Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment of Musculoskeletal Function
Structure and Function of the Articular System
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM
The junction of two or
more bones is called a joint
(articulation). There are three basic kinds of joints: synarthrosis,
amphiarthro-sis, and diarthrosis joints. Synarthrosis joints are immovable, as
exemplified by the skull sutures. Amphiarthrosis joints, such as the vertebral
joints and the symphysis pubis, allow limited mo-tion. The bones of
amphiarthrosis joints are joined by fibrous car-tilage. Diarthrosis joints are
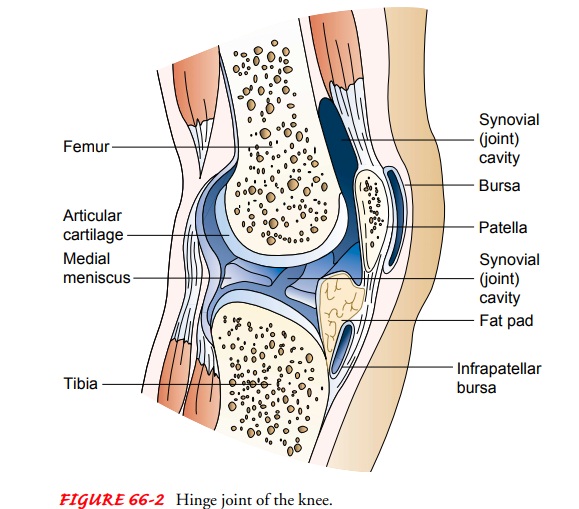
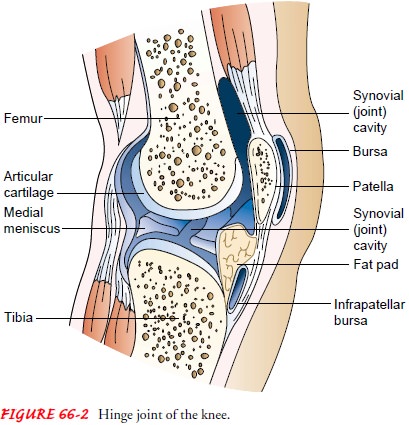
freely movable joints (Fig. 66-2).
There are several types of diarthrosis joints:
·Ball-and-socket joints, best exemplified
by the hip and theshoulder, permit full freedom of movement.
·Hinge joints permit bending in one
direction only and arebest exemplified by the elbow and the knee.
·Saddle joints allow movement in two
planes at right anglesto each other. The joint at the base of the thumb is a
sad-dle, biaxial joint.
·Pivot joints are characterized by
the articulation between theradius and the ulna. They permit rotation for such
activities as turning a doorknob.
· Gliding joints allow for limited movement in all directions andare represented by the joints of the carpal bones in the wrist.
The ends of the
articulating bones of a typical movable joint are covered with smooth hyaline
cartilage. A tough, fibrous sheath called the joint capsule surrounds the articulating bones. The capsule is lined
with a membrane, the synovium, which
secretes the lubricating and shock-absorbing synovial fluid into the joint
capsule. Therefore, the bone surfaces are not in direct contact. In some
synovial joints (eg, the knee), fibrocartilage disks (eg, medial meniscus) are
located between the articular cartilage surfaces. These disks provide shock
absorption.
Ligaments (fibrous
connective tissue bands) bind the articu-lating bones together. Ligaments and
muscle tendons, which pass over the joint, provide joint stability. In some
joints, interosseous ligaments (eg, the cruciate ligaments of the knee) are
found within the capsule and add stability to the joint.
A bursa is a sac filled with synovial fluid that cushions the
move-ment of tendons, ligaments, and bones at a point of friction. Bur-sae are
found at the elbow, shoulder, knee, and some other joints.
Related Topics