The World after World War II | History - UNO and Global Disputes | 12th History : Chapter 15 : The World after World War II
Chapter: 12th History : Chapter 15 : The World after World War II
UNO and Global Disputes
UNO and
Global Disputes
The Second World War proved that the League of
Nation was a failure. World leaders realised the need for the creation of an
effective organisation to prevent another war.
At Dumbarton Oaks, a mansion in Georgetown, Washington,
representatives of China, the Soviet Union, the United States and the United
Kingdom met (August 21–October 7, 1944) and formulated proposals for a world
organisation. The Moscow declaration of 1943 recognised the need for an
international organisation to replace the League of Nations. Subsequently, at
the Yalta Conference held in February 1945, decisions on the voting system in
security council and a few other issues were raised. After holding
deliberations and negotiations at the San Francisco Conference, held in April,
1945, the Charter of the United Nations was finalised.

On 24 October 1945 the UNO came into existence with
51 members. The main organs of the UN are the General Assembly, the Security
Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the
International Court of Justice, and the UN Secretariat.The Norwegian Foreign
Minister, Trygve Lie, was elected the first UN Secretary-General. In addition
to its main organs UNO has currently 15 specialised agencies. Some of the
prominent agencies are International Labour Organisation (ILO - Geneva), Food
and Agriculture Organisation (FAO - Rome), International Monetary Fund (IMF -
Washington (D.C)), United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural
Organisation (UNESCO - Paris), World Health Organisation (WHO - Geneva), and World
Bank (Washington (D.C)).

Role of UNO in resolving Global disputes
"Since wars begin in the minds of men, it is
in the minds of men that the defences of peace must be constructed".
(Preamble to the Constitution of UNO).
UNO Headquarters

The birth of UNO coincided with the beginning of
the Cold War. During this period the UNO played an important role in preventing
wars. But in disputes involving the permanent members of the Security Council
the UNO was a mute spectator. UN has an army known as the UN Peace-keeping
Force. Member states contribute soldiers to this force. The UN soldiers are
referred to as Blue Helmets, because of their light blue helmets.
Problem of Palestine
After the Second World War the Jews demanded a
homeland in Palestine. Arabs opposed the demand and the matter was referred to
the UN. In May 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution of
establishing the U.N. Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) to investigate
and make recommendations. According to the UNSCOP report, Arabs were in
possession of about 85 percent of the land and only about 5.8 percent was owned
by Jews. Despite these facts, the recommendation of the UNSCOP was that
Palestine should be partitioned into two states, with the majority Arabs surrendering
land to the Jews for their new state. Under the proposal, 45 percent of the
land would be for the Arab state, compared to 55 percent for the Jewish state.
On 14 May 1948 a new state called Israel was formed.

Recognition to Nationalist China

In 1949, in the context of Mao Tse Tung forming a
Communist government in mainland China, Chiang Kai-shek fled to the island of
Formosa where he headed the Nationalist government. USSR then proposed that a
representative of Communist China should replace the representative of
Nationalist China on the Security Council. Since this was not accepted USSR
decided to boycott the Security Council and all other UN organs. The People’s
Republic of China became a permanent member in the Security Council only from
1971.
The Korean War (1950-53)
Korea, ruled by Japan since 1910, was divided by
the 38th parallel into two zones in 1945. The northern zone, with a third of
the population and most of the industry, was occupied by the USSR. The southern
zone with two-thirds of the population and most of the farming areas, was
controlled by the United States. In the elections held under the supervision of
UNO, in South Korea Syngman Rhee became president. In North Korea, USSR set up the
People’s Democratic Republic, a Communist government, headed by Kim Il Sung.
Soon after, the Russians and Americans withdrew their forces. The South Korean
president openly proclaimed his ambition to unite the whole country by force.
Open warfare began on 25 June 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea

The Security Council met immediately. In the
absence of the USSR, it passed a resolution calling for an end to the fighting.
The members of the UN were asked to help in the matter. Sixteen members
contributed forces, and forty-five countries gave aid in some form. The
American General MacArthur commanded the United Nations forces. In August 1950,
with the USSR returning to the Security Council, the General Assembly at the
initiative of US passed the ‘Uniting for Peace’ resolution. This clearly set
the precedent that if the Security Council could not reach an agreement to
intervene in a crisis, then the General Assembly should meet in emergency
session and recommend the use of armed force if necessary. USSR regarded this
resolution as illegal. The fighting ended with the signing of an armistice in
July 1953. The war had increased the importance of the General Assembly.
Suez Crisis, 1956

Suez Canal connects the Red sea with the
Mediterranean Sea. It was constructed by Ferdinand de Lesseps, a Frenchman,
after obtaining permission from the Egyptian Pasha. Soon the ownership passed
on to the British. It was the main link between Asia and Europe. In July 1956,
the Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalised the Suez Canal, which
was until then privately owned by the Anglo-French Suez Canal Corporation. On
29 October, the Israeli army invaded the Sinai Peninsula. The following day,
French and British aircrafts bombed Egyptian air bases. On 5 November 1956,
British and French troops landed at the Egyptian town of Port Said. The issue
was taken up by the Security Council but Britain and France vetoed the
resolution. The General Assembly, at the initiative of the US, which became
apprehensive of Soviet invasion, called for an emergency session and condemned
the invasion. Israel, Great Britain and France stopped fighting and decided to
withdraw their forces from Egypt. The General Assembly voted to create a United
Nations Emergency Force, called UNEF. The force would not be a fighting force,
but a peace force sent with the consent of both sides. On December 22 the UN
evacuated British and French troops and Israeli forces withdrew in March 1957.
Nasser emerged a victor and a hero for the cause of pan-Arab and Egyptian
nationalism.
Hungarian Crisis, 1956

The Hungarian leader Rakosi, appointed as premier
during the regime of Stalin was dismissed in 1953. It resulted in the election
of Imre Nagy as premier. But Nagy enjoyed support neither from his government
nor from the Russians. Rakosi continued to control the Communist Party. Writers
and intellectuals led the protest, demanding the resignation of Rakosi. Though
Rakosi was removed from power in July 1956, the opposition continued. A
rebellion organised by a few intellectuals broke out in Budapest on 23 October.
Though it began as a peaceful demonstration it soon developed into a national
rising against Soviet Russia and its puppet regime in Hungary. On 26 October
the Russians agreed to Nagy becoming premier again. On his assumption of office
he started introducing a multiparty system and set up a coalition government.
Enraged by the development, Soviet Russia sent its army into Hungary on 4
November and crushed the rebellion.
The Hungarian Uprising occurred simultaneously with
the Anglo-French-Israeli attack on Egypt in the Suez affair. The matter was
taken up at the Security Council which decided to demand the immediate
withdrawal of Russian forces from Hungary. Russians vetoed the Security Council
resolution and so the same resolution was passed by the Assembly. But nothing
came out of the resolution. The failure of the United Nations to influence
USSR’s actions in Hungary showed that if a Great Power was determined to defy
the UNO and had the power to do it, the UN was helpless.
Along with the leak of Khrushchev's secret speech,
this had a major impact on the international communist movement, with large
numbers (especially of writers and intellectuals) resigning from communist
parties across the world.
Arab–Israeli War
As the United Nations voted to partition Palestine into a Jewish state and an Arab state in November 1947, conflict broke out almost immediately between Jews and Arabs in Palestine. On the eve of the British forces’ withdrawal (May 15, 1948), Israel declared independence. The war came to an end with the intervention of the UN General Assembly passing a resolution affirming the right of Palestinian refugees from the 1947–48 war to return to their homes and to receive compensation for their losses. Israel joined the UN the following year. From the start, when Israel was created, there was little involvement of the UN in making political decisions. UN peacekeepers were stationed on the Israeli– Egyptian border, and the UN Refugee Works Agency (UNRWA) was established to provide help for the refugees until such time as they returned home.
By 1966 the U.S. providing began to Israel with
advanced planes and missiles. The Cold War had come to the Middle East, and the
UN was out of the scene. Over the next few months, tensions increased between
Israel and the surrounding Arab states. In April 1967 there were artillery
exchanges between Israel and Syria. The U.S. Sixth Fleet remained off the Syrian
coast. Egyptian President Nasser symbolically asked the UN to move its troops
and observers, then inside Egyptian territory, to the Israeli border. The UN
told Nasser that he could not ask for UN troop movement. So his choice was to
demand the complete withdrawal of the UN troop. On May 23 Egypt closed the
Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping. In early June Israel attacked Egypt,
destroying virtually all of Cairo’s air force on the ground.

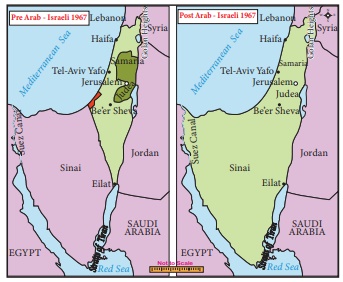
At the end of the Six Day War Israel occupied the
remaining parts of Palestine, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and East
Jerusalem, plus the Syrian Golan Heights and the Egyptian Sinai. Two hundred
fifty thousand more Palestinians were forced into exile, and a million more
remain under Israeli military occupation even now. While referring to the
Palestinians only in the context of refugees, rather than reaffirming their
national rights, the resolution of the UN unequivocally called for the
withdrawal of Israeli armed forces from the occupied territories. The
resolution was drafted largely by the four powers of the Security Council – the
limited reference to Palestinian rights was a reflection of US influence on the
proceedings.
For years following the 1967 war, the UN voted
repeatedly in favour of an international peace conference, under its own
auspices, with all parties to the conflict (including the Palestine Liberation
Organisation led by Yasser Arafat) to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict
once and for all. But the U.S. always vetoed it. In the Cold War context,
Moscow and Washington played an increasingly larger role either in escalating
or containing tension in the region.
Palestine Liberation Organisation
(PLO) was formed in 1964 to federate various Palestinian groups that previously
had operated as clandestine resistance movements. It came into prominence after
the Arab-Israeli War of June 1967. The PLO was engaged in a protracted
guerrilla wars against Israel until the 1980s, before entering into peace negotiations
in the 1990s. Yasser Arafat was its outstanding leader.
Related Topics