Recruitment Methods | Human Resource Management - Sources of Recruitment | 12th Commerce : Chapter 10 : Human Resource Management : Recruitment Methods
Chapter: 12th Commerce : Chapter 10 : Human Resource Management : Recruitment Methods
Sources of Recruitment
Sources of Recruitment
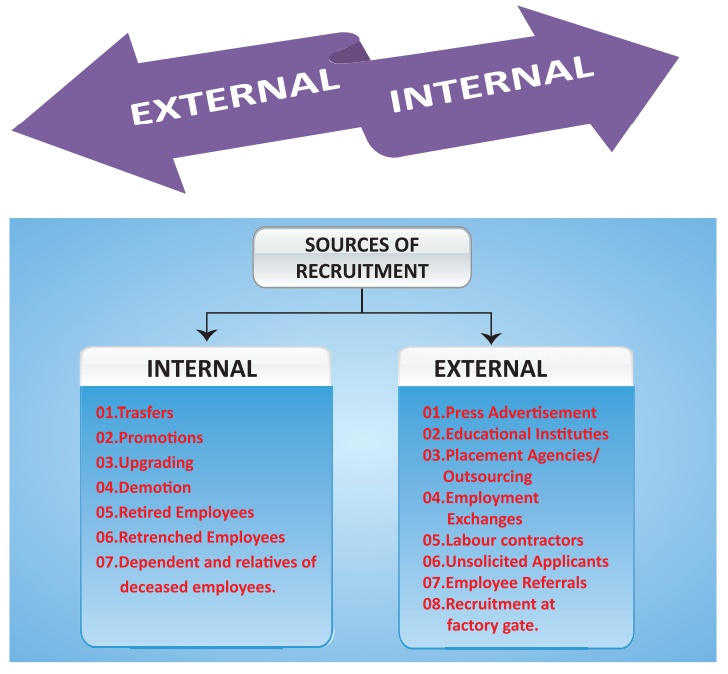
There are basically two ways by which an
organisation can recruit its employees namely Internal and External sources.
External sources can further be classified into Direct and Indirect sources.
Internal Sources – Transfer, Upgrading, Promotion, Demotion,
Recommendation by existing Employees, Job rotation, Retired employees,
Dependants, Previous applicants, Acquisitions and Mergers
External Sources
i. Direct – Advertisements, Unsolicited applicants, Walk ins,
Campus Recruitment, Recruitment at Factory gate, Rival firms, e Recruitment
ii. Indirect – Employee referral,
Government/ Public Employment Exchanges, Employment
Agencies, Employment Consultancies, Professional Associations, Deputation, Word
of mouth, Labour Contractors, Job Portals, Outsourcing, Poaching
i. Internal Sources
The following are the internal sources of
Recruitment
i. Transfer - The simplest way by
which an employee requirement can be filled is through transfer of employee
from one department with surplus staff to that of another with deficit staff.
ii. Upgrading – Performance appraisal helps in the process
of moving employees from a lower position to a higher position
iii. Promotion – Based on seniority and merits of the
employees they are given opportunity to move up in the organisational hierarchy
iv. Demotion – Movement of employee from a higher
position to a lower position because of poor performance continuously to make
him realise the significance of performance
v. Recommendation by existing Employees – A family member, relative or friend of an existing employee can
be recruited and placed
vi. Job rotation – One single employee managing to learn how
to perform in more than one job on rotation. This familiarises the employees
with all kind of jobs performed and becomes a source.
vii. Retention – The retiring
employees can be used to meet the requirement after
superannuation as per management discretion
viii. Retired employees - The employees who have already retired
can be called to fill the vacancy as they have the required qualification and
experience
ix. Dependants – The legal heir or the dependent employee
may be given a chance to replace the deceased.
x. Previous applicants – The applicants who have already
applied for any job advertised in the past whose name appears in the data base
but not selected at that point of time can be utilised
xi. Acquisitions and Mergers – This is another way by which the organisation
acquires another business unit or merging with another establishment.
ii. External Sources
A. Direct
i. Advertisements – The employer can advertise in dailies,
journals, magazines etc. about the vacancies in the organisation specifying the
nature of work, nature of vacancy, qualification and experience required,
salary offered, mode of applying and the time limit within which the candidate
has to apply.
ii. Unsolicited applicants – These are the applications of job
seekers who voluntarily apply for the vacancies not yet notified by the
organisations.
iii. Walkins– Walk-in applicants
with suitable qualification and requirement can be
another source of requirement.
iv. Campus Recruitment – The organisations visit the educational
institutions to identify and recruit suitable candidates.
v. Recruitment at Factory gate – Usually casual or temporary unskilled employees
are recruited by this way. They are recruited at factory gate and paid on
hourly or daily basis.
vi. Rival firms – This is also called
poaching where the efficient employees of rival companies are drawn to the
organisations by higher pay and benefits. For example Salesmen, Chartered
Accountants, Management professionals etc.
vii. e-Recruitment – The organisations
which carry out recruitment online methods is said to follow e
recruitment. The advancement in technology and communication has made it
possible to reach out prospective applicants globally online. It has become
inevitable external source of recruitment.
B. Indirect
i. Employee referral – The existing
employees of the organisation may recommend some of their relatives or known
people who will be suitable for the existing vacancies. Based on the credibility
of the employee the referrals will be considered.
ii. Government/Public Employment Exchanges – These are exchanges established
by Government which facilitates recruitment throughout the country. It makes
available the information required through the data base for the employer as
well as the job seeker by bridging the gap between them.
iii. Private Employment Agencies – These are similar to Public employment exchanges
except that the ownership is the hands of Private parties. It connects the job
provider and the job seeker by providing the relevant and required information.
iv. Employment Consultancies – These
types of firms facilitate recruitment on behalf of client companies at cost.
Usually they provide data relating to executives andtop level personnel for
which service theycharge consultation fees also known asRecruitment Process
Outsourcing.
v. Professional Associations – Organisations seeking applicants of high calibre and
repute with technical knowledge approach professional associations like
Institute of Chartered Accounts, The Indian Medical Association, The Institute
of Training and Development, The Institute of Engineers, All India Management
Association etc. to identify the right person.
vi. Deputation – A person who is
already an employee of an organisation can be deputed for a specific job for
a specified period as a short term solution.
vii. Word of mouth – The information
relating to job seekers is collected through people of repute who pass on
the message about the vacancy to their known people.
viii. Labour Contractors – Organisations recruit unskilled and
manual labourers through these contractors.
ix. Job Portals – Using internet job
portals organisations can screen for the prospective candidates and fill
up their vacancies.
Related Topics