Chapter: Civil : Soil Mechanics -Shear strength
The vane shear test
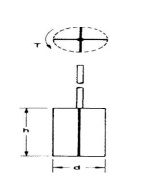
The vane shear test
This test is used for the in-situ determination of the undrained strength of intact, fully saturated clays; the test is not suitable for other types of soil. In particular, this test is very suitable for soft clays, the shear strength of which may be significantly altered by the sampling process and subsequent handling. Generally, this test is only used in clays having undrained strengths less than 100 kN/m2. This test may not give reliable results if the clay contains sand or silt laminations. Details of the test are given in BS 1377 (Part 9). The equipment consists of a Stainless steel vane (Figure) of four thin rectangular blades, carried on the end of a high-tensile steel rod; the rod is enclosed by a sleeve packed with grease. The length of the vane is equal to twice its overall width, typical dimensions being 150 mm by 75 mm and 100 mm by 50 mm. preferably the diameter of the rod should no t exceed 12.5 mm.
The vane and rod are pu shed into the clay below the bottom of a bo rehole to a depth of at least three times the boreholediameter;if care istaken thisc an bedonewithout appreciable disturbance of the clay. Steadybearingsare usedtokeeptherod and sleeve centralin the b oreholecasing. The test can also be carri ed outin soft clays, without a borehole, b y direct penetration of the vane from groundlevel; in this case a shoe is requiredto prot ect the vane during penetration.
Torque is applied gra dually tothe upper end ofthe rodbymeans ofsuitable equipment until the clay fails in shear due to rotation of the van e. Shear failure takes place over the surface and ends of a cylinder having a diameter equ al to the overall width of the vane. The rate of rotation of the vane should be within th e range of 6-12 per minute. The shear stren gth is calculated from the expression
T = Pi Cn(d2h/2 + d2/6)
where T is the torque at failure, d the overall vane width and h the vane length. However, the shear strength over t he cylindrical vertical surface may be differe nt from that over the two horizontal end su rfaces, as a result of anisotropy. The shear strength is normally determined at intervals over the depth of interest. If, after the initial test, the vane is rotated rapidly through several revolutions the clay will become rem oulded and the shear strength in this condition could then be determined if required. Small, hand-operated vane testers are also available for use in exposed clay strata.
Related Topics