the
property has been mortgaged, the auditor should obtain a certificate from the
mortgagee regarding the possession of title deed and outstanding amount of
loan.
3. When
the property has been acquired in the current year, then the cost may be
verified with the help of the bank passbook. He should vouch all the payments
made in this connection.
4. He
should see that the property account should be shown in the Balance Sheet at
cost price including the legal and registration charges less depreciation
up-to-date.
5. He
should also see that a separate account for building and land on which it is
constructed is maintained. It is necessary because depreciation is provided for
building and not for the land.
(B) Leasehold Property
Leasehold
is an accounting term for an asset being leased. The asset is typically
property such as a building or space in a building.
·
The property which is on lease (rent).
·
The property (plot/flat/villa/mall/ factories)
which is leased by the landlord for a certain period of time to the lessee (tenant
/leaseholder/renter/ occupant/dweller).
·
The (tenants) have been given the right to use
during that specified time by the landlord.
·
The ownership of the property returns to the
landlord when the lease comes to an end.
Auditor’s Duty
1. The auditor should verify this by inspecting the
lease agreement or contract to find out value and duration. He should see that
the terms and conditions of lease are properly complied with.
2. In case
property has been mortgaged, the auditor should obtain a certificate from the
mortgagee regarding the possession of title deed.
3. Where
the leasehold property has been sub-let, the counter part of the tenant’s
agreement should also be examined.
4. The
auditor should physically inspect the properties.
5. The
auditor should also note that proper provision has been made for depreciation
of lease problem and for any possible claims arising there under.
2. Plant and Machinery
A plant
is an asset with a useful life of more than one year that is used in producing
revenues in a business’s operations. Plant is recorded at cost and depreciation
is reported during their useful life.
Auditor's Duty
1. When the
machines are purchased in the current accounting period, the invoices and the
agreement with the vendors should be verified.
2. The
auditor should ` examine the plant register in which particulars about the
cost, records about sales, provision for depreciation, etc., are available.
3. He
should prepare a list of each machine from the plant register and should get
the list certified by the works manager as he is not a technical person and
therefore he has to depend upon the advice of the works manager regarding their
valuation, etc.
4. He
should see that plant and machinery account is shown in the Balance Sheet at cost
less depreciation after making proper adjustment for purchases and sales during
the year under audit.
5.
In case any plant and machinery has been
scrapped, destroyed or sold, he should ascertain that the profit or loss
arising thereon has been correctly determined.
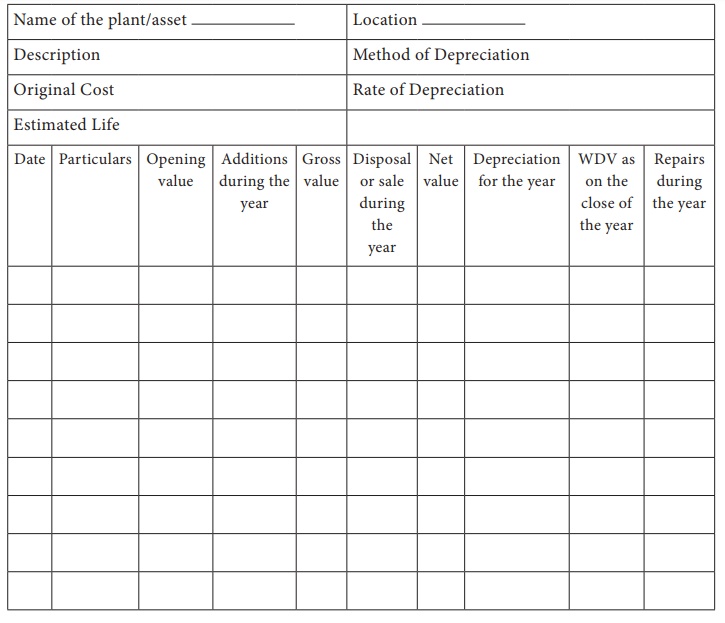
A proforma of plant & machine register is given below
3. Furniture, Fixtures and Fittings
They are
items of movable equipment that are used to furnish an office. Examples are
chairs, desks, shelves, book cases, filing and other similar items.
Auditor's Duty
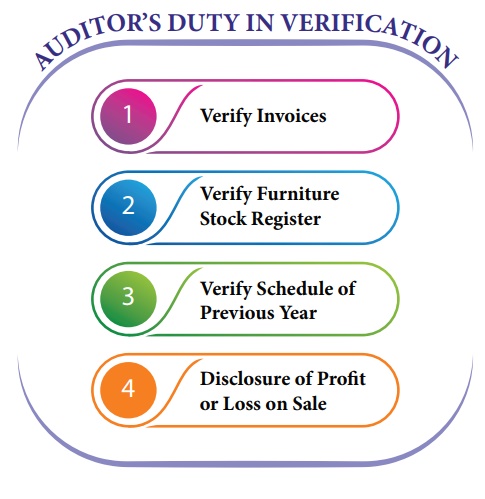
1. Verify Invoices: When
assets have been acquired during the
current accounting period, the auditor should examine the purchase invoice of
the dealers.
2. Verify Furniture Stock Register: He should verify furniture stock register
and ask the management to prepare an inventory to reconcile it with the stock
register.
3. Verify Schedule of Previous Year: He
should compare furniture schedule of previous year with that of current year to
ascertain the existence, purchase or sales of asset during the year.
4. Disclosure of Profit or Loss on Sale: He
should examine that any profit or loss on sale of furniture during the year is
properly disclosed in books of accounts.
VALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
1.
Valuation
of Land: Land which does not have
depreciated value, is valued at cost price.
2.
Valuation
of Other Fixed Assets: Other fixed assets like Buildings, Plant,
machinery, office equipment, furniture and fixtures should be valued at going
concern value.
3.
Depreciation:
Auditor should ensure that
adequate amount of depreciation has been provided, taking into account the
working life and usage of the asset.
4.
Disclosure
in Balance Sheet: He should
verify that furniture, fittings and fixtures are disclosed in Balance Sheet at
cost less depreciation.
Related Topics