Cooperative Organisation | Commerce - Types of Cooperatives | 11th Commerce : Chapter 7 : Cooperative Organisation
Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 7 : Cooperative Organisation
Types of Cooperatives
Types of Cooperatives
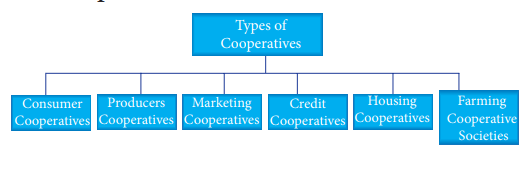
The Cooperatives can be broadly
classified into two viz., Credit Cooperatives and Non- Credit Cooperatives. The
credit cooperatives can be further classified into Agricultural credit and
non-Agricultural credit coopertives. However for beginners the coopertives are
classified as follows.
A. Consumers Cooperatives
Consumer cooperatives are organized by
consumers that want to achieve better prices or quality in the goods or
services they purchase. In contrast to traditional retail stores or service
providers, a consumer cooperative exists to deliver goods or services rather
than to maximize profit from selling those goods or services. They also supply
essential commodities through Public Distribution System (PDS). Nationally, the
most widely used cooperative form is the credit union, with some 90 million
members. Credit union assets have grown a hundred- fold in three decades.
Credit unions are essentially cooperatives of people that use banking services.
Students’ cooperative stores,
Cooperative provision stores and supermarkets set up on cooperative societies
of India are examples of this type.
B. Producers Cooperatives
Producer cooperatives are established
and operated by producers. Producers can decide to work together or as separate
entities to help increase marketing possibilities and production efficiency.
They are organized to process, market, and distribute their own products. This
helps lessen costs and strains in each area with a mutual benefit to each
producer.
Example,
Cooperative weavers’ societies,
Cooperative carpenting units, Cooperative match factories.
C. Marketing Cooperatives
Cooperative marketing societies are
associations of small producers formed for the purpose of marketing their
produce. The marketing cooperatives perform certain marketing functions such as
grading, warehousing, advertising etc., They secure better prices for their
members by transporting goods even to distant markets. Advance is also given to
members against produce deposited with the society. Thus they are a boon to
agriculturists, small producers and artisans, who in the absence of these
cooperatives would be forced to sell at low prices to middlemen.
D. Credit Cooperatives
Cooperative credit societies are those
formed for the purpose of providing short- term financial help to their
members.
Agriculturists, artisans, industrial
workers, salaried employees, etc., form these credit societies. Being unable to
obtain financial accommodation from banks they
are at the mercy of money-lenders who charge
exorbitant rates of interest. Ending this exploitation and encouraging thrift
among members is the objective of these societies. Credit societies may be
agricultural credit societies or non-agricultural credit societies.

H. Housing Cooperatives
These cooperative housing societies are
meant to provide residential accommodation to their members on ownership basis
or on rent. People who intend to build houses of their own join together and
form housing societies. These societies
advance loans to members, repayable over a period of 15 to
20 years. Housing building societies, on the other hand, construct houses for
their members instead of granting loans to them. These are house construction
societies which acquire land, construct houses and rent them to members. The
member-tenant, however, can own the houses after paying the cost.
F. Cooperative Farming Societies
When various farmers in a village pool
their land together and agree to treat the pooled piece of land as one big farm
for the purpose of cultivation, purchase the necessary inputs for the
cultivation, and market the crops jointly, they are assumed to have formed a
cooperative farming society. Such a society, for its proper working elects its
office bearers on the basis of one member-one-vote.
The office bearers look after the proper
cultivation of new farm that emerges after the land of various farmers has been
pooled. The ownership of the land still lies with the respective members of the
society and they withdraw from the society whenever they so like.
Besides land the farmers also contribute
variousproductiveassetsaswellastheirlabour for the purpose of cultivations.
Whereas they get rent for their land and productive assets, they get wages, for
their labour.
Related Topics