Chapter: Mechanical : Mechatronics : Mechatronics, Sensors And Transducers
Selection of Displacement, Position & Proximity Sensor
SELECTION OF DISPLACEMENT, POSITION &
PROXIMITY SENSOR:
Size of
the displacement (mm)
Displacement
type (Linear or angular)
Resolution
required
Accuracy
Required
Material
of the object
Cost
DISPLACEMENT
SENSORS
Displacement
sensors are con tact type sensor
Types of Displacement sensors:
Potentiometer
Strain
gauge
Capacitive
sensors
Linear
variable differential tr ansformer
POTENTIOMETER
PRINCIPLE:
It works
on variable resistance transduction principle
Linear or Rotary potentiometer is a variable
resistance displacement tran sducer which uses the variable resistance
transduction prin ciple in which the displacement or rotation isco
nverted into a potential differencedue to the movement ofsli
ding contact over a resistiveelement
CONSTRUCTION
& WORKING:
A
resistor with three terminals.
Two end
terminal & one mid dle terminal (wiper)
Two end
terminal are connected to external input voltage
One
middle and one end term inal as output voltage
The
slider determines the ma gnitude of the potential difference developed
Characteristics:
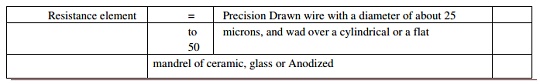
Resistance element = Precision Drawn wire with a diameter o f
about 25
to microns, and wad over a cylindrical or a
flat
50
mandrel of
ceramic, glass or Anodized
Aluminium. 2 mm to 500 mm in case of linear pot.
= For high resolution, w ire is made by using ceramic (cermet)
or conductive plastic
film d ue to
low noise levels.
Wipers (Sliders) = Tempered phosphor bronze, beryllium copper
or other precious alloys.
Wire Material = Strong, ductile and protected from surfa ce
corrosion by enamelling or oxidation.
Materials &e alloys
of copper nickel, Nickel chromium, and silver palladium.
= Resistivity of wire
ranges from 0.4 µΩm to 13 µΩm
Resistance range = 20Ω to 200KΩ and for plastic 500Ω to 80KΩ
Accuracy = Higher
temperature coefficient of
resistance than the
wire and so temperature changes have a greater effect Accuracy.
STRAIN
GAUGE:
Strain gauges
are passive type
resistance sensor whose
electrical resistance change
when it is
stretched or compressed (mechanically strained) under the
application of force.
The
electrical resistance is changed due to the change in length (increases) and
cross sectional area
(decreases) of the strain gauge.
This
change in resistance is then usually converted into voltage by connecting one,
two or four
similar gauges as an arm of a Wheatstone bridge (known as
Strain Gauge Bridge) and applying excitation to
the bridge. The bridge output voltage is then a measure of
strain, sensed by each strain gauge.
Unbonded Type Strain Gauges:
In unbonded type, fine wire filaments (resistance wires) are
stretched around rigid and electrically insulated pins on two frames.
One frame
is fixed and the other is movable.
The
frames are held close with a spring loaded mechanism.
Due to
the relative motion between two frames, the resistance wires are strained.
This strain is then can be detected through measurement of the
change in electrical resistance since they are not cemented with the surfaces,
they can be detached and reused.
Bonded Type Strain Gauges:
Bonded type strain gauges consists of resistance
elements arranged in the form of a grid of fine wire, which is cemented to a
thin paper sheet or very thin Bakelite sheet, and covered with a protective
sheet of paper or thin Bakelite.
The paper sheet is then bonded to the surface to be strained.
The gauges have a bonding material which acts an adhesive material during
bonding process of a surface with the gauge element.
Classification of Bonded Type Strain Gauges:
Fine wire
gauges
Metal
foil gauges
Semiconductor
filament type
Fine Wire Gauges:
Wire of 3
to 25 microns diameter is arranged in the form of grid consisting of parallel
loops
Metal Foil Gauges:
A thin foil of metal, deposited as a grid pattern onto a
plastic backing material using polyimide
Foil pattern is terminated at both ends with large metallic
pads Entire gauge size 5- 15mm
Adhesive directly
bonded to the gauge usually epoxy
Semiconductor Filament Type:
The
gauges are produced in wafers from silicon or germanium crystals
Special
impurities such as boron is added
It is
mounted on an epoxy resin backing with copper on nickel leads
Filament
about 0.05mm thick 0.25mm wide and 1.25 to 12mm length
CAPACITIVE SENSORS:
It is
used for measuring, displacement, velocity, force etc..
Principle:
It is passive type sensors in
which equal and opposite charges are generated on the plates due
to voltage applied across the plate which is separated by
dielectric material.
Formula:
By Changing the Distance between Two Plates:
The
displacement is measured due to the change in capacitance
By
Varying the Area of Overlap:
The
displacement causes the area of overlap to vary
The capacitance is directly proportional to the area of the
plates and varies linearly with changes in the displacement between the plates
By Varying the Dielectric Constant:
The change in capacitance can be measured due to change in
dielectric constant as a result of displacement.
When the dielectric material is moved due to the displacement,
the material causes the dielectric constant to vary in the region where the two
electrodes are separated that results in a charge in capacitance.
Push Pull Sensor:
Push pull displacement sensor is used to overcome the
non-linearity error.
The sensor consists of three plates with the upper pair
forming one capacitor and the lower pair forming another capacitor.
The
displacement moves central plate between the two other plates.
If the
central plate moves downwards.
The plate
separation of the upper capacitor increases and the separation of the lower one
decreases.
LINEAR VARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMER:
It
consists of three symmetrically spaced coils.
The
centre coil is primary coil and other two are secondary coil
Secondary coils are connected in series opposition and equally
positioned with respect to primary coil
The
output voltage is proportional to the displacement of the core from null
position
PROXIMITY SENSORS
Proximity
sensors are non – contact type sensor.
Types of Proximity Sensor:
Eddy
current proximity sensor
Inductive
proximity sensor
Pneumatic
proximity sensor
Proximity
switches
EDDY CURRENT PROXIMITY SENSOR:
PRINCIPLE:
When a
coil is supplied with alternating current, an alternating magnetic
field is produced which
induces an EMF on it. If
there is a metal near to this alternating magnetic field, on EMF
is induced in it.
The EMF cause current to flow. This current flow
is eddy current.
CONSTRUCTION & WORKING:
It has
two identical coils.
One reference coil & another sensing coil which senses the
magnetic current in the object. Eddy current start to flow due to AC(conducting
object) close to sensor
Eddy current produce a magnetic field to oppose the magnetic
field generated by sensing coil. Due to this opposition reduction flux is
created. To detect 0.001mm
INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSORS:
It
consists of coil wound round a core.
Metal is
close to coil Inductance changes occurs.
It is
suitable for ferrous metals
PNEUMATIC PROXIMITY SWITCHES:
It is
suitable for sensing non conducting materials
Air is
allowed to escape from the front side of the sensor.
When
there is no object air escapes freely.
When there
is an object, the escaping air is blocked and return backed to system.
It is
used to measure the range 3mm to 12mm
PROXIMITY SWITCHES:
It is
used in robotics for sensing elements
It is also used in NC machines, material handling
systems and assembly lines. Micro switch
Reed
switch
Photo sensitive switch Mechanical switch
Micro Switch:
It is limit switch operated by levers, rollers & cams
It is switch which requires physical contact and small force
to close the contacts. Example a belt conveyor.
Reed Switch:
It is a non – contact proximity switch that consists of two
magnetic switch contacts enclosed in a glass tube fined with
an inert gas.
When magnet is closed switch is operated. Used for high speed
applications.
Photo Sensitive Devices:
It is
used to sense opaque object.
Photo
detector receives a beam of light produced by the LED.
Object is
passed the beam gets broken or reflected when is detected.
Related Topics