Chapter: Mechanical : Mechatronics : Mechatronics, Sensors And Transducers
Temperature Sensors
TEMPERATURE SENSORS
Bimetallic Strips:
A Bimetallic thermostat consists of two different metal strips
bounded together and they cannot move relative to each other.
These metals have different coefficients of expansion and when
the temperature changes the composite strips bends into a curved strip, with
the higher coefficient metal on the outside of the curve.
The basic principle in this is all metals try to change their
physical dimensions at different rates when subjected to same change in
temperature.
This
deformation may be used as a temperature- controlled switch, as in the simple
thermostat.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs):
The materials used for RTDs are Nickel, Iron, Platinum,
Copper, Lead, Tungsten, Mercury, Silver, etc.
The resistance of most metals increases over a limited
temperature range and the relationship between Resistance and Temperature is
shown below.
The Resistance temperature detectors are simple and resistive
elements in the form of coils of wire The equation which is used to find the
linear relationship in RTD is
Constructional Details of RTDs:
The platinum, nickel and copper in the form wire are the most
commonly used materials in the RTDs.
Thin film platinum elements are often made by depositing the
metal on a suitable substrate wire-wound elements involving a platinum wire
held by a high temperature
glass
adhesive inside a ceramic tube.
Thermistors:
Thermistor is a semiconductor device that has a negative
temperature coefficient of resistance in contrast to positive coefficient
displayed by most metals.
Thermistors are small pieces of material made from mixtures of
metal oxides, such as Iron, cobalt, chromium, Nickel, and Manganese.
The shape
of the materials is in terms of discs, beads and rods.
The thermistor is an extremely sensitive device because its
resistance changes rapidly with temperature.
The resistance of conventional metal-oxide thermistors
decreases in a very non-linear manner with an increase in temperature.
The change in resistance per degree change in temperature is
considerably larger than that which occurs with metals.
The resistance-temperature relationship for a thermistor can
be described by an equation of the form
Rt
= Keβ/t
Where Rt, is the resistance at temperature
t, with K and β being constant. Thermistors have many
advantages when compared with other temperature sensors.
The simple series circuit for measurement of temperature using
a thermistor and the variation of resistance with temperature for a typical
thermistor.
The thermistor is an extremely sensitive device because its
resistance changes rapidly with temperature.
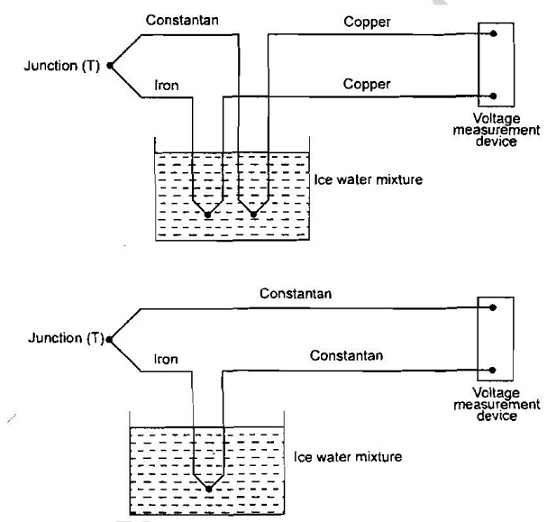
Thermocouples:
Thermocouples
are based on the See back Effect.
The thermocouple temperature measurement is based on a creation
of an electromotiveforce (emf).
"When two dissimilar metals are joined together an e.m.f
will exist between the two points A and B, which is primarily a function of the
junction temperature. The above said
to be
principle is See back effect..
The
thermocouple consist of one hot junction and one cold junction
Hot
junction is inserted where temperature is measured
Cold
junction is maintained at a constant reference temperature.
Related Topics