Chapter: Business Science : Marketing Management : Buyer Behavior
Understanding Industrial & Individual Buyer Behaviour
Understanding Industrial & Individual Buyer
Behaviour
Buyer
behaviour is the study of when, why, how, and where people do or do not buy
[[Product (business)|product).It blends elements from psychology, sociology,
social anthropology and economics.
It
attempts to understand the buyer decision making process, both individually and
in groups. It studies characteristics of individual consumers such as
demographics and behavioural variables in an attempt to understand people's
wants. It also tries to assess influences on the consumer from groups such as
family, friends, reference groups, and society in general.
Customer
behaviour study is based on consumer buying behaviour, with the customer
playing the three distinct roles of user, payer and buyer. Relationship
marketing is an influential asset for customer behaviour analysis as it has a
keen interest in the re-discovery of the true meaning of marketing through the
re-affirmation of the importance of the customer or buyer. A greater importance
is also placed on consumer retention, customer relationship management,
personalisation, customisation and one-to-one marketing. Social functions can
be categorized into social choice and welfare functions.
Each
method for vote counting is assumed as a social function but if Arrow’s
possibility theorem is used for a social function, social welfare function is
achieved. Some specifications of the social functions are decisiveness,
neutrality, anonymity, monotonocity, unanimity, homogeneity and weak and strong
Pareto optimality. No social choice function meets these requirements in an
ordinal scale simultaneously. The most important characteristic of a social
function is identification of the interactive effect of alternatives and
creating a logical relation with the ranks. Marketing provides services in
order to satisfy customers. With that in mind, the productive system is
considered from its beginning at the production level, to the end of the cycle,
the consumer (Kioumarsi et al., 2009).
Belch and
Belch define consumer behaviour as 'the process and activities people engage in
when searching for, selecting, purchasing, using, evaluating, and disposing of
products and services so as to satisfy their needs and desires'.'
1.Industrial buyer behavior
theory
It is
considered as highly important to be aware of why a customer or buyer makes a purchase.
Without such an understanding, businesses find it hard to respond to the
customer ‟ s needs and wants (Parkinsson & Baker, 1986). It is important to
be aware of the differences between consumer buying and industrial buying
because the industrial buyer behavior differs from consumer buying in many
aspects such as; using more variables and greater difficulty to identify
process participants (Moriarty, 1984). The industrial buying is described by
Parkinsson & Baker (1986) as the buy of a product which is made to please
the entire organization instead of satisfying just one individual. Industrial
buying behavior is considered as being a elementary concept when it comes to
investigating buyer behavior in all types of organizations (ibid). Also, in
industrial buying situations there is a perception of greater use of marketing
information, greater exploratory objective in information collection and
greater formalization. (Deshpande & Zaltman, 1987)
The
article by Johnston & Lewin (1996) illustrates that the broad amount of
research conducted consolidated the existence and relevance of three important
dimensions when investigating industrial buyer behavior.
1.
How the buyer
decision process looks like when organizations stands in front of different
buying situations.
2.
The buying
decision center and factors influencing the buying process within the
organization
3.
The different criterion’s
used by industrial buyers when buying a product/service.
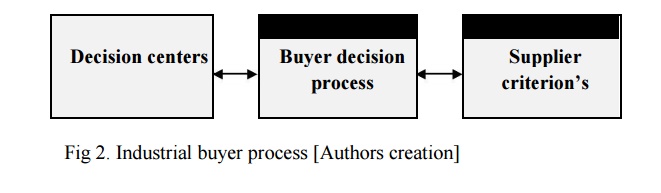
Fig 2.
Industrial buyer process [Authors creation]
These
three dimensions are considered as highly relevant for this research and will
therefore be used throughout the study [fig 2]. In order to increase knowledge
about the industrial buyer behavior, these three dimensions will be further
described in more detail in the coming chapters of the theoretical framework.
2. Situations affecting the
Industrial buyer behavior
We
consider it to be crucial to describe the essential circumstances that
influence the buyer behavior and thereafter we will continue with describing
other relevant factors. Robinson et al. (1967) argues that there are some
circumstances during a purchase being more important than the actual
product/service being bought. Based on these assumptions the authors studies
different buying situations and present these situations in three main
categories, so called
―buy-classes‖;
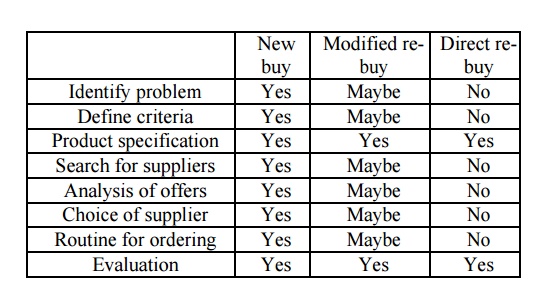
(1) new task; (2) straight re-buy; (3) modified re-buy (ibid). In a new task buying situation the
product/service is completely new to the organization. The buyer has insufficient
or no experience and knowledge about the product/service in order to compare
alternative suppliers with each other. The buyer and the influencers need to
gather relevant information before the decision to purchase is made. A straight re-buy is the most common form
of industrial purchase situation where the buying organization requires little
or no information about the product/service. This situation is considered as
routine buying and the industrial buyer most often have well developed criterion
‟s that
have been often used before.
(ibid).
Evaluating criterion‟s, suppliers and other stages in the process are
considered as unnecessary in this situation since the same product has been
bought before. However, the first step of the process (need recognition) is
taken into consideration. On the other hand,
a modified re-buy occurs after the buyer have bought a new product or made
a straight re-buy. The industrial buyer reevaluates the supplier, product,
prices and services; however this doesn‟t mean that the buyer will change
product or supplier. According to Robinson et al (1967) there are four factors
leading to a modified re-buy; cost reductions, disaffection with current
supplier, development of product or better offerings from another supplier surrounding
price, quality or service. In this case the buying organization puts most focus
in evaluating suppliers. (ibid)
3.Buyer decision process
After
defining the different circumstances influencing the buyer behavior we argue
that it is important to define the actual buying decision process. In order for
a marketer to be successful [s]he needs to examine the complex subject of buyer
decision processes (Kotler et al, 2007). The buying process involves different
stages that organizations phase during and after a purchase. Yet, this buying
process may differ a lot depending on what type of product that will be bought
(ibid). The authors Robinsson et al (1967) illustrate this process by
developing a model which lays down how the process of deciding to buy a product
looks like for industrial organizations. This model is separated into eight
different buy-phases. These phases will be described in more detail below;
1. Need recognition: This is the first step in the
buyer process where a problem or need
is identified by someone in the organization
2. Definition of the characteristics of the item
needed: In this stage a description of
alternative solutions is presented and questions like; what does the company
need? Which service attributes and quanities are needed ?
3. Development of the specifications: A more
detailed technical specification of the
product/service is presented. This information will be vital for the coming
stages.
4. Search for supplier; The
buying organization searchs for suppliers that can offer them the wanted product/service. When dealing with more complex
and costly products/services the buying organization spends more time finding
their supplier.
5. Acquistion and analysis of proposals: The
most qualifying suppliers are chosen and
their different proposals are analyzed. If the buying organization are buying
more complex and expensive products/services the suppliers need to make formal
presentations of alternativ solutions responding to the organizations need.
This stage is similar to the previous stage and occur almost always in
parallel. However, if the buyer have very little information from the beginning
then these stages are more separable.
6. Evaluation of suppliers: The
members of the buying decision center evaluate the supplier by the product/service attributes offered (which
attributes matter most?), brand belief (opinions about the brand)
1. Selection of an order routine: This
phase starts by sending an order to the supplier.
However, the buying process is not finished until the product/service has been
delivered and the buying organization has accepted it. Preparation of the order
before it is sent to the supplier, control and evaluation of the order are some
of the activities done in this phase
2.
Evaluation: Post
purchase evaluation to see whether the supplier and the product/service fulfilled the requirements and preferences.
4.Buyer decision center
A group
of individuals within an organization form the buyer decision center. According
to Cyert & March (1992), all organizations have their own decision center.
However, this center might differ in terms of size and structure from one
organization to another. The term of decision center implies to all members
being a part of the industrial buying decision process (Robinson et al., 1967).
According to Cyert & March (1992), the decision center consists of
individuals having different goals such as profit, sales, market shares and
production. According to Parkinsson & Baker (1986) when a organization
identify their buying center it is important to tackle two important factors;
1.
Roles in the
decision center
2.
Factors
influencing the members
1.
Roles in
the decision center
In every
decision center there are different members having different roles and
authorities and according to Webster & Wind (1972) this decision center can
be a very complex environment consisting of initiators, buyers, users,
influencers, decision makers and gatekeepers. The initiators are the
individuals within the organization that first recognizes the need for a
product or service. The buyers have the formal authority and responsibility for
choosing suppliers, deciding buyer conditions and price negotiations. (ibid)
While the
users are the actual individuals that will use the product and they are best
equipped with the right knowledge and experience to evaluate the product. The
influencer do not have any direct authority when it comes to the buyer
decision, however, they still affect the decision outcome. The decision makers
have a formal authority and responsibility to make the final decision. Finally,
the gatekeepers control the information flow in this decision making process
and thereby they affect the process indirectly (Webster &Wind, 1972).
6.Factors influencing the buying
center
The
variables are; (1) conditions of the buying situation, (2) personal
characteristics and (3) organizational structure characteristics. These
variables are illustrated in the model below:
7.Conditions of the buying
situation
According
to Samaniego & Cillian (2004) there are five different variables that
influences the buying center; (1) Buyclasses;
have a direct influence on the buying center. According to the industrial
buying theory, the buying center searches for more information if they are
facing a new task and thereby it decreases uncertainty. (2) Level of complexity; this variable consists of two types of
areas; the complexity of the buying situation and; the complexity of the
product (Dadzie, Johntson et al 1999). According to Bonoma (1982), the higher
the level of complexity (buying situation & product), the more individuals
involved in the buying center.
(3) Importance; the
degree of importance is defined as how much the purchase has influence on the organizations
productivity and profitability. Bonoma (1982) argues if the degree of importance
and complexity is low, one single individual can hold all roles in the decision
center. (4) Risk; if the industrial
buyer experience greater risk with the purchase the degree of influence and
involvement in the buying center increases. This is done in order to reduce and
minimize potential risks.
(5)Time pressure; According
to Speakman & Mariarty (1984) referred by G.Samaniego & G.Cillian (2004) the degree of
involvement and influence reduces when there is a high time pressure.
8.Personal characteristics
According
to Samaniego & Cillian (2004) there are two different variables related to
the personal characteristics that influences the buying center. (1) Personal influence; the more an
individual is involved in the buying process the greater the possibility for
the individual to feel motivated to participate and influence the buying
center. (2) Personal experience; the
greater individual experience [in terms of buying] increases the involvement
and influence on the buying center.
According
to Samaniego & Cillian (2004) there are five different variables related to
the organizational structure that influences the buying center; (1) Size; Size and the structure of an
organization determine the size and complexity of the buying center , (2) Specialization; higher degree of
specialization within an organization leads to higher involvement and influence
on the buying center, (3)
Standardization; higher level of standardization increases the
possibilities to develop well structured buying centers and thereby decreases
the degree of involvement and influence, (4)
Centralization; a higher degree of decentralization indicates that a larger
number of departments within the organization are involved, which in turn
signify that more individuals are involved and influence the buying center, (5) Formality;
Different
types of formalities such as rules, policies and different procedures for
certain activities influence the buying center and thereby the buying process
(ibid).
Supplier selection criterions
According to Axelsson (1998), there is always a
step in the buying process where the buying center evaluates different
suppliers based on some certain criterions. The author presents important
factors that need to be addressed when choosing a certain supplier. These factors
where brought from an earlier research where organizations where asked what
they considered to be the most important factors when evaluating a supplier
(ibid). These factors
are as follows;
1. Price
2. Product quality
3. Accessibility to information
4. Service & Support.
5. Delivery costs
6. Delivery time
7. Stability in the delivery
8. Participation in the Product
9. Supplier flexibility Geographic
10. localization Technological
11. standard
12. ISO-certification
However, the authors Cebi & Bayraktar (2003)
also present some other important factors when evaluating a supplier such as;
1 Supplier reputation
2. Earlier experience with Supplier
3 . Guarantees of results
4. supplier knowledge and competence Direct
5. communication and contact
9.The buy grid framework
It is not easy to develop a model that fits in all
situations for industrial buyer behavior. The buyer decision process will most
often change from one situation to another depending on which factors influence
the decision in each specific situation (Parkinson & Baker, 1986). However,
Robinson et al (1967) have developed a model called the Buy grid framework
where they combine the eight staged buyer decision in process [fig 4] with the
three different buying situations. This framework illustrates the process of an
industrial buyer moving through finding a need/identifying a problem towards
purchasing and evaluating it. Depending on the buyclass the different steps
become more or less important.
10.Theoretical Framework
To be able to analysis the industrial buying
behavior a clear understanding of how these different fields relates to each
other. Figure 5 visualizes the relation between the buying center, buy grid
framework and the suppliers criterions. This aims to help us in our analysis,
it visualizes the relationships and how it affects each other.
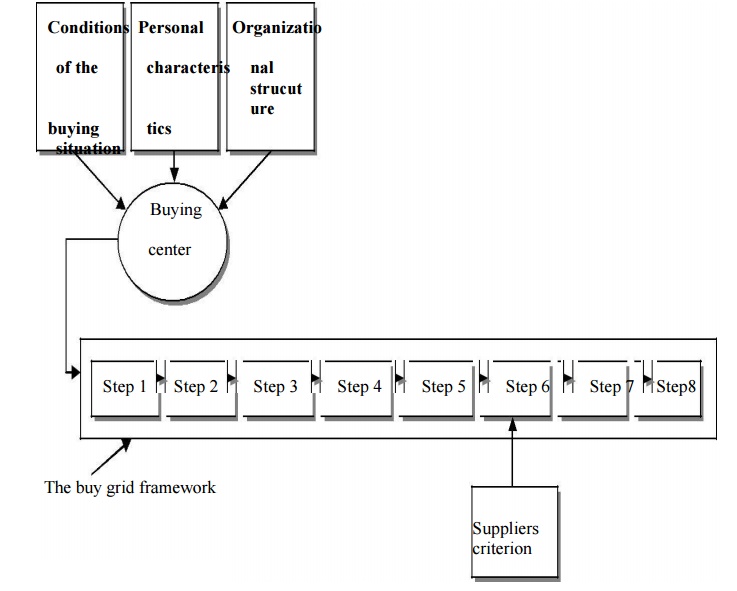
Step 1:
Planning
Step2 :
Define the objective
Step3
:Understand consumer
Step4
:Define problem
Step5
:Information search
Step6
:Evaluation of alternatives
Step7
:Purchase
Step8 :Postpurchase Evaluation
Related Topics