Chapter: Civil : Soil Mechanics -Shear strength
Laboratory determination of shear parameters- Direct shear test
Laboratory
determination of shear parameters - Direct
shear test
The shear
strength parameters for a particular soil can be determined by means of
laboratory tests on specimens taken from representative samples of the in-situ
soil. Great care and judgment are required in the sampling operation and in the
storage and handling of samples prior to testing, especially in the case of
undisturbed samples where the object is to preserve the in-situ structure and
water content of the soil. In the case of clays, test specimens may be obtained
from tube or block samples, the latter normally being subjected to the least
disturbance. Swelling of a clay specimen will occur due to the release of the
in-situ total stresses. Shear strength test procedure is detailed in BS 1377
(Parts 7 and 8) [7].
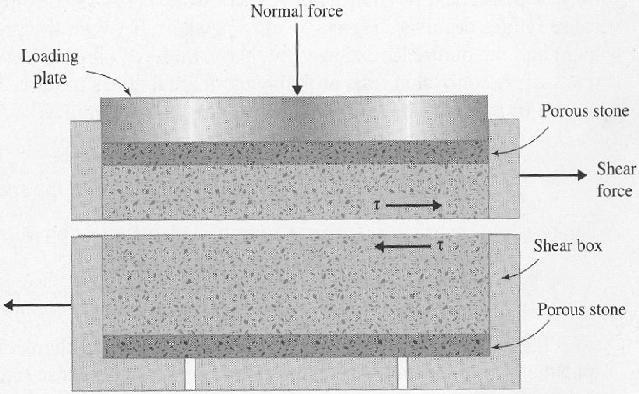
The
specimen is confined in a metal box (known as the shear box) of square or
circular cross-section split horizontally at mid-height, a small clearance
being maintained between the two halves of the box. Porous plates are placed
below and on top of the specimen if it is fully or partially saturated to allow
free drainage: if the specimen is dry, solid metal plates may be used. The
essential features of the apparatus are shown diagrammatically in Figure. A
vertical force (N) is applied to the specimen through a loading plate and shear
stress is gradually applied on a horizontal plane by causing the two halves of
the box to move relative to each other, the shear force (T) being measured
together with the corresponding shear displacement (l). Normally, the change in
thickness (h) of the specimen is also measured. If the initial thickness of the
specimen is h0 then the shear strain can be represented by l/hr and the
volumetric strain (v) by h/h. A number of specimens of the soil are tested,
each under a different vertical force, and the value of shear stress at failure
is plotted against the normal stress for each test. The shear strength
parameters are then obtained from the best line fitting the plotted points.
The test
suffers from several disadvantages, the main one being that drainage conditions
cannot be controlled. As pore water pressure cannot be measured, only the total
normal stress can be determined, although this is equal to the effective normal
stress if the pore water pressure is zero. Only an approximation to the state
of pure shear is produced in the specimen and shear stress on the failure plane
is not uniform, failure occurring progressively from the edges towards the
centre of the specimen. The area under the shear and vertical loads does not
remain constant throughout the test. The advantages of the test are its
simplicity and, in the case of sands, the ease of specimen preparation.
Related Topics