Chapter: Data Warehousing and Data Mining : Clustering and Applications and Trends in Data Mining
Type of Data in Clustering Analysis
TYPE OF
DATA IN CLUSTERING ANALYSIS
Data structure Data matrix (two
modes) object by variable Structure
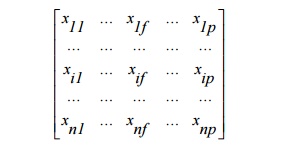
Dissimilarity matrix (one mode)
object –by-object structure
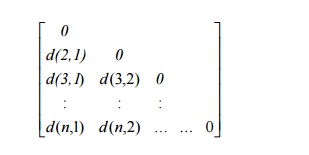
We describe how object dissimilarity can be computed for object by
Interval-scaled variables,
Binary variables, Nominal, ordinal, and ratio variables, Variables of
mixed types
Interval-Scaled
variables (continuous measurement of a roughly linear scale) Standardize data
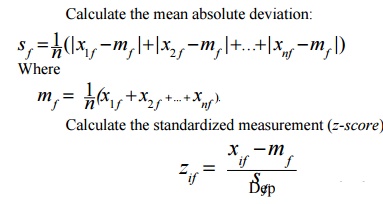
Using mean absolute deviation is more robust than using standard
deviation
Similarity and Dissimilarity Between Objects
Distances are normally used to measure the similarity or dissimilarity
between two data objects
Some popular ones include: Minkowski
distance:

Also, one can use weighted distance, parametric
Pearson product moment correlation, or other dissimilarity measures
Binary Variables
A
contingency table for binary data
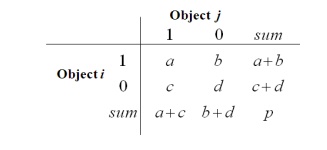
Distance
measure for symmetric binary variables:
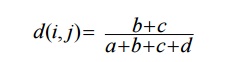
Distance
measure for asymmetric binary variables:
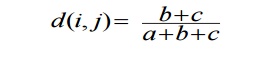
Jaccard
coefficient (similarity measure for asymmetric binary variables):
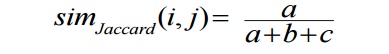
Categorical variables
A
generalization of the binary variable in that it can take more than 2 states,
e.g., red, yellow, blue, green
Method 1:
Simple matching
m: # of
matches, p: total # of variables
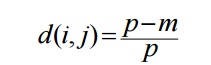
![]() Method 2: use a large number of
binary variables
Method 2: use a large number of
binary variables
creating a new binary variable for each of the M nominal states
Ordinal Variables
An ordinal variable can be discrete or continuous
Order is important, e.g., rank
Can be treated like interval-scaled
replace xif by their rank
map the
range of each variable onto [0, 1] by replacing i-th object in the f-th
variable
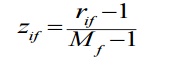
compute the dissimilarity using methods for
interval-scaled variables
Ratio-scaled variable:
a
positive measurement on a nonlinear scale, approximately at exponential scale,
such as AeBt or
Ae-Bt
Methods:
treat them like interval-scaled variables—not a good choice! (why?—the scale can
be distorted)
apply logarithmic transformation yif = log(xif)
treat them as continuous ordinal data treat their
rank as interval-scaled
Variables of Mixed Types
A
database may contain all the six types of variables symmetric binary,
asymmetric binary,
nominal,
ordinal, interval and ratio
One may
use a weighted formula to combine their effects
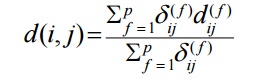
Vector
Objects
Vector
objects: keywords in documents, gene features in micro-arrays, etc.
Broad
applications: information retrieval, biologic taxonomy, etc.
Cosine
measure
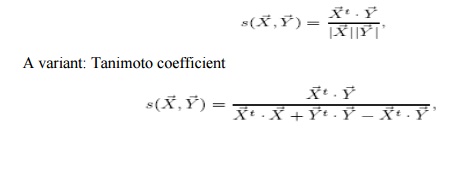
Related Topics